NER实战之模型加载与训练:(NLP实战/命名实体识别/文本标注/Doccano工具使用/关键信息抽取/Token分类/源码解读/代码逐行解读/文本BIO处理/文本分类/序列标注)
6 模型加载解读
6.1 模型加载
现在数据和标签都有了,现在应该需要训练我们的模型了吧?
class NerDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, encodings, labels):
self.encodings = encodings
self.labels = labels
def __getitem__(self, idx):
item = {key: torch.tensor(val[idx]) for key, val in self.encodings.items()}
item['labels'] = torch.tensor(self.labels[idx])
return item
def __len__(self):
return len(self.labels)
train_encodings.pop("offset_mapping") # 训练不需要这个
val_encodings.pop("offset_mapping")
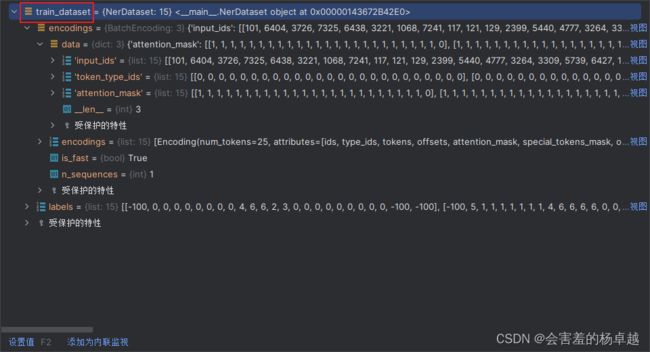
train_dataset = NerDataset(train_encodings, train_labels)
val_dataset = NerDataset(val_encodings, val_labels)训练数据中有很多东西的:
- input_ids:需要,这是建模所必须的,最重要的东西
- token_type_ids:需要
- attention_mask:也需要
- offset_mapping:不需要了,建模和他没有关系了,这是我们自己用来做对齐操作的
所以把offset去除:
train_encodings.pop("offset_mapping") # 训练不需要这个
val_encodings.pop("offset_mapping")再把数据做成NerDataset的所需要的格式:
train_dataset = NerDataset(train_encodings, train_labels)
val_dataset = NerDataset(val_encodings, val_labels)其实NerDataset这个函数啥也没做,接下来要做模型的训练了,在我的文章中我一直强调我们的NLP任务中是一个语言模型,所以它是一个预训练模型,是别人训练好的,我们把它加载出来。
那我们这里就应该加载一个Token分类的预训练模型:
from transformers import AutoModelForTokenClassification, TrainingArguments, Trainer
model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained('ckiplab/albert-base-chinese-ner',num_labels=7,
ignore_mismatched_sizes=True,
id2label=id2tag,
label2id=tag2id
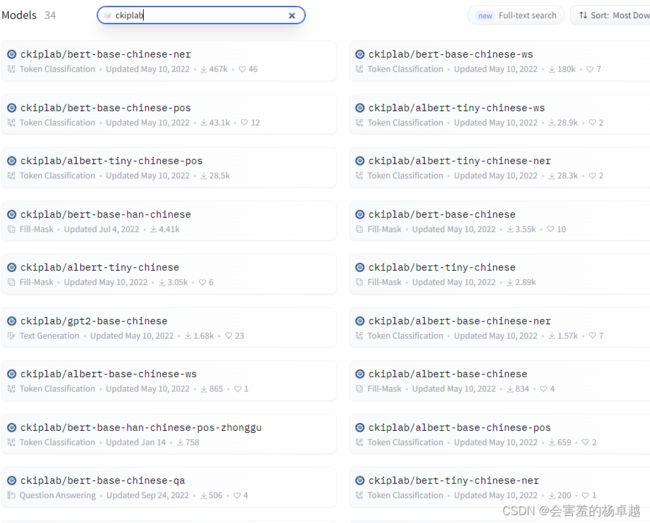
)这里的ckiplab是一个台湾的实验室的名字,看过我的文章的同学看到albert、base、chinese都应该很熟悉:albert-base-chinese-ner,这个模型就这样直接拿来用了。在HuggingFace中这种中文的预训练模型挺多的:
直接搜ckiplab这个就能搜出很多了,第一个加载量也就467k。
但是我们用这个模型,我们需要改一改,改什么呢?
人家这个模型,跟我们的任务不太一样,我们要做的是一个7分类,看下代码的参数都是什么意思:
- num_labels=7:我们的7个标签,7分类
- ignore_mismatched_sizes=True:不一致的部分不加载权重
- id2label=id2tag:告诉这个模型你的labels和id对应关系是什么
- label2id=tag2id:和上面一样,将我们前面制定好的加载进去就行了
在执行前面的代码的时候,执行过程中是会先下载这个模型的,这个时候你该上梯子就得上梯子了,执行页面的提示:
Some weights of AlbertForTokenClassification were not initialized from the model checkpoint at ckiplab/albert-base-chinese-ner and are newly initialized because the shapes did not match:
- classifier.weight: found shape torch.Size([73, 768]) in the checkpoint and torch.Size([7, 768]) in the model instantiated
- classifier.bias: found shape torch.Size([73]) in the checkpoint and torch.Size([7]) in the model instantiated
You should probably TRAIN this model on a down-stream task to be able to use it for predictions and inference.
