Flutter(五)容器类组件
布局类组件包含多个子组件,而容器类组件只包含一个子组件
目录
- 填充(Padding)
- 装饰容器(DecoratedBox)
- 变换(Transform)
-
- Transform.translate 平移
- Transform.rotate 旋转
- Transform.scale 缩放
- RotatedBox
- 容器组件(Container)
-
- 实例
- 剪裁(Clip)
-
- 自定义裁剪(CustomClipper)
- 空间适配(FittedBox)
- 页面骨架(Scaffold)
-
- AppBar 一个导航栏骨架
- Drawer 抽屉菜单
- BottomNavigationBar 底部导航栏
- FloatingActionButton 漂浮按钮
填充(Padding)
Padding({
...
EdgeInsetsGeometry padding,
Widget child,
})
我们看看EdgeInsets提供的便捷方法:
fromLTRB(double left, double top, double right, double bottom)://分别指定四个方向的填充。
all(double value) : //所有方向均使用相同数值的填充。
only({left, top, right ,bottom })://可以设置具体某个方向的填充(可以同时指定多个方向)。
symmetric({ vertical, horizontal })://用于设置对称方向的填充,vertical指top和bottom,horizontal指left和right
示例:
class PaddingTestRoute extends StatelessWidget {
const PaddingTestRoute({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Padding(
//上下左右各添加16像素补白
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Column(
//显式指定对齐方式为左对齐,排除对齐干扰
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: const <Widget>[
Padding(
//左边添加8像素补白
padding: EdgeInsets.only(left: 8),
child: Text("Hello world"),
),
Padding(
//上下各添加8像素补白
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 8),
child: Text("I am Jack"),
),
Padding(
// 分别指定四个方向的补白
padding: EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(20, 0, 20, 20),
child: Text("Your friend"),
)
],
),
);
}
}
装饰容器(DecoratedBox)
DecoratedBox可以在其子组件绘制前(或后)绘制一些装饰(Decoration),如背景、边框、渐变
const DecoratedBox({
Decoration decoration,//绘制的装饰
//在哪儿绘制,background:在子组件之后绘制,即背景装饰。
//foreground:在子组件之上绘制,即前景。
DecorationPosition position
Widget? child
})
我们通常会直接使用BoxDecoration类,它是一个Decoration的子类,实现了常用的装饰元素的绘制
BoxDecoration({
Color color, //颜色
DecorationImage image,//图片
BoxBorder border, //边框
BorderRadiusGeometry borderRadius, //圆角
List<BoxShadow> boxShadow, //阴影,可以指定多个
Gradient gradient, //渐变
BlendMode backgroundBlendMode, //背景混合模式
BoxShape shape = BoxShape.rectangle, //形状
})
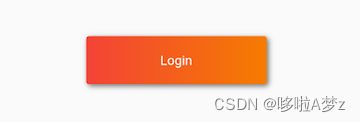
下面我们实现一个带阴影的背景色渐变的按钮:
DecoratedBox(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: LinearGradient(colors:[Colors.red,Colors.orange.shade700]), //背景渐变
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(3.0), //3像素圆角
boxShadow: [ //阴影
BoxShadow(
color:Colors.black54,
offset: Offset(2.0,2.0),
blurRadius: 4.0
)
]
),
child: Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 80.0, vertical: 18.0),
child: Text("Login", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
)
)
变换(Transform)
Transform.translate 平移
DecoratedBox(
decoration:BoxDecoration(color: Colors.red),
//默认原点为左上角,左移20像素,向上平移5像素
child: Transform.translate(
offset: Offset(-20.0, -5.0),
child: Text("Hello world"),
),
)
Transform.rotate 旋转
DecoratedBox(
decoration:BoxDecoration(color: Colors.red),
