Godot 4 源码分析 - 碰撞
碰撞功能应该是一个核心功能,它能自动产生相应的数据,比如目标对象进入、离开本对象的检测区域。
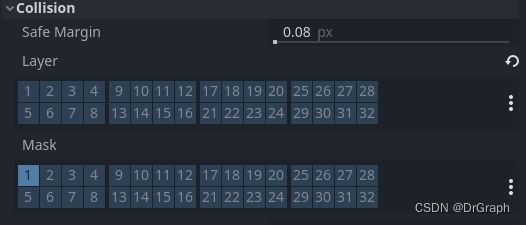
基于属性设置,能碰撞的都具备这样的属性:Layer、Mask.
在Godot 4中,Collision属性中的Layer和Mask属性是用于定义碰撞过滤的重要参数。它们允许控制哪些物体可以与该节点进行碰撞检测。
-
Layer(图层):
- Layer是所有节点都具有的属性,用于将节点分组到不同的图层中。Layer是一组位掩码(bitmask),每个位代表一个特定的碰撞图层。每个物体都可以分配一个或多个碰撞图层。通过将物体分配到特定的碰撞图层,可定义其所属的逻辑组
- 每个节点可以属于一个或多个图层。你可以在节点的属性面板中的Layer部分选择一个或多个图层。
- Layer属性定义了节点所属的图层。默认情况下,节点属于基本图层(Base Layer)。
- 使用不同图层将场景中的节点分组,可以使你能够仅与特定图层上的节点进行碰撞检测。
-
Mask(掩码):
- Mask也是所有节点都具有的属性,用于指定该节点对碰撞的兴趣。Mask也是一组位掩码,用于指示物体可以与哪些碰撞图层的物体发生碰撞检测。每个物体都可以指定一个碰撞掩码。通过设置碰撞掩码,可定义物体与哪些碰撞图层的物体发生碰撞
- 每个节点都有一个掩码值。可以在节点的属性面板中的Collision属性下设置掩码。
- Mask属性定义了该节点对哪些图层的节点感兴趣,该节点将与这些图层中的其他节点进行碰撞检测。
- 每个节点的掩码值是一个32位的整数,每一位代表一个图层。0表示不兴趣该图层,1表示兴趣该图层。可以使用位操作(如按位与和按位或)来设置和检查掩码值。
通过使用Layer和Mask属性,你可以灵活地控制碰撞检测,使得只特定图层中的节点相互交互。例如,你可以设置一个节点仅与属于某个特定图层的节点进行碰撞,而忽略其他图层的节点。
需要注意的是,为了让两个节点进行碰撞检测,它们的Layer和Mask需要同时满足一定条件。具体而言,一个节点的Layer值必须包含在另一个节点的Mask值中,同时另一个节点的Layer值必须包含在该节点的Mask值中。
通过合理设置Layer和Mask属性,可在Godot 4中创建精细且灵活的碰撞过滤系统,以实现各种复杂的物理效果和游戏机制。
假设有两个碰撞图层,一个是"Player",另一个是"Enemy"。有一个玩家角色和一些敌人,想要确保玩家和敌人之间发生碰撞,但是敌人之间不发生碰撞。
-
对于玩家对象:将其分配到"Player"碰撞图层,并将其Collision Mask设置为"Enemy"的位掩码。这将使玩家只与"Enemy"图层的物体发生碰撞。
-
对于敌人对象:将它们分配到"Enemy"碰撞图层,并将其Collision Mask设置为"Player"的位掩码。这将使敌人只与"Player"图层的物体发生碰撞。
对于敌人对象之间,可将它们分配到相同的碰撞图层并设置相应的碰撞掩码,以确保它们不会互相碰撞。
通过这种方式,可在复杂的场景中更精细地控制碰撞的交互,使碰撞逻辑更加清晰和可管理。
从理解角度来说,逻辑说起来复杂,技术上实现很简单
Layer与Mask应该都是32位整数,对象A有Layer与Mask属性,对象B也有Layer与Mask属性
如果 A.Layer & B.Mask 非零,则 A要与B发生碰撞
如果 A.Mask & B.Layer非零,则B要与A发生碰撞
还是有点绕,再多想一下,以下是我自己的想法,不一定正确:
其实,Layer与Mask都是逻辑概念,虚拟的。在真实场景中,A、B都占据相应的空间位置(3D)或平面位置(2D),在运行过程中,A、B至少有一个能动,它们的相对位置可能会变化,在某个时刻会有交叠。这个时候,godot引擎知道,因为它能实时计算。那么,godot发现两个对象发生交叠了,怎么办呢?
