sentinel 简单使用
sentinel
-
- 1. springboot 整合 Sentinel
-
- 1.1 sentinel-dashboard 安装
- 1.2 客户端配置
- 1.3 编写测试用例
- 1.4 @SentinelResource各项属性简介
- 1.5 持久化限流配置
- 2. sentinel 源码学习
前言:在学习该框架之前,我们先来了解一些问题。
问题一:百万级并发请求,服务器真的会宕机吗?
答:对于服务端来说,当请求量达到了 tomcat 设置的最大连接数,请求任务会加入任务队列中等待被执行,但如果任务队列也满了,则会直接拒绝其它请求。所以合理的设置 tomcat 的参数,是能避免服务端因为请求数过大而宕机的。但对于服务端的物理机,因为 socket 是四元组,理论上 tcp的连接是没有上限的,但是每个连接都会消耗内存,但当某一时刻,tcp 连接突增,应用层 tomcat 来不及拒绝关闭多余的 tcp 连接,导致物理机内存爆满从而宕机,这种问题可以规避吗,nginx 可以限制服务器物理机进来的 tcp 连接数,同时 naginx 也能对单个请求接口进行限流。
问题二:既然 nginx、服务器tomcat 可以规避并发请求数过多导致服务器宕机问题,同时 nginx 还支持对单个接口设置限流。为什么还要有 sentinel、hystrix 这些框架来对单个接口进行限流呢?
答:tomcat 线程数的设置跟每个接口运算类型有关( CPU 密集和 IO 密集)。对于 IO 密集计算,为了使 cpu 不会空等线程阻塞,可以设置稍微多一点线程数来充分利用 cpu。但对于 CPU 密集计算,应当设置和物理机 cpu 核心一样的线程数,这样不会有过多的上下文切换消耗。但整个服务的各个接口都不一样,有时要折中设置一个合理的线程数,让服务达到最大吞吐量。在这种背景下,会有一些问题需要我们注意:
- 如果存在服务器中的某个接口会产生比较大的内存消耗,当某一刻所有的请求都落在这个接口上,也就是线程池中的线程全部执行这个接口的任务,可能会导致服务器内存爆满而宕机。这时候可以使用 nginx 和 sentinel 对这个指定的接口进行限流,而 tomcat 参数并不好修改。
- 如果存在服务器中的某个接口的业务操作 IO 阻塞延迟过久,当某一刻所有的请求都落在这个接口上,也就是线程池中的线程全部执行这个接口的任务,那么tomcat 线程都被这个接口长时间占用,对于其它接口服务请求则会出现没有线程来处理的情况,从而导致超时,服务不可用。这时候同样使用 nginx 和 sentinel 对这个指定的接口进行限流,而 tomcat 参数并不好改。
- 对于并发高的接口,比如秒杀接口,假如秒杀接口正常业务处理能达到的QPS是2000,目前只有5台机器,但是现在却有10并发的请求量,如果要使得用户能正常请求,不至于页面拒绝连接、超时等情况,那么必须对秒杀接口进行限流降级,使大部分用户直接降级处理。那么同样可以使用 nginx 和 sentinel 对这个接口进行限流降级。
这里有人会问,既然都可以使用 nginx 限流,为啥还要用 sentinel。并且 sentinel 限流在业务层,请求会到 tomcat 并且占用 tomcat 线程,而 nginx 直接对用户请求限流降级,请求都不用进入服务器 tomcat,似乎 nginx 效率更高?那什么情况下要使用 sentinel 限流呢?
