Java实现二叉树结构的增删
二叉树结构
二叉树介绍
在进行链表结构开发的过程之中会发现所有的数据按照收尾相连的状态进行保存,那么当要进行某一个数据查询的时候(判断该数据是否存在),这种情况下它所面对的时间复杂度是“O(n)"。
如果说现在它的数据量小(不超过三十个)的情况下,那么性能上是不会有太大差别的,而一旦保存的数据量很大,这个时候时间复杂度就会严重损耗程序的运行性能,那么对于数据的存储结构就必须发生改变,应该可以尽可能的减少检索次数为出发点进行设计,对于现在的数据结构而言,最好的性能就是“O(logn),所以现在要想实现它就可以利用二叉树的结构来完成。
构造二叉树的原理
如果想要实现一颗树结构的定义,那么就需要去考虑数据的存储形式。
在二叉树的实现之中其基本的实现原理如下:取一个数据为保存的根节点,小于根节点的数据要放在节点的左子树,而大于节点的数据要放在该节点的右子树。
如果要进行数据检索的话,此时就需要进行每个节点的判断,但判断是区分左右的,所以不会整个结构都进行判断处理,那么它的时间复杂度就是 O(logn)。
二叉树的遍历
而对于二叉树而言,在进行数据获取的时候也有三种形式:
(1) 前序遍历(根-左-右)
(2)中序遍历(左-根-右)
(3) 后序遍历(左-右-根)
二叉树基础实现
在实现二叉树的处理之中最为关键性的问题在于数据的保存,而且数据由于牵扯到对象比较的问题,那么一定要有比较器的支持,而这个比较器首选的一定就是Comparable,所以本次将保存一个 Person 类数据
@Data
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "【Person类对象】" +
"姓名:'" + name + '\'' +
", 年龄=" + age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return this.age - o.getAge();
}
}
随后如果要想进行数据的保存,首先一定需要有一个节点类。节点类里面由于牵扯所以必须使用 comparable(可以区分大小);
/**
* 实现二叉树操作
*
* @param 要进行二叉树的实现
*/
class BinaryTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private class Node {
private Comparable<T> data;
private Node parent;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Node(Comparable<T> data) {
this.data = data;
}
/**
* 实现节点数据的适当位置存储
*
* @param newNode 创建的新节点
*/
public void addNode(Node newNode) {
if (newNode.data.compareTo((T) this.data) <= 0) { // 比当前节点小
if (this.left == null) { // 没有左子树
this.left = newNode;
} else { // 需要像左边继续判断
this.left.addNode(newNode); // 继续向下判断
newNode.parent = this; // 保存父节点
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = newNode;
} else {
this.right.addNode(newNode);
}
}
}
/**
* 实现所有数据获取处理,按照中序遍历的形式完成
*/
public void toArrayNode() {
if (this.left != null) { // 有左子树
this.left.toArrayNode(); // 递归调用
}
BinaryTree.this.returnData[BinaryTree.this.foot++] = this.data;
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.toArrayNode();
}
}
}
// -----------------------以下为二叉树的功能实现-----------------------
private Node root;// 保存的是根节点
private int count;
private int foot = 0;
private Object[] returnData;
/**
* 进行数据的保存
*
* @param data 要保存的数据内容
* @throws NullPointerException 保存数据为空抛出的异常
*/
public void add(Comparable<T> data) {
if (data == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("保存的数据不能为空");
}
// 所有的数据本身不具备节点关系的匹配,那么就一定要让其保存在Node节点之中
Node newNode = new Node(data);// 保存节点
if (this.root == null) { // 没有根节点,则第一个节点就作为根节点
this.root = newNode;
} else { // 需要为其保存到一个合适的节点
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
this.count++;
}
/**
* 对象数组的形式返回数据,如果没有数据返回空
*
* @return 全部数据
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
if (this.count == 0) {
return null;
}
this.returnData = new Object[this.count];
this.foot = 0;
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.returnData;
}
}
public class JavaAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree<Person> tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.add(new Person("小明", 12));
tree.add(new Person("小红", 18));
tree.add(new Person("小蓝", 22));
tree.add(new Person("小白", 25));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(tree.toArray()));
}
}
在进行数据添加的时候只是实现了节点关系的保存,而这种关系保存后的结果就是所有数据都属于有序排列。
