[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]
前言:
长短期记忆网络(LSTM,Long Short-Term Memory)是一种时间循环神经网络,是为了解决一般的RNN(循环神经网络)存在的长期依赖问题而专门设计出来的。
目录:
- 背景简介
- LSTM Cell
- LSTM 反向传播算法
- 为什么能解决梯度消失
- LSTM 模型的搭建
一 背景简介:
1.1 RNN
RNN 忽略![]() 模型可以简化成如下
模型可以简化成如下
图中Rnn Cell 可以很清晰看出在隐藏状态![]() 。
。
得到 ![]() 后:
后:
一方面用于当前层的模型损失计算,另一方面用于计算下一层的![]()
由于RNN梯度消失的问题,后来通过LSTM 解决
1.2 LSTM 结构
二 LSTM Cell
LSTMCell(RNNCell) 结构
前向传播算法 Forward
2.1 更新: forget gate 忘记门
![]()
将值朝0 减少, 激活函数一般用sigmoid
输出值[0,1]
2.2 更新: Input gate 输入门
![]()
决定是不是忽略输入值
2.3 更新: 候选记忆单元
![]()
2.4 更新: 记忆单元
![]()
2.5 更新: 输出门
决定是否使用隐藏值
![]()
2.6. 隐藏状态
![]()
2.7 模型输出
![]()
LSTM 门设计的解释一:
输入门 ,遗忘门,输出门 不同取值组合的时候,记忆单元的输出情况
三 LSTM 反向传播推导
3.1 定义两个![]()
![]()
![]()
3.2 定义损失函数
损失函数![]() 分为两部分:
分为两部分:
时刻t的损失函数 ![]()
时刻t后的损失函数![]()
3.3 最后一个时刻![]() 的
的
这里面要注意这里的![]()
证明一下第二项,主要应用到微分的两个性质,以及微分和迹的关系:
... 公式1: 微分和迹的关系
因为
带入上面公式1:
所以
3.4 链式求导过程
求导结果:
这里详解一下推导过程:
这是一个符合函数求导:先把h 写成向量形成
------------------------------------------------------------
第一项:
设
则
其中:(利用矩阵求导的定义法 分子布局原理)
是一个对角矩阵
几个连乘起来就是第一项
第二项
参考:
其中:
其它也是相似,就有了上面的求导结果
四 为什么能解决梯度消失
4.1 RNN 梯度消失的原理
,复旦大学邱锡鹏书里面 有更加详细的解释,通过极大假设:
在梯度计算中存在梯度的k 次方连乘 ,导致 梯度消失原理。
4.2 LSTM 解决梯度消失 解释1:
通过上面公式发现梯度计算中是加法运算,不存在连乘计算,
极大概率降低了梯度消失的现象。
4.3 LSTM 解决梯度 消失解释2:
记忆单元c 作用相当于ResNet的残差部分.
比如![]() 时候,
时候,![]() ,不会存在梯度消失。
,不会存在梯度消失。
五 模型的搭建
我们最后发现:
![]() 的维度必须一致,都是hidden_size
的维度必须一致,都是hidden_size
通过![]() ,则
,则 ![]() 最后一个维度也必须是hidden_size
最后一个维度也必须是hidden_size
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Aug 3 15:11:19 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Aug 2 15:34:25 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
import torch
from torch import nn
from d21 import torch as d21
def normal(shape,devices):
data = torch.randn(size= shape, device=devices)*0.01
return data
def get_lstm_params(input_size, hidden_size,categorize_size,devices):
#隐藏门参数
W_xf= normal((input_size, hidden_size), devices)
W_hf = normal((hidden_size, hidden_size),devices)
b_f = torch.zeros(hidden_size,devices)
#输入门参数
W_xi= normal((input_size, hidden_size), devices)
W_hi = normal((hidden_size, hidden_size),devices)
b_i = torch.zeros(hidden_size,devices)
#输出门参数
W_xo= normal((input_size, hidden_size), devices)
W_ho = normal((hidden_size, hidden_size),devices)
b_o = torch.zeros(hidden_size,devices)
#临时记忆单元
W_xc= normal((input_size, hidden_size), devices)
W_hc = normal((hidden_size, hidden_size),devices)
b_c = torch.zeros(hidden_size,devices)
#最终分类结果参数
W_hq = normal((hidden_size, categorize_size), devices)
b_q = torch.zeros(categorize_size,devices)
params =[
W_xf,W_hf,b_f,
W_xi,W_hi,b_i,
W_xo,W_ho,b_o,
W_xc,W_hc,b_c,
W_hq,b_q]
for param in params:
param.requires_grad_(True)
return params
def init_lstm_state(batch_size, hidden_size, devices):
cell_init = torch.zeros((batch_size, hidden_size),device=devices)
hidden_init = torch.zeros((batch_size, hidden_size),device=devices)
return (cell_init, hidden_init)
def lstm(inputs, state, params):
[
W_xf,W_hf,b_f,
W_xi,W_hi,b_i,
W_xo,W_ho,b_o,
W_xc,W_hc,b_c,
W_hq,b_q] = params
(H,C) = state
outputs= []
for x in inputs:
#input gate
I = torch.sigmoid((x@W_xi)+(H@W_hi)+b_i)
F = torch.sigmoid((x@W_xf)+(H@W_hf)+b_f)
O = torch.sigmoid((x@W_xo)+(H@W_ho)+b_o)
C_tmp = torch.tanh((x@W_xc)+(H@W_hc)+b_c)
C = F*C+I*C_tmp
H = O*torch.tanh(C)
Y = (H@W_hq)+b_q
outputs.append(Y)
return torch.cat(outputs, dim=0),(H,C)
def main():
batch_size,num_steps =32, 35
train_iter, cocab= d21.load_data_time_machine(batch_size, num_steps)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()参考
CSDN
https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6519110.html
57 长短期记忆网络(LSTM)【动手学深度学习v2】_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/34d285ddd7fc45f3aee4936c2985cf6a.jpg)
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ea3ee3dab78e4d73997c3d18854dc735.jpg)
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3e9a904b4fa5481cb5005fc83c348cbf.jpg)
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/0c2947fbbfbb4aaabeaee6be1a9862c0.jpg)
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/494feb7be7614f0cbdbf6015cffd27b5.jpg)
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第6张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b94fffc671b041c1be213f63e01cb4f2.jpg)
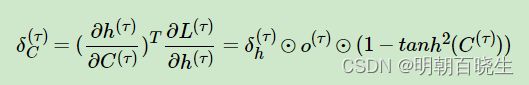
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第7张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/57362d2441e84ee285a9bc3a44c98923.jpg)
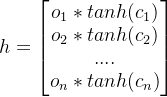
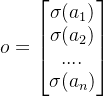
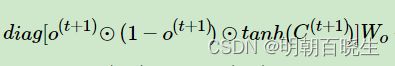
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第8张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/254360d0495d48cc9fc5f51c0a0019e3.jpg)
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第9张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/fafc1d41b70d496fb19eafe0560738fd.jpg)
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第10张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b36dd88877574a53be4772f333194deb.jpg)
![[PyTorch][chapter 46][LSTM -1]_第11张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/608c2363aaf8433d92163a6d90d1a984.jpg)