child: Transform.rotate(
//旋转90度
angle:math.pi/2 ,
child: Text("Hello world"),
),
)
Transform.scale 缩放
DecoratedBox(
decoration:BoxDecoration(color: Colors.red),
child: Transform.scale(
scale: 1.5, //放大到1.5倍
child: Text("Hello world")
)
);
Transform的变换是应用在绘制阶段,而并不是应用在布局(layout)阶段,所以无论对子组件应用何种变化,其占用空间的大小和在屏幕上的位置都是固定不变的,因为这些是在布局阶段就确定的
由于矩阵变化只会作用在绘制阶段,所以在某些场景下,在UI需要变化时,可以直接通过矩阵变化来达到视觉上的UI改变,而不需要去重新触发build流程,这样会节省layout的开销,所以性能会比较
RotatedBox
RotatedBox和Transform.rotate功能相似,它们都可以对子组件进行旋转变换,但是有一点不同:RotatedBox的变换是在layout阶段,会影响在子组件的位置和大小
容器组件(Container)
Container是一个组合类容器,它本身不对应具体的RenderObject,它是DecoratedBox、ConstrainedBox、Transform、Padding、Align等组件组合的一个多功能容器,所以我们只需通过一个Container组件可以实现同时需要装饰、变换、限制的场景
Container({
this.alignment,
this.padding, //容器内补白,属于decoration的装饰范围
Color color, // 背景色
Decoration decoration, // 背景装饰
Decoration foregroundDecoration, //前景装饰
double width,//容器的宽度
double height, //容器的高度
BoxConstraints constraints, //容器大小的限制条件
this.margin,//容器外补白,不属于decoration的装饰范围
this.transform, //变换
this.child,
...
})
实例
Container(
margin: EdgeInsets.only(top: 50.0, left: 120.0),
constraints: BoxConstraints.tightFor(width: 200.0, height: 150.0),//卡片大小
decoration: BoxDecoration( //背景装饰
gradient: RadialGradient( //背景径向渐变
colors: [Colors.red, Colors.orange],
center: Alignment.topLeft,
radius: .98,
),
boxShadow: [
//卡片阴影
BoxShadow(
color: Colors.black54,
offset: Offset(2.0, 2.0),
blurRadius: 4.0,
)
],
),
transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(.2),//卡片倾斜变换
alignment: Alignment.center, //卡片内文字居中
child: Text(
//卡片文字
"5.20", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 40.0),
),
)

Container组件margin和padding属性的区别:
Container(
margin: EdgeInsets.all(20.0), //容器外补白
color: Colors.orange,
child: Text("Hello world!"),
),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20.0), //容器内补白
color: Colors.orange,
child: Text("Hello world!"),
),
事实上,Container内margin和padding都是通过Padding 组件来实现的,上面的示例代码实际上等价于:
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: DecoratedBox(
decoration: BoxDecoration(color: Colors.orange),
child: Text("Hello world!"),
),
),
DecoratedBox(
decoration: BoxDecoration(color: Colors.orange),
child: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: Text("Hello world!"),
),
),
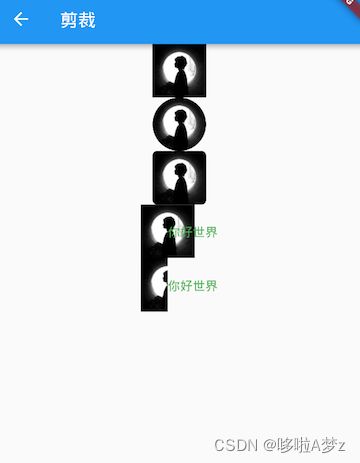
剪裁(Clip)
ClipOval 子组件为正方形时剪裁成内贴圆形;为矩形时,剪裁成内贴椭圆
ClipRRect 将子组件剪裁为圆角矩形
ClipRect 默认剪裁掉子组件布局空间之外的绘制内容(溢出部分剪裁)
ClipPath 按照自定义的路径剪裁
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class ClipTestRoute extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// 头像
Widget avatar = Image.asset("imgs/avatar.png", width: 60.0);
return Center(
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
avatar, //不剪裁
ClipOval(child: avatar), //剪裁为圆形
ClipRRect( //剪裁为圆角矩形