数据删除
基本规则:
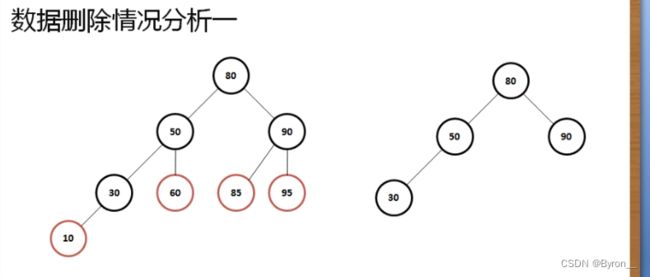
1、如果待删除节点没有子节点
- 直接删掉即可
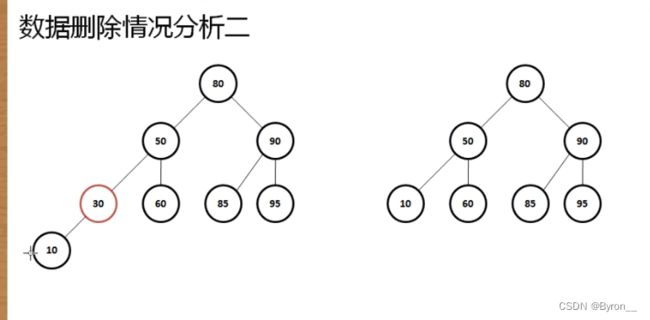
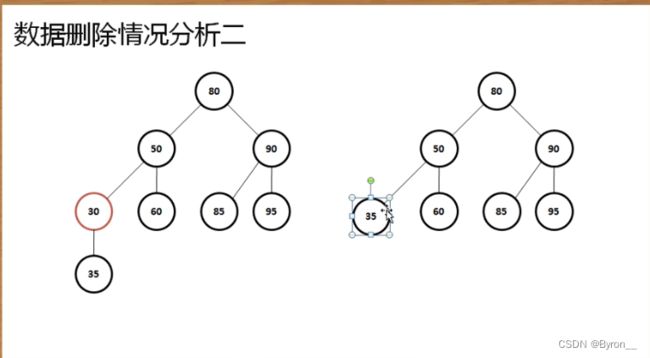
2、待删除节点只有一个子节点
那么直接删掉,并用其子节点去顶替它;
这个时候考虑两种情况分析,只有一个左子树。
只有一个右子树的情况。
左右子树操作一样,只要删除一个节点。
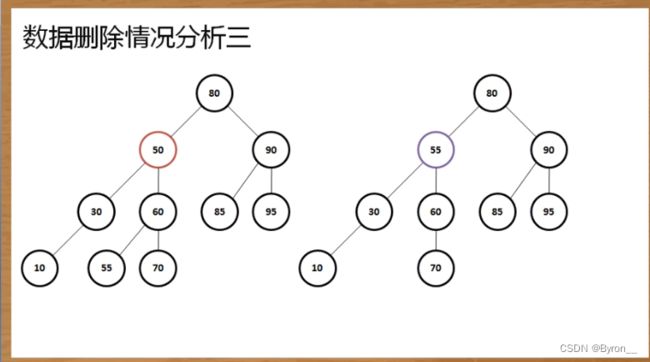
3、如果待删除节点有两个子节点
这种情况比较复杂︰首选找出它的后继节点,一直分析至最底层节点,哪个更接近于删除节点就使用哪个顶替
一般来说就是使用待删除节点(设为Z)的下一层右节点(设为A),则递归寻找A的最底层左节点,如果最后一层为右节点,则倒数第二层(设为B),使用B替换Z
在Node中增加获取功能:
/**
* 获取节点对象
* @param data 比较的对象
* @return 节点对象
*/
public Node get(Comparable<T> data) {
if (this.data.compareTo((T) data) == 0) {
return this;
} else if (this.data.compareTo((T) data) > 0) {
if (this.left == null) {
return null;
} else {
return this.left.get(data);
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
return null;
} else {
return this.right.get(data);
}
}
}
在 BinaryTree 类里面进行节点的处理。
/**
* 执行数据的删除处理
*
* @param data 要删除的数据
*/
public void remove(Comparable<T> data) {
Node removeNode = this.root.get(data);
if (removeNode != null) {
if (removeNode.left == null && removeNode.right == null) {
removeNode.parent.left = null;
removeNode.parent.right = null;
removeNode.parent = null; // 直接断开父节点引用
} else if (removeNode.left != null && removeNode.right == null) { // 左不为空
removeNode.parent.left = removeNode.left;
removeNode.left.parent = removeNode.parent;
} else if (removeNode.left == null && removeNode.right != null) { // 右不为空
removeNode.parent.left = removeNode.right;
removeNode.right.parent = removeNode.parent;
} else { // 两边都有节点,则将右边节点中最左边的节点找到,改变其指向
Node moveNode = removeNode.right; // 移动的节点
int num = 0;
while (moveNode.left != null) { // 现在还有左边的结点
num++;
moveNode = moveNode.left; // 一直向左找
} // 可以删除节点的右节点的最小左节点
removeNode.parent.left = moveNode;
moveNode.parent = removeNode.parent;
moveNode.left = removeNode.left;
if (num == 0) {// 下面只有一个左节点和一个右节点
moveNode.parent.right = null;
} else {
moveNode.parent.left = null ; // 断开原本连接
moveNode.right = removeNode.right; // 改变原始右节点指向
}
}
count--;
}
}
总结:具有基础功能的二叉树代码:
/**
* 实现二叉树操作
*
* @param 要进行二叉树的实现
*/
class BinaryTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private class Node {
private Comparable<T> data;
private Node parent;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Node(Comparable<T> data) {
this.data = data;
}
/**
* 实现节点数据的适当位置存储
*
* @param newNode 创建的新节点
*/
public void addNode(Node newNode) {
if (newNode.data.compareTo((T) this.data) <= 0) { // 比当前节点小
if (this.left == null) { // 没有左子树
this.left = newNode;
newNode.parent = this;
} else { // 需要像左边继续判断
newNode.parent = this.left; // 保存父节点
this.left.addNode(newNode); // 继续向下判断
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = newNode;
} else {
this.right.addNode(newNode);
}
}
}
/**
* 实现所有数据获取处理,按照中序遍历的形式完成
*/
public void toArrayNode() {
if (this.left != null) { // 有左子树
this.left.toArrayNode(); // 递归调用
}
BinaryTree.this.returnData[BinaryTree.this.foot++] = this.data;
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.toArrayNode();
}
}
/**
* 获取节点对象
* @param data 比较的对象
* @return 节点对象
*/
public Node get(Comparable<T> data) {
if (this.data.compareTo((T) data) == 0) {
return this;
} else if (this.data.compareTo((T) data) > 0) {