那就检查A、B的Layer与Mask。
- 如果 A.Layer & B.Mask 非零,则B能检测到A,触发B的body_entered信号,实参为A。
- 如果 B.Layer & A.Mask 非零,则A能检测到B,触发A的body_entered信号,实参为B。
其实上面的说法不严谨,因为body_entered信号不应该连续发送,而是有个进出状态。整体连起来应该就是:
- A、B分别维护自己的body_map,知道与自己交叠的对象列表。这个工作不能交给godot引擎做,它多忙的,还是各自管好自己的事
- 从源码看出,检测进出的状态标志,还是A、B自己完成,也就是说,遍历所有的监控对象monitored_bodies,看与自己的??状态E->value,若为0,则啥事没有,不再监控该对象。如果>0,则为AREA_BODY_ADDED,表示进入。如果<0,则为AREA_BODY_REMOVED,表示离开。
void GodotArea2D::call_queries() {
if (!monitor_callback.is_null() && !monitored_bodies.is_empty()) {
if (monitor_callback.is_valid()) {
Variant res[5];
Variant *resptr[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
resptr[i] = &res[i];
}
for (HashMap::Iterator E = monitored_bodies.begin(); E;) {
if (E->value.state == 0) { // Nothing happened
HashMap::Iterator next = E;
++next;
monitored_bodies.remove(E);
E = next;
continue;
}
res[0] = E->value.state > 0 ? PhysicsServer2D::AREA_BODY_ADDED : PhysicsServer2D::AREA_BODY_REMOVED;
res[1] = E->key.rid;
res[2] = E->key.instance_id;
res[3] = E->key.body_shape;
res[4] = E->key.area_shape;
HashMap::Iterator next = E;
++next;
monitored_bodies.remove(E);
E = next;
Callable::CallError ce;
Variant ret;
monitor_callback.callp((const Variant **)resptr, 5, ret, ce);
if (ce.error != Callable::CallError::CALL_OK) {
ERR_PRINT_ONCE("Error calling event callback method " + Variant::get_callable_error_text(monitor_callback, (const Variant **)resptr, 5, ce));
}
}
} else {
monitored_bodies.clear();
monitor_callback = Callable();
}
}
if (!area_monitor_callback.is_null() && !monitored_areas.is_empty()) {
if (area_monitor_callback.is_valid()) {
Variant res[5];
Variant *resptr[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
resptr[i] = &res[i];
}
for (HashMap::Iterator E = monitored_areas.begin(); E;) {
if (E->value.state == 0) { // Nothing happened
HashMap::Iterator next = E;
++next;
monitored_areas.remove(E);
E = next;
continue;
}
res[0] = E->value.state > 0 ? PhysicsServer2D::AREA_BODY_ADDED : PhysicsServer2D::AREA_BODY_REMOVED;
res[1] = E->key.rid;
res[2] = E->key.instance_id;
res[3] = E->key.body_shape;
res[4] = E->key.area_shape;
HashMap::Iterator next = E;
++next;
monitored_areas.remove(E);
E = next;
Callable::CallError ce;
Variant ret;
area_monitor_callback.callp((const Variant **)resptr, 5, ret, ce);
if (ce.error != Callable::CallError::CALL_OK) {
ERR_PRINT_ONCE("Error calling event callback method " + Variant::get_callable_error_text(area_monitor_callback, (const Variant **)resptr, 5, ce));
}
}
} else {
monitored_areas.clear();
area_monitor_callback = Callable();
}
}
}
- 根据是否为AREA_BODY_ADDED确定body_in标志。若为body_in,则触发tree_entered、tree_exiting信号,如果本对象在工作场景中,则触发body_entered,参数为node。顺便还触发了body_shape_entered信号,看着用吧。
- 若body_in为false,则触发tree_entered、tree_exiting。如果本对象在工作场景中,则触发body_exited、body_shape_exited
void Area2D::_body_inout(int p_status, const RID &p_body, ObjectID p_instance, int p_body_shape, int p_area_shape) {
bool body_in = p_status == PhysicsServer2D::AREA_BODY_ADDED;
ObjectID objid = p_instance;
Object *obj = ObjectDB::get_instance(objid);
Node *node = Object::cast_to(obj);
HashMap::Iterator E = body_map.find(objid);
if (!body_in && !E) {