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(5.0),
child: avatar,
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Align(
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
widthFactor: .5,//宽度设为原来宽度一半,另一半会溢出
child: avatar,
),
Text("你好世界", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.green),)
],
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
ClipRect(//将溢出部分剪裁
child: Align(
alignment: Alignment.topLeft,
widthFactor: .5,//宽度设为原来宽度一半
child: avatar,
),
),
Text("你好世界",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.green))
],
),
],
),
);
}
}
自定义裁剪(CustomClipper)
如果我们只想截取图片中部40×30像素的范围应该怎么做?这时我们可以使用CustomClipper来自定义剪裁区域
1.自定义一个CustomClipper
class MyClipper extends CustomClipper<Rect> {
//getClip()是用于获取剪裁区域的接口,由于图片大小是60×60,我们返回剪裁区域为Rect.fromLTWH(10.0, 15.0, 40.0, 30.0),即图片中部40×30像素的范围
@override
Rect getClip(Size size) => Rect.fromLTWH(10.0, 15.0, 40.0, 30.0);
//shouldReclip决定是否重新剪裁。
//剪裁区域始终不变化时应该返回false,这样就不会触发重新剪裁,避免不必要的性能开销。
//剪裁区域发生变化(比如在对剪裁区域执行一个动画),那么变化后应该返回true来重新执行剪裁。
@override
bool shouldReclip(CustomClipper<Rect> oldClipper) => false;
}
2.通过ClipRect来执行剪裁
DecoratedBox(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.red
),
child: ClipRect(
clipper: MyClipper(), //使用自定义的clipper
child: avatar
),
)

可以看到我们的剪裁成功了,但是图片所占用的空间大小仍然是60×60(红色区域),这是因为组件大小是是在layout阶段确定的,而剪裁是在之后的绘制阶段进行的,所以不会影响组件的大小,这和Transform原理是相似的。
空间适配(FittedBox)
子组件大小超出了父组件大小时,如果不经过处理的话 Flutter 中就会显示一个溢出警告并在控制台打印错误日志

可以看到右边溢出了 45 像素。
如果让 Text 文本在超过父组件的宽度时不要换行而是字体缩小,
还有比如父组件的宽高固定,而 Text 文本较少,这时候我们想让文本放大以填充整个父组件空间该怎么做呢?
上面这两个问题的本质就是:子组件如何适配父组件空间,Flutter 提供了一个 FittedBox 组件
const FittedBox({
Key? key,
this.fit = BoxFit.contain, // 适配方式
this.alignment = Alignment.center, //对齐方式
this.clipBehavior = Clip.none, //是否剪裁
Widget? child,
})
1.FittedBox 在布局子组件时会忽略其父组件传递的约束,可以允许子组件无限大
2.FittedBox 对子组件布局结束后就可以获得子组件真实的大小
3.FittedBox 知道子组件的真实大小和父组件的约束就可以通过指定的适配方式(BoxFit 枚举中指定)适配显示。
实例:一行不够显示缩放布局
class SingleLineFittedBox extends StatelessWidget {
const SingleLineFittedBox({Key? key,this.child}) : super(key: key);
final Widget? child;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return LayoutBuilder(
builder: (_, constraints) {
return FittedBox(
child: ConstrainedBox(
constraints: constraints.copyWith(
minWidth: constraints.maxWidth,
maxWidth: double.infinity,
//maxWidth: constraints.maxWidth
),
child: child,
),
);
},
);
}
}
我们将最小宽度(minWidth)约束指定为屏幕宽度,因为Row必须得遵守父组件的约束,所以 Row 的宽度至少等于屏幕宽度,所以就不会出现缩在一起的情况;
同时我们将 maxWidth 指定为无限大,则就可以处理数字总长度超出屏幕宽度的情况

无论长数字还是短数字,我们的SingleLineFittedBox 都可以正常工作,大功告成
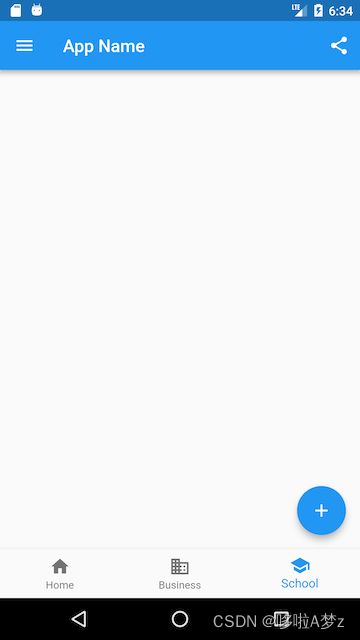
页面骨架(Scaffold)
我们实现一个页面,它包含:
- 一个导航栏
- 导航栏右边有一个分享按钮
- 有一个抽屉菜单
- 有一个底部导航
- 右下角有一个悬浮的动作按钮
class ScaffoldRoute extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_ScaffoldRouteState createState() => _ScaffoldRouteState();
