通过反射获取类的属性与方法【Java】
写在前面的话:
- 参考资料:尚硅谷视频
- 本章内容:如何通过反射获取类的属性、方法
- IDE:eclipse
- JDK:Java8
目录
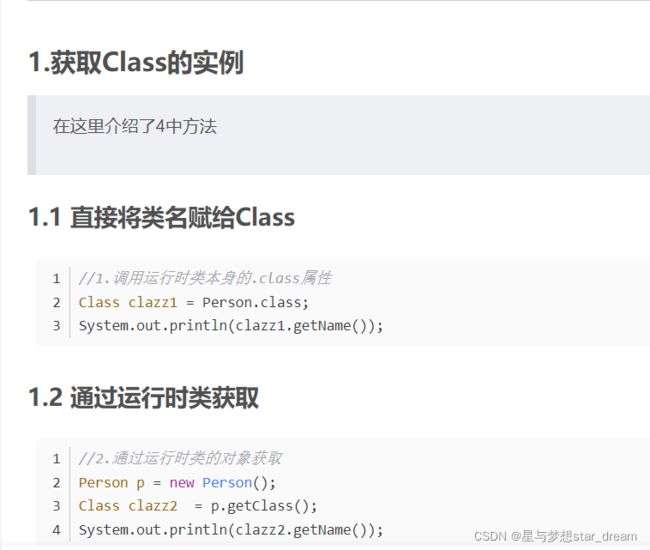
1.获取Class类的实例
2.获取属性
2.1 获取声明为public的属性
2.1.1 如果将Person类的属性的修饰符设定为非public
2.1.2 获取父类的public的属性
2.2 获取声明的属性
2.3 getDeclaredFields()与getFields()区别
2.4 通过属性获取权限修饰符、变量类型和变量名
2.4.1 获取权限修饰符
2.4.2 获取变量类型
2.4.3 获取变量名
3.获取方法
3.1 getMethods()和getDeclaredMethods()
3.2 获取注解
3.2.1 如何创建注解?
3.2.2 使用自定义注解
3.2.3 获取注解
3.3 获取权限修饰符
3.4 获取返回值类型
3.5 获取方法名
3.6 获取参数列表
3.7 获取异常
1.获取Class类的实例
可以参考这篇文章:Java反射 星与梦想star_dream的文章
2.获取属性
2.1 获取声明为public的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();上述代码只能够获取声明为public的属性
代码演示:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestConstructor {
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
String str = new String("exer03.Person");
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class clazz = (Class) Class.forName(str);
//获取运行时类的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();
for(int i = 0;i < fields.length;i++) {
System.out.println(fields[i]);//打印输出
}
}
}
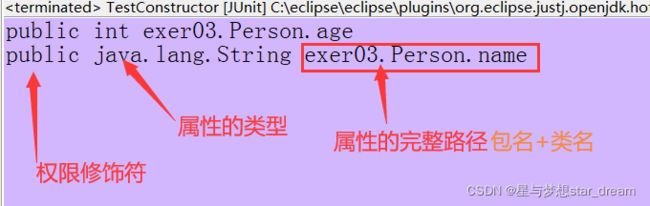
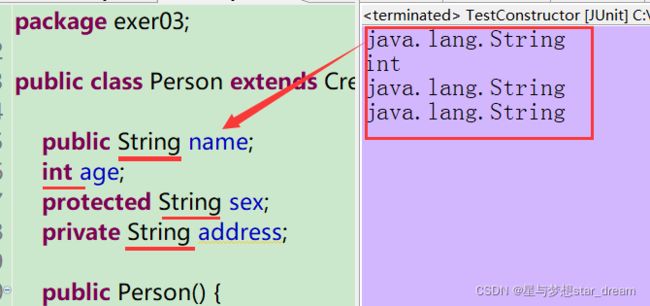
在Person类中,声明的属性有name、age
而通过Field[] fields = clazz.getFields(); 获取的属性,结果如下:
2.1.1 如果将Person类的属性的修饰符设定为非public
通过Field[] fields = clazz.getFields(); 获取的属性,结果如下:
通过上述讲解,可以知道Field[] fields = clazz.getFields(); 获取的属性的修饰符为public
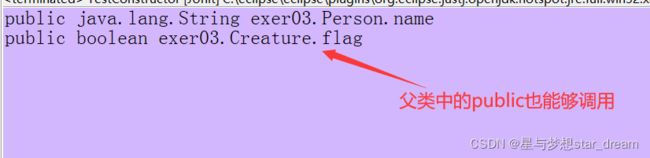
2.1.2 获取父类的public的属性
父类Creature
public class Creature {
public boolean flag;
}
子类Person
2.2 获取声明的属性
只要在类中声明的属性,都可以通过反射获取到
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();代码演示:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestConstructor {
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
String str = new String("exer03.Person");
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class clazz = (Class) Class.forName(str);
//获取运行时类的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
} 在Person类中,声明的属性有name、age、sex、address
而通过Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); 获取的属性,结果如下:
2.3 getDeclaredFields()与getFields()区别
- getDeclaredFields() 只可以访问本类当中的属性
- getFields()只能访问声明为public的属性
- getDeclaredFields() 可以访问声明为任意权限修饰符的属性
- getFields() 可以访问父类中的声明为public的属性
2.4 通过属性获取权限修饰符、变量类型和变量名
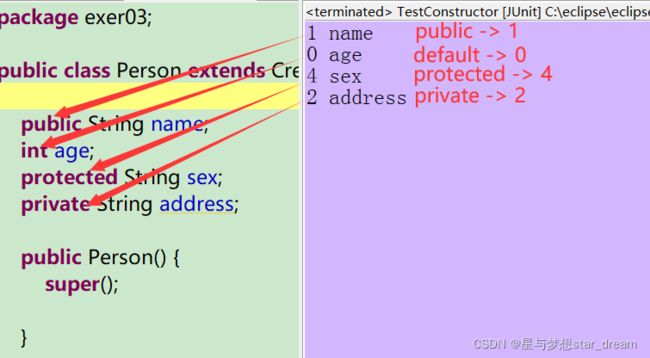
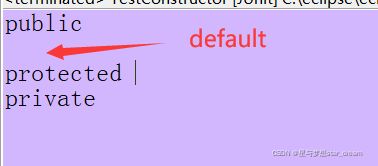
2.4.1 获取权限修饰符
int i = field.getModifiers();//返回值为int型返回类型说明:
- 权限修饰符为default 返回值0
- 权限修饰符为public 返回值1
- 权限修饰符为private 返回值2
- 权限修饰符为protected 返回值4
使用Modifier.toString(int i) 以字符串形式打印出来
String str1 = Modifier.toString(i);//i 是指 0 1 2 4等代码示例:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestConstructor {