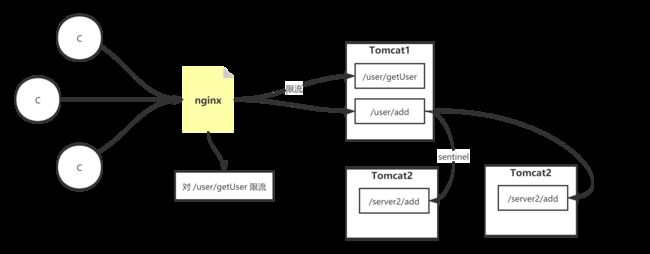
微服务之间没有 nginx 这层网关,那么必须要使用 sentinel 来进行限流。直接对客户端的接口则用nginx来进行限流。
本人业务上,有一个用户数据上传的接口,该接口耗时严重,它是直接对外的,但是却使用的是 sentinel 进行限流,主要在限流降级函数中,将用户的数据上传 mq 做异步处理。如果用 nginx 则不好做。
1. springboot 整合 Sentinel
1.1 sentinel-dashboard 安装
Sentinel包括服务端和客户端,服务端有可视化界面,可以查看客户端各项指标、配置客户端限流策略等。
- 下载:从官网下载Sentinel,下载地址:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/releases, 这里下载的是 sentinel-dashboard-1.8.1.jar 文件
- 驱动:通过命令启动sentinel服务端:java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.1.jar,默认启动8080端口。启动成功之后,通过如下地址可以进行访问:http://localhost:8080,默认登录账号密码均为 sentinel。
此时还没启动客户端,所以界面是空的。
1.2 客户端配置
这里以springBoot项目整合sentinel为例,springboot是2.2.5版本。
maven中加入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cspgroupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-coreartifactId>
<version>1.8.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.75version>
dependency>
然后,在yml配置文件里面,配置服务端地址:
spring:
application:
name: myService
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080
port: 8719 # Sentinel api端口 ,默认8719,假如被占用了会自动从8719开始依次+1扫描。直至找到未被占用的端口
1.3 编写测试用例
@Override
@SentinelResource("gcTest")
public List<User> gcTest(User user) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2];
int i = method0();
for (int j = 1; j < 100; j++) {
int a = 1/j;
}
User user1 = new User();
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < 3000; j++) {
list.add(new User());
}
method1();
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2];
return list;
}
这里在service层对需要限流的方法加上@SentinelResource,value = "getTest"代表资源名标识符。
服务刚启动是看不到服务名的,需要先访问才可以看到。
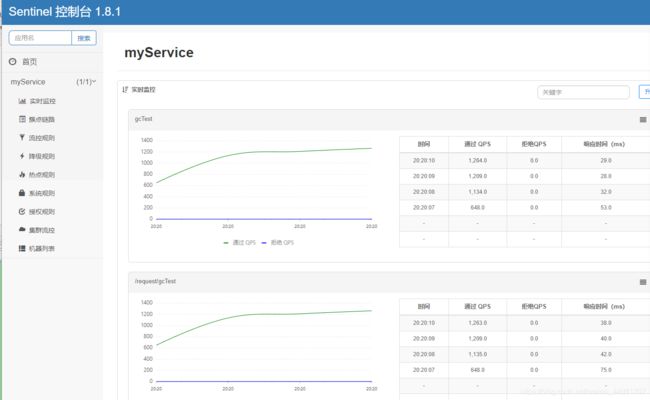
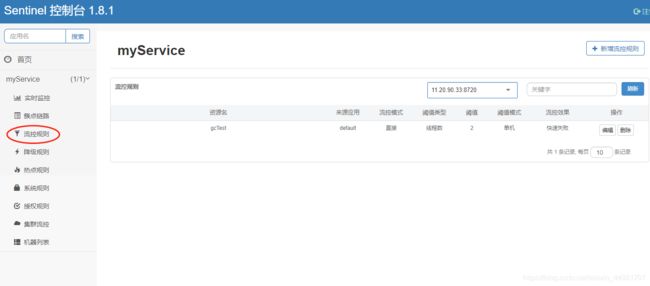
然后我们可以在簇点链路上对资源名进行各项配置,这里只演示流控规则限流配置。
配置成功后如下:
再查看我们的实时监控
对于拒绝的请求,服务器会抛出异常:
20:34:15.120 [http-nio-8081-exec-63] ERROR org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/].[dispatcherServlet] - Servlet.service() for servlet [dispatcherServlet] in context with path [] threw exception [Request processing failed; nested exception is java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException] with root cause
com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowException: null
当请求被拒绝时,配置限流降级方法:
@Override
@SentinelResource(value = "gcTest", blockHandler = "blockHandler")
public List<User> gcTest(User user) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2];
int i = method0();
for (int j = 1; j < 100; j++) {
int a = 1/j;
}
User user1 = new User();
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < 3000; j++) {
list.add(new User());
}
method1();
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 2];
return list;
}
public List<User> blockHandler(User user, BlockException e) {
System.out.println("限流成功");
return null;
}
输出:
限流成功
限流成功
限流成功
......
