深度学习--A `Concatenate` layer requires inputs with matching shapes except for the concatenation axis.
- 在使用Unet模型时,输入的大小不是2的次方,在上采样时会出现如下报错:
A `Concatenate` layer requires inputs with matching shapes except for the concatenation axis.
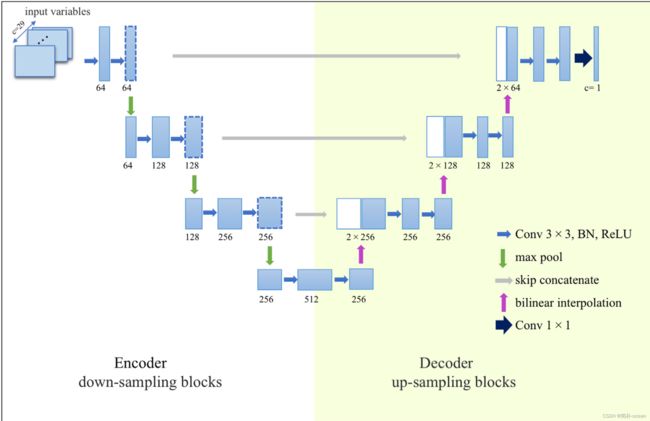
Unet模型
- 图片引用自 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aosl.2022.100322
Unet模型主要包含两个部分,下采样以及上采样,每次下采样包含2次卷积和一次池化,如下所示:
def conv_block(x, filter_size, size, dropout, batch_norm=False):
conv = layers.Conv2D(size, (filter_size, filter_size), padding="same")(x)
if batch_norm is True:
conv = layers.BatchNormalization(axis=3)(conv)
conv = layers.Activation("relu")(conv)
conv = layers.Conv2D(size, (filter_size, filter_size), padding="same")(conv)
if batch_norm is True:
conv = layers.BatchNormalization(axis=3)(conv)
conv = layers.Activation("relu")(conv)
if dropout > 0:
conv = layers.Dropout(dropout)(conv)
return conv
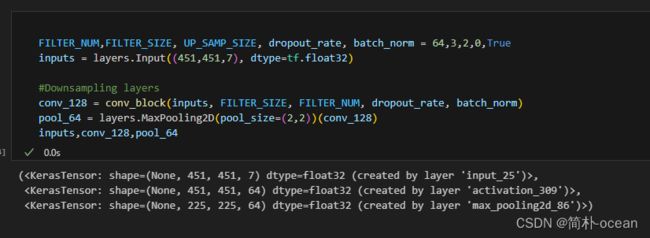
FILTER_NUM,FILTER_SIZE, UP_SAMP_SIZE, dropout_rate, batch_norm = 64,3,2,0,True
inputs = layers.Input((451,451,7), dtype=tf.float32)
#Downsampling layers
conv_128 = conv_block(inputs, FILTER_SIZE, FILTER_NUM, dropout_rate, batch_norm)
pool_64 = layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))(conv_128)
inputs,conv_128,pool_64
输入的数据维度为:widthxlengthxheight,或者也可以理解为气象海洋数据中的lonxlatxheightl
可以发现,经过两次卷积操作后,空间维度减小了一半而高度维度增加到了64,空间维度减小是因为池化层,高度维度为64是因为使用了3个滤波器,更多的滤波器意味着更多的特征图被计算。
重复上述的操作,完成所有的下采样过程,得到如下结果:

然后进行上采样过程:
# Upsampling layers
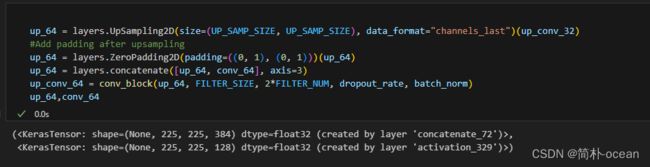
up_16 = layers.UpSampling2D(size=(UP_SAMP_SIZE, UP_SAMP_SIZE), data_format="channels_last")(conv_8)
# Add padding after upsampling
up_16 = layers.concatenate([up_16, conv_16], axis=3)
up_conv_16 = conv_block(up_16, FILTER_SIZE, 8*FILTER_NUM, dropout_rate, batch_norm)
up_16 ,up_conv_16