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
String str = new String("exer03.Person");
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class clazz = (Class) Class.forName(str);
//获取运行时类的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field : fields) {
//1.获取属性的权限修饰符
int i = field.getModifiers();//返回值为int型
String str1 = Modifier.toString(i);
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
} 结果截图:
2.4.2 获取变量类型
Class c = field.getType();//返回值类型:Class代码示例:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestConstructor {
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
String str = new String("exer03.Person");
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class clazz = (Class) Class.forName(str);
//获取运行时类的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field : fields) {
//1.获取属性的权限修饰符
// int i = field.getModifiers();//返回值为int型
// String str1 = Modifier.toString(i);
// System.out.print(str1 + " ");
//2.获取属性的变量类型
Class c = field.getType();
System.out.print(c.getName() + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
} 结果截图:
2.4.3 获取变量名
System.out.println(field.getName());代码演示:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestConstructor {
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
String str = new String("exer03.Person");
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class clazz = (Class) Class.forName(str);
//获取运行时类的属性
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field : fields) {
//1.获取属性的权限修饰符
int i = field.getModifiers();//返回值为int型
String str1 = Modifier.toString(i);
System.out.print(str1 + " ");
//2.获取属性的变量类型
Class c = field.getType();
System.out.print(c.getName() + " ");
//3.获取属性的变量名
System.out.println(field.getName());
System.out.println();
}
}
} 效果截图:
3.获取方法
3.1 getMethods()和getDeclaredMethods()
获取方法与获取属性相似!同样具有两种方法
- Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
- Method[] methods2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestMethon {
@Test
public void test1() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
//getMethods():获取运行时类及其父类的声明为public的方法
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
//getDeclaredMethods() : 获取运行时类的所有方法
Method[] methods2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods2) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
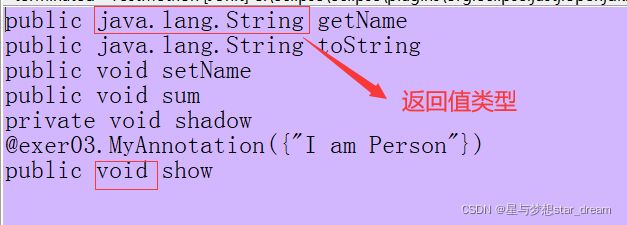
} 结果截图:
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();得到的结果
Method[] methods2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();得到的结果
| 1 | 注解 |
| 2 | 权限修饰符 |
| 3 | 返回值类型 |
| 4 | 方法名 |
| 5 | 形参列表 |
| 6 | 异常 |
3.2 获取注解
Annotation[] annotation = method.getAnnotations();3.2.1 如何创建注解?
