立志10天学会C++基础应用—day01
文章目录
- 前言
- 第一天感觉很实用的快捷键
- 一、常识
-
- A01打印c++HelloWorld.cpp
- A02变量.cpp
- A03常量.cpp
- A04标识符命名规则.cpp
- A05整型.cpp
- A06sizeof的用法.cpp
- A07实型.cpp
- A08字符型.cpp
- A09转义字符.cpp
- A10字符串类型.cpp
- A11布尔类型.cpp
- A12数据的输入.cpp
- 二、算术运算符
-
- A13算术运算符.cpp
- A14赋值运算符.cpp
- A15比较运算符.cpp
- A16逻辑运算符.cpp
- 三、选择结构
-
- A17选择结构.cpp
- A18选择结构的应用.cpp
- A19三目运算符.cpp
- A20switch语句.cpp
- 总结
前言
下面的文章小王留着以后复盘用,比较通俗易懂了属于是。考完研已经快一个月了,小王必须尽快恢复状态,不开心的就让他过去吧,学业一定不可以落下,纵有疾风起,人生不言弃,与诸君共勉!

第一天感觉很实用的快捷键
第一次用vs
(自动对齐)快捷键:Ctrl+K+D(三个键同时按下)
注释:Ctrl + K + C
取消注释:Ctrl + K + U
一、常识
注:一个工程下面不可两个及以上cpp文件中出现main函数,也就是你只能在一个cpp里有main函数
A01打印c++HelloWorld.cpp
#include https://blog.csdn.net/hanhanwanghaha宝藏女孩的成长日记 欢迎您的关注!
欢迎关注微信公众号:宝藏女孩的成长日记 让这个可爱的宝藏女孩在努力的道路上与你一起同行! 如有转载,请注明出处(如不注明,盗者必究)
A02变量.cpp
#include A03常量.cpp
#include A04标识符命名规则.cpp
#include A05整型.cpp
#include A06sizeof的用法.cpp
#include https://blog.csdn.net/hanhanwanghaha 宝藏女孩的成长日记 欢迎您的关注!
欢迎关注微信公众号:宝藏女孩的成长日记 让这个可爱的宝藏女孩在努力的道路上与你一起同行! 如有转载,请注明出处(如不注明,盗者必究)
A07实型.cpp
#include A08字符型.cpp
#include A09转义字符.cpp
#include A10字符串类型.cpp
#include A11布尔类型.cpp
#include A12数据的输入.cpp
#include 二、算术运算符
A13算术运算符.cpp
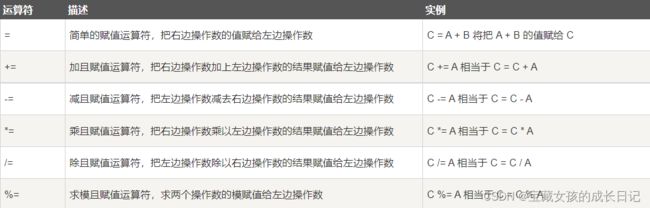
#include A14赋值运算符.cpp
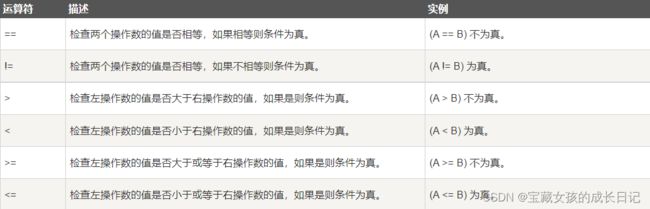
#include A15比较运算符.cpp
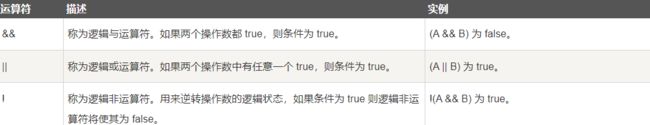
#include A16逻辑运算符.cpp
#include 三、选择结构
A17选择结构.cpp
#include A18选择结构的应用.cpp
#include A19三目运算符.cpp
#include A20switch语句.cpp
#include 总结
https://blog.csdn.net/hanhanwanghaha宝藏女孩的成长日记 欢迎您的关注!
欢迎关注微信公众号:宝藏女孩的成长日记 让这个可爱的宝藏女孩在努力的道路上与你一起同行! 如有转载,请注明出处(如不注明,盗者必究)、
C++大部分和C Python java的语法是差不多的,反正语言都是有贯通性的 ,但还是有一些语法上的差别感觉,
而且很多都是离散数学学过的吧, 第一天接触的都是很基础的东西 明天加大分量。终于干完咯!去看武林外传啦!!!