if (this.left == null) {
return null;
} else {
return this.left.get(data);
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) {
return null;
} else {
return this.right.get(data);
}
}
}
}
// -----------------------以下为二叉树的功能实现-----------------------
private Node root;// 保存的是根节点
private int count;
private int foot = 0;
private Object[] returnData;
/**
* 进行数据的保存
*
* @param data 要保存的数据内容
* @throws NullPointerException 保存数据为空抛出的异常
*/
public void add(Comparable<T> data) {
if (data == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("保存的数据不能为空");
}
// 所有的数据本身不具备节点关系的匹配,那么就一定要让其保存在Node节点之中
Node newNode = new Node(data);// 保存节点
if (this.root == null) { // 没有根节点,则第一个节点就作为根节点
this.root = newNode;
} else { // 需要为其保存到一个合适的节点
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
this.count++;
}
/**
* 对象数组的形式返回数据,如果没有数据返回空
*
* @return 全部数据
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
if (this.count == 0) {
return null;
}
this.returnData = new Object[this.count];
this.foot = 0;
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.returnData;
}
/**
* 执行数据的删除处理
*
* @param data 要删除的数据
*/
public void remove(Comparable<T> data) {
Node removeNode = this.root.get(data);
if (removeNode != null) {
if (removeNode.left == null && removeNode.right == null) {
removeNode.parent.left = null;
removeNode.parent.right = null;
removeNode.parent = null; // 直接断开父节点引用
} else if (removeNode.left != null && removeNode.right == null) { // 左不为空
removeNode.parent.left = removeNode.left;
removeNode.left.parent = removeNode.parent;
} else if (removeNode.left == null && removeNode.right != null) { // 右不为空
removeNode.parent.left = removeNode.right;
removeNode.right.parent = removeNode.parent;
} else { // 两边都有节点,则将右边节点中最左边的节点找到,改变其指向
Node moveNode = removeNode.right; // 移动的节点
int num = 0;
while (moveNode.left != null) { // 现在还有左边的结点
num++;
moveNode = moveNode.left; // 一直向左找
} // 可以删除节点的右节点的最小左节点
removeNode.parent.left = moveNode;
moveNode.parent = removeNode.parent;
moveNode.left = removeNode.left;
if (num == 0) {// 下面只有一个左节点和一个右节点
moveNode.parent.right = null;
} else {
moveNode.parent.left = null ; // 断开原本连接
moveNode.right = removeNode.right; // 改变原始右节点指向
}
}
count--;
}
}
}
public class JavaAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree<Person> tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.add(new Person("小明-80", 80));
tree.add(new Person("小明-50", 50));
tree.add(new Person("小明-60", 60));
tree.add(new Person("小明-30", 30));
tree.add(new Person("小明-35", 35));
tree.add(new Person("小明-90", 90));
tree.add(new Person("小明-10", 10));
tree.add(new Person("小明-55", 55));
tree.add(new Person("小明-70", 70));
tree.add(new Person("小明-85", 85));
tree.add(new Person("小明-95", 95));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(tree.toArray()));
tree.remove(new Person("小明-30", 30));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(tree.toArray()));
}
}
@Data
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "【Person类对象】" +
"姓名:'" + name + '\'' +
", 年龄=" + age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return this.age - o.getAge();
}
}
PS:以上内容参考于阿里云培训