要想获取注解,就一定要有注解!
代码示例:(自定义注解)
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.PARAMETER;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.TYPE;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String[] value();
}3.2.2 使用自定义注解
代码示例:
在一个类中的方法上,添加注解
@MyAnnotation(value = "I am Person")
public void show() {
System.out.println("我是Person类");
}3.2.3 获取注解
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestMethon {
@Test
public void test2() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
//1.获取注解
Annotation[] annotation = method.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation a : annotation) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//获取方法名
System.out.print(method.getName() + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
} 结果截图:
3.3 获取权限修饰符
获取权限修饰符,与前面获取属性的权限修饰符一样。
int i = method.getModifiers();
代码演示:
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestMethon {
@Test
public void test2() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
//1.获取注解
Annotation[] annotation = method.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation a : annotation) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//2.获取权限修饰符
int i = method.getModifiers();
String str = Modifier.toString(i);
System.out.print(str + " ");
//获取方法名
System.out.print(method.getName() + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
} 效果截图:
3.4 获取返回值类型
Class returnType = method.getReturnType();代码示例:
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestMethon {
@Test
public void test2() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
//1.获取注解
Annotation[] annotation = method.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation a : annotation) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//2.获取权限修饰符
int i = method.getModifiers();
String str = Modifier.toString(i);
System.out.print(str + " ");
//3.获取返回类型
Class returnType = method.getReturnType();
System.out.print(returnType.getName() + " ");
//获取方法名
System.out.print(method.getName() + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
} 效果截图:
3.5 获取方法名
System.out.print(method.getName() + " ");3.6 获取参数列表
Class[] param = method.getParameterTypes();打印输出参数列表
Class[] param = method.getParameterTypes();
System.out.print("(");
for(int j = 0;j < param.length;j++) {
if(j == param.length - 1) {
System.out.print(param[j].getName() + " args-" + j);
}else {
System.out.print(param[j].getName() + " args-" + j + ",");
}
}
System.out.print(")");代码示例
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestMethon {
@Test
public void test2() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
//1.获取注解
Annotation[] annotation = method.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation a : annotation) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//2.获取权限修饰符
int i = method.getModifiers();
String str = Modifier.toString(i);
System.out.print(str + " ");
//3.获取返回类型
Class returnType = method.getReturnType();
System.out.print(returnType.getName() + " ");
//4.获取方法名
System.out.print(method.getName() + " ");
//5.获取参数列表
Class[] param = method.getParameterTypes();
System.out.print("(");
for(int j = 0;j < param.length;j++) {
if(j == param.length - 1) {
System.out.print(param[j].getName() + " args-" + j);
}else {
System.out.print(param[j].getName() + " args-" + j + ",");
}
}
System.out.print(")");
System.out.println();
}
}
} 效果截图:
3.7 获取异常
Class[] exceptions = method.getExceptionTypes();打印输出异常
Class[] exceptions = method.getExceptionTypes();
if(exceptions.length != 0) {
//如果有异常,则加上throws
System.out.print(" throws ");
}
for(int j = 0;j < exceptions.length;j++) {
System.out.print(exceptions[j].getName() + " ");
}代码示例(差不多是打印完整的方法结构)
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestMethon {
@Test
public void test2() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
//1.获取注解
Annotation[] annotation = method.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation a : annotation) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//2.获取权限修饰符
int i = method.getModifiers();
String str = Modifier.toString(i);
System.out.print(str + " ");
//3.获取返回类型
Class returnType = method.getReturnType();
System.out.print(returnType.getName() + " ");
//4.获取方法名
System.out.print(method.getName());
//5.获取参数列表
Class[] param = method.getParameterTypes();
System.out.print("(");
for(int j = 0;j < param.length;j++) {
if(j == param.length - 1) {
System.out.print(param[j].getName() + " args-" + j);
}else {
System.out.print(param[j].getName() + " args-" + j + ",");
}
}
System.out.print(")");
//6.获取异常
Class[] exceptions = method.getExceptionTypes();
if(exceptions.length != 0) {
//如果有异常,则加上throws
System.out.print(" throws ");
}
for(int j = 0;j < exceptions.length;j++) {
System.out.print(exceptions[j].getName() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} 效果截图:
完