return; //does not exist because it was likely removed from the tree
}
lock_callback();
locked = true;
if (body_in) {
if (!E) {
E = body_map.insert(objid, BodyState());
E->value.rid = p_body;
E->value.rc = 0;
E->value.in_tree = node && node->is_inside_tree();
if (node) {
node->connect(SceneStringNames::get_singleton()->tree_entered, callable_mp(this, &Area2D::_body_enter_tree).bind(objid));
node->connect(SceneStringNames::get_singleton()->tree_exiting, callable_mp(this, &Area2D::_body_exit_tree).bind(objid));
if (E->value.in_tree) {
emit_signal(SceneStringNames::get_singleton()->body_entered, node);
}
}
}
E->value.rc++;
if (node) {
E->value.shapes.insert(ShapePair(p_body_shape, p_area_shape));
}
if (!node || E->value.in_tree) {
emit_signal(SceneStringNames::get_singleton()->body_shape_entered, p_body, node, p_body_shape, p_area_shape);
}
} else {
E->value.rc--;
if (node) {
E->value.shapes.erase(ShapePair(p_body_shape, p_area_shape));
}
bool in_tree = E->value.in_tree;
if (E->value.rc == 0) {
body_map.remove(E);
if (node) {
node->disconnect(SceneStringNames::get_singleton()->tree_entered, callable_mp(this, &Area2D::_body_enter_tree));
node->disconnect(SceneStringNames::get_singleton()->tree_exiting, callable_mp(this, &Area2D::_body_exit_tree));
if (in_tree) {
emit_signal(SceneStringNames::get_singleton()->body_exited, obj);
}
}
}
if (!node || in_tree) {
emit_signal(SceneStringNames::get_singleton()->body_shape_exited, p_body, obj, p_body_shape, p_area_shape);
}
}
locked = false;
unlock_callback();
}
到此,就该关注monitored_bodies,它在add_body_to_query、remove_body_from_query中维护
void GodotArea2D::add_body_to_query(GodotBody2D *p_body, uint32_t p_body_shape, uint32_t p_area_shape) {
BodyKey bk(p_body, p_body_shape, p_area_shape);
monitored_bodies[bk].inc();
if (!monitor_query_list.in_list()) {
_queue_monitor_update();
}
}
void GodotArea2D::remove_body_from_query(GodotBody2D *p_body, uint32_t p_body_shape, uint32_t p_area_shape) {
BodyKey bk(p_body, p_body_shape, p_area_shape);
monitored_bodies[bk].dec();
if (!monitor_query_list.in_list()) {
_queue_monitor_update();
}
}但这没看到Layer与Mask属性的作用。那就倒查。最终发现在GodotCollisionObject2D类中:
_FORCE_INLINE_ bool collides_with(GodotCollisionObject2D *p_other) const {
return p_other->collision_layer & collision_mask;
}果然,与猜测的一致。具体调用collides_with是在一些setup函数中。
bool GodotAreaPair2D::setup(real_t p_step) {
bool result = false;
if (area->collides_with(body) && GodotCollisionSolver2D::solve(body->get_shape(body_shape), body->get_transform() * body->get_shape_transform(body_shape), Vector2(), area->get_shape(area_shape), area->get_transform() * area->get_shape_transform(area_shape), Vector2(), nullptr, this)) {
result = true;
}
process_collision = false;
has_space_override = false;
if (result != colliding) {
if ((int)area->get_param(PhysicsServer2D::AREA_PARAM_GRAVITY_OVERRIDE_MODE) != PhysicsServer2D::AREA_SPACE_OVERRIDE_DISABLED) {
has_space_override = true;
} else if ((int)area->get_param(PhysicsServer2D::AREA_PARAM_LINEAR_DAMP_OVERRIDE_MODE) != PhysicsServer2D::AREA_SPACE_OVERRIDE_DISABLED) {
has_space_override = true;
} else if ((int)area->get_param(PhysicsServer2D::AREA_PARAM_ANGULAR_DAMP_OVERRIDE_MODE) != PhysicsServer2D::AREA_SPACE_OVERRIDE_DISABLED) {