}
class _ScaffoldRouteState extends State<ScaffoldRoute> {
int _selectedIndex = 1;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar( //导航栏
title: Text("App Name"),
actions: <Widget>[ //导航栏右侧菜单
IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.share), onPressed: () {}),
],
),
drawer: MyDrawer(), //抽屉
bottomNavigationBar: BottomNavigationBar( // 底部导航
items: <BottomNavigationBarItem>[
BottomNavigationBarItem(icon: Icon(Icons.home), title: Text('Home')),
BottomNavigationBarItem(icon: Icon(Icons.business), title: Text('Business')),
BottomNavigationBarItem(icon: Icon(Icons.school), title: Text('School')),
],
currentIndex: _selectedIndex,
fixedColor: Colors.blue,
onTap: _onItemTapped,
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton( //悬浮按钮
child: Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed:_onAdd
),
);
}
void _onItemTapped(int index) {
setState(() {
_selectedIndex = index;
});
}
void _onAdd(){
}
}
效果图
AppBar 一个导航栏骨架
AppBar({
Key? key,
this.leading, //导航栏最左侧Widget,常见为抽屉菜单按钮或返回按钮。
this.automaticallyImplyLeading = true, //如果leading为null,是否自动实现默认的leading按钮
this.title,// 页面标题
this.actions, // 导航栏右侧菜单
this.bottom, // 导航栏底部菜单,通常为Tab按钮组
this.elevation = 4.0, // 导航栏阴影
this.centerTitle, //标题是否居中
this.backgroundColor,
... //其他属性见源码注释
})
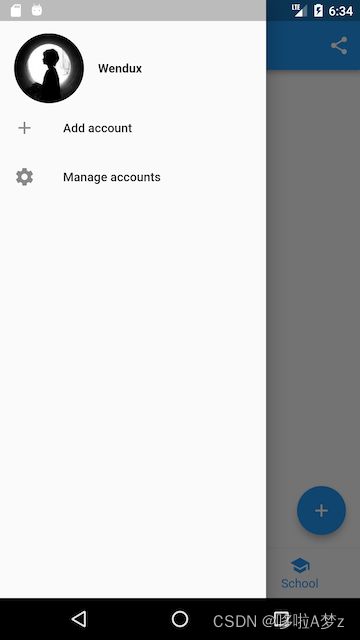
Drawer 抽屉菜单
Scaffold的drawer和endDrawer属性可以分别接受一个Widget来作为页面的左、右抽屉菜单
class MyDrawer extends StatelessWidget {
const MyDrawer({
Key? key,
}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Drawer(
child: MediaQuery.removePadding(
context: context,
//移除抽屉菜单顶部默认留白
removeTop: true,
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(top: 38.0),
child: Row(
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16.0),
child: ClipOval(
child: Image.asset(
"imgs/avatar.png",
width: 80,
),
),
),
Text(
"Wendux",
style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
)
],
),
),
Expanded(
child: ListView(
children: <Widget>[
ListTile(
leading: const Icon(Icons.add),
title: const Text('Add account'),
),
ListTile(
leading: const Icon(Icons.settings),
title: const Text('Manage accounts'),
),
],
),
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
BottomNavigationBar 底部导航栏
BottomNavigationBar和BottomNavigationBarItem两种组件来实现
bottomNavigationBar: BottomAppBar(
color: Colors.white,
shape: CircularNotchedRectangle(), // 底部导航栏打一个圆形的洞
child: Row(
children: [
IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.home)),
SizedBox(), //中间位置空出
IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.business)),
],
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceAround, //均分底部导航栏横向空间
),
)
FloatingActionButton 漂浮按钮
floatingActionButton属性来设置一个FloatingActionButton,同时通过floatingActionButtonLocation属性来指定其在页面中悬浮的位置
完。