警告的意思就是,原本模型的73分类和7分类是不一样的,就是有一层网络是不同的。
这是没有连接梯子的提示:
requests.exceptions.ConnectionError: (ProtocolError('Connection aborted.', ConnectionResetError(10054, '远程主机强迫关闭了一个现有的连接。', None, 10054, None)), '(Request ID: 2b313f4a-5b60-41bc-a256-5fa068e7703e)')
将模型打印出来看看:
AlbertForTokenClassification(
(albert): AlbertModel(
(embeddings): AlbertEmbeddings(
(word_embeddings): Embedding(21128, 128, padding_idx=0)
(position_embeddings): Embedding(512, 128)
(token_type_embeddings): Embedding(2, 128)
(LayerNorm): LayerNorm((128,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0, inplace=False)
)
(encoder): AlbertTransformer(
(embedding_hidden_mapping_in): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=768, bias=True)
(albert_layer_groups): ModuleList(
(0): AlbertLayerGroup(
(albert_layers): ModuleList(
(0): AlbertLayer(
(full_layer_layer_norm): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
(attention): AlbertAttention(
(query): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(key): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(value): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(attention_dropout): Dropout(p=0, inplace=False)
(output_dropout): Dropout(p=0, inplace=False)
(dense): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=768, bias=True)
(LayerNorm): LayerNorm((768,), eps=1e-12, elementwise_affine=True)
)
(ffn): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=3072, bias=True)
(ffn_output): Linear(in_features=3072, out_features=768, bias=True)
(activation): ReLU()
(dropout): Dropout(p=0, inplace=False)
)
)
)
)
)
)
(dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
(classifier): Linear(in_features=768, out_features=7, bias=True)
)这就是别人网络的结构,上面就不看了,看最后的输出层,数字768,是我们的老朋友了
经过一堆的self_attention后输出特征,每个词都对应768维向量,每个词做一个7分类。
6.2 评估标准
接下来我们需要制作评估标准了,把预测值和标签拿到之后,可以自己定义评估方法是什么,更多的时候是用现成的,这里就是用这4个:
- precision:精确率
- recall:召回率
- f1:F1分数
- accuracy:准确率
对机器学习的指标不了解的同学,可以参考这篇文章,有比较详细的解释:
机器学习 分类任务 评价指标_机器学习分类评价指标_会害羞的杨卓越的博客-CSDN博客
6.3 训练参数配置
checkpoint = 'bert-base-chinese'
num_train_epochs = 1000
per_device_train_batch_size=8
per_device_eval_batch_size=8- 第一行:训练完成的时候,需要保存模型,指定保存的模型是什么
- 第二行:训练的迭代次数
- 第三行:训练的batch_size
- 第四行:验证的batch_size
指定训练的参数
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir='./output', # 输入路径
num_train_epochs=num_train_epochs, # 训练epoch数量
per_device_train_batch_size=per_device_train_batch_size, # 每个GPU的BATCH
per_device_eval_batch_size=per_device_eval_batch_size,
warmup_steps=500, # warmup次数
weight_decay=0.01, # 限制权重的大小
logging_dir='./logs',
logging_steps=10,
save_strategy='steps',
save_steps=1000,
save_total_limit=1,
evaluation_strategy='steps',
eval_steps=1000
)- output:模型保存的路径
- num_train_epochs:训练epoch数量
- per_device_train_batch_size:每个GPU的BATCH
- per_device_eval_batch_size:验证集的
- warmup_steps:warmup次数,预热次数
- weight_decay:限制权重的大小
- logging_dir:日志位置
- logging_steps:pycharm中每10次迭代打印一次结果
- save_strategy:按照什么样的方式保存模型
- save_steps:按照每迭代一千次保存模型
- save_total_limit:总共保存模型次数(次数达到了就删除最开始保存的一个)
- evaluation_strategy:按照什么样的方式做验证集
- eval_steps:按照每迭代一千次做验证集
6.4 训练
把前面配置好的参数传进去:
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=val_dataset,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics
)- model:模型
- args:参数
- train_dataset:训练集
- eval_dataset:验证集
- compute_metrics:评估标准
训练,评估:
trainer.train()
trainer.evaluate()为了保险起见,再保存一次模型:
model.save_pretrained("./checkpoint/model/%s-%sepoch" % (checkpoint, num_train_epochs))