上采样过程实际上就是通过转置卷积(或者称为反卷积)操作来恢复特征图的尺寸和维度,并且通过跳跃连接与下采样路径的对应层进行融合,以重新细化和合并信息,从而进行准确的分割预测,重复一次上采样操作,结果没有问题

继续上采样,发现出现报错:
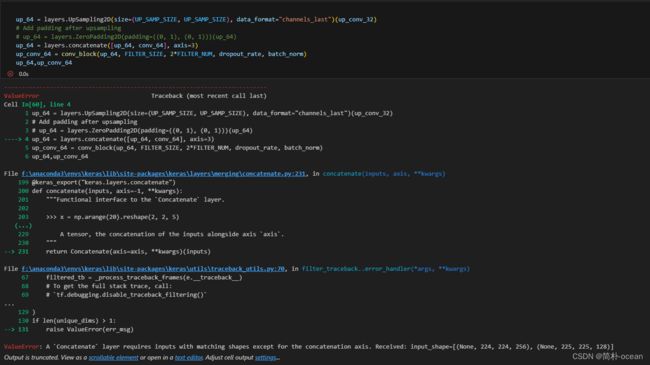
为什么呢。可以发现是在通过跳跃连接与下采样路径的对应层进行融合的时候出现的报错,那么为什么会报错呢?查看一下up_64

发现是下采样中的conv_64与上采样中的up_64维度不一致导致的,这是因为在下采样过程中,通过池化,使得451/2=225.5,而程序自动将其向下取整为225,225经过池化又变为(225/2=112.5)112。
说白了就是当输入的数据大小为奇数时,其经过池化层会向下取值
在本次试验中,下采样的空间维度大小变化为:
451 → → → 225 → → → 112 → → → 56 → → → 28
而在上采样过程中尺寸变化为:
28 → → → 56 → → → 112 → → → 224 → → → 448
所以,这就导致在合并时出现维度不一致的报错。
解决方法
方法1:
- 修改输入的尺寸为2的次方,如
128、256、512等
方法2:
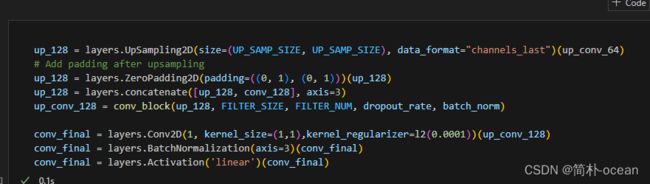
- 在合并之前,主动将其填充一致,如下所示
up_64 = layers.UpSampling2D(size=(UP_SAMP_SIZE, UP_SAMP_SIZE), data_format="channels_last")(up_conv_32)
#Add padding after upsampling
up_64 = layers.ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0, 1), (0, 1)))(up_64)
up_64 = layers.concatenate([up_64, conv_64], axis=3)
up_conv_64 = conv_block(up_64, FILTER_SIZE, 2*FILTER_NUM, dropout_rate, batch_norm)
up_64,conv_64
这样就解决了,也可以加个条件判断的函数,在出现维度不一致时,自动填充,避免手动填充的麻烦:
def auto_padding(input_tensor, target_tensor):
input_shape = tf.shape(input_tensor)[1:3]
target_shape = tf.shape(target_tensor)[1:3]
padding_height = target_shape[0] - input_shape[0]
padding_width = target_shape[1] - input_shape[1]
pad_top = padding_height // 2
pad_bottom = padding_height - pad_top
pad_left = padding_width // 2
pad_right = padding_width - pad_left
padded_tensor = tf.pad(input_tensor, [[0, 0], [pad_top, pad_bottom], [pad_left, pad_right], [0, 0]])
return padded_tensor
# Upsampling layers
up_16 = layers.UpSampling2D(size=(UP_SAMP_SIZE, UP_SAMP_SIZE), data_format="channels_last")(conv_8)
up_16 = auto_padding(up_16, conv_16)
up_16 = layers.concatenate([up_16, conv_16], axis=3)
up_conv_16 = conv_block(up_16, FILTER_SIZE, 8*FILTER_NUM, dropout_rate, batch_norm)