has_space_override = true;
}
process_collision = has_space_override;
if (area->has_monitor_callback()) {
process_collision = true;
}
colliding = result;
}
return process_collision;
}
bool GodotBodyPair2D::setup(real_t p_step) {
check_ccd = false;
if (!A->interacts_with(B) || A->has_exception(B->get_self()) || B->has_exception(A->get_self())) {
collided = false;
return false;
}
collide_A = (A->get_mode() > PhysicsServer2D::BODY_MODE_KINEMATIC) && A->collides_with(B);
collide_B = (B->get_mode() > PhysicsServer2D::BODY_MODE_KINEMATIC) && B->collides_with(A);
report_contacts_only = false;
if (!collide_A && !collide_B) {
if ((A->get_max_contacts_reported() > 0) || (B->get_max_contacts_reported() > 0)) {
report_contacts_only = true;
} else {
collided = false;
return false;
}
}
//use local A coordinates to avoid numerical issues on collision detection
offset_B = B->get_transform().get_origin() - A->get_transform().get_origin();
_validate_contacts();
const Vector2 &offset_A = A->get_transform().get_origin();
Transform2D xform_Au = A->get_transform().untranslated();
Transform2D xform_A = xform_Au * A->get_shape_transform(shape_A);
Transform2D xform_Bu = B->get_transform();
xform_Bu.columns[2] -= offset_A;
Transform2D xform_B = xform_Bu * B->get_shape_transform(shape_B);
GodotShape2D *shape_A_ptr = A->get_shape(shape_A);
GodotShape2D *shape_B_ptr = B->get_shape(shape_B);
Vector2 motion_A, motion_B;
if (A->get_continuous_collision_detection_mode() == PhysicsServer2D::CCD_MODE_CAST_SHAPE) {
motion_A = A->get_motion();
}
if (B->get_continuous_collision_detection_mode() == PhysicsServer2D::CCD_MODE_CAST_SHAPE) {
motion_B = B->get_motion();
}
bool prev_collided = collided;
collided = GodotCollisionSolver2D::solve(shape_A_ptr, xform_A, motion_A, shape_B_ptr, xform_B, motion_B, _add_contact, this, &sep_axis);
if (!collided) {
oneway_disabled = false;
if (A->get_continuous_collision_detection_mode() == PhysicsServer2D::CCD_MODE_CAST_RAY && collide_A) {
check_ccd = true;
return true;
}
if (B->get_continuous_collision_detection_mode() == PhysicsServer2D::CCD_MODE_CAST_RAY && collide_B) {
check_ccd = true;
return true;
}
return false;
}
if (oneway_disabled) {
return false;
}
if (!prev_collided) {
if (shape_B_ptr->allows_one_way_collision() && A->is_shape_set_as_one_way_collision(shape_A)) {
Vector2 direction = xform_A.columns[1].normalized();
bool valid = false;
for (int i = 0; i < contact_count; i++) {
Contact &c = contacts[i];
if (c.normal.dot(direction) > -CMP_EPSILON) { // Greater (normal inverted).
continue;
}
valid = true;
break;
}
if (!valid) {
collided = false;
oneway_disabled = true;
return false;
}
}
if (shape_A_ptr->allows_one_way_collision() && B->is_shape_set_as_one_way_collision(shape_B)) {
Vector2 direction = xform_B.columns[1].normalized();
bool valid = false;
for (int i = 0; i < contact_count; i++) {
Contact &c = contacts[i];
if (c.normal.dot(direction) < CMP_EPSILON) { // Less (normal ok).
continue;
}
valid = true;
break;
}
if (!valid) {
collided = false;
oneway_disabled = true;
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
这就没有必要再跟下去了。至于这些setup函数什么时候被调用,可以用一个实际项目调试来看看。
主要核心思想是理解碰撞的Layer与Mask配置问题。