1.4 @SentinelResource各项属性简介
- value
作用:资源名
是否必须:是
- entryType
作用:entry类型,标记流量的方向,指明是出口流量,还是入口流量;取值 IN/OUT ,默认是OUT。
是否必须:否
- blockHandler
作用:处理BlockException的函数名称。函数要求:
- 必须是 public
- 返回类型与原方法一致
- 参数类型需要和原方法相匹配,并在最后加 BlockException 类型的参数。
- 默认需和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,可配置 blockHandlerClass ,并指定blockHandlerClass里面的方法。
是否必须:否
- blockHandlerClass
作用:存放blockHandler的类。对应的处理函数必须static修饰,否则无法解析,其他要求:同blockHandler。
是否必须:否
- fallback
作用:用于在抛出异常的时候提供fallback处理逻辑。fallback函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了 exceptionsToIgnore 里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。函数要求:
- 返回类型与原方法一致
- 参数类型需要和原方法相匹配,Sentinel 1.6开始,也可在方法最后加 Throwable 类型的参数。
- 默认需和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,可配置 fallbackClass ,并指定fallbackClass里面的方法。
是否必须:否
- fallbackClass
作用:存放fallback的类。对应的处理函数必须static修饰,否则无法解析,其他要求:同fallback。
是否必须:否
- defaultFallback
作用:用于通用的 fallback 逻辑。默认fallback函数可以针对所有类型的异常(除了 exceptionsToIgnore 里面排除掉的异常类型)进行处理。若同时配置了 fallback 和 defaultFallback,以fallback为准。函数要求:
- 返回类型与原方法一致
- 方法参数列表为空,或者有一个 Throwable 类型的参数。
- 默认需要和原方法在同一个类中。若希望使用其他类的函数,可配置 fallbackClass ,并指定 fallbackClass 里面的方法。
是否必须:否
- exceptionsToIgnore
作用:指定排除掉哪些异常。排除的异常不会计入异常统计,也不会进入fallback逻辑,而是原样抛出。
是否必须:否
- exceptionsToTrace
作用:要跟踪的异常类列表
是否必须:否
1.5 持久化限流配置
一旦重启服务,之前设置的Sentinel限流规则等将会消失,因为它存储在sentinel的客户端内存中,需要将配置规则持久化。
// TODO
2. sentinel 源码学习
首先查看SentinelResourceAspect类
@Aspect
public class SentinelResourceAspect extends AbstractSentinelAspectSupport {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource)")
public void sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut() {
}
@Around("sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut()")
public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);
SentinelResource annotation = originMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelResource.class);
if (annotation == null) {
// Should not go through here.
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for SentinelResource annotation");
}
String resourceName = getResourceName(annotation.value(), originMethod);
EntryType entryType = annotation.entryType();
int resourceType = annotation.resourceType();
Entry entry = null;
try {
// sentinel逻辑入口方法
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());
// 执行源方法方法
Object result = pjp.proceed();
return result;
} catch (BlockException ex) {
return handleBlockException(pjp, annotation, ex);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore();
// The ignore list will be checked first.
if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) {
throw ex;
}
if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) {
traceException(ex);
return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex);
}
// No fallback function can handle the exception, so throw it out.
throw ex;
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());
}
}
}
}
是不是一目了然,切面类使用自定义注解@SentinelResource实现了AOP功能,invokeResourceWithSentinel是环绕方法。
// TODO