《算法竞赛·快冲300题》每日一题:“房间划分”
《算法竞赛·快冲300题》将于2024年出版,是《算法竞赛》的辅助练习册。
所有题目放在自建的OJ New Online Judge。
用C/C++、Java、Python三种语言给出代码,以中低档题为主,适合入门、进阶。
文章目录
- 题目描述
- 题解
- C++代码
- Java代码
- Python代码
“ 房间划分” ,链接: http://oj.ecustacm.cn/problem.php?id=1830
题目描述
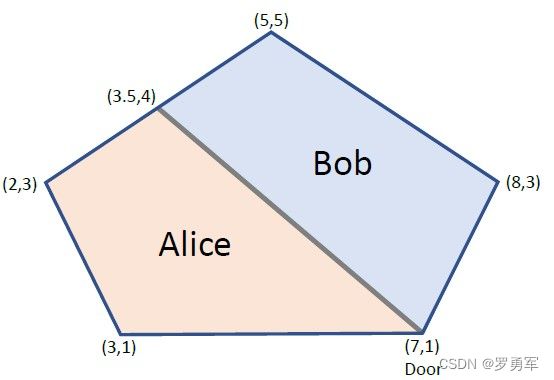
【题目描述】 给定一个凸多边形房间,现在需要将房间划分成等面积的两部分。
房间只有一个门,可以视为一个顶点,需要沿着直线将房间划分成两部分。
直线的一端必须是门,另一端必须是墙角或者墙壁。
如下图所示,最终需要求解出直线另一端点的坐标。
【输入格式】 第一行为正整数n,表示凸多边形的顶点数量,3≤n≤200000。
接下来n行。每行两个整数x和y表示顶点坐标, − 1 0 7 ≤ x , y ≤ 1 0 7 -10^7≤x,y≤10^7 −107≤x,y≤107。
输入保证顶点是按照逆时针的顺序进行输入,没有重复的两个点,且第一个点视为门。
【输出格式】 输出另一端点的坐标x和y,以一个空格分隔。
输出的每个数字的绝对误差小于 1 0 − 6 10^{-6} 10−6均视为正确。
【输入样例】
5
7 1
8 3
5 5
2 3
3 1
【输出样例】
3.5 4
题解
求面积是叉积的经典应用。
以门为起点,与其他所有顶点连线,把多边形分成多个三角形。对每个三角形求面积,所有三角形面积之和是多边形的面积。然后找到平分总面积的直线所在的那个三角形,直线的终点在这个三角形边上。。
【重点】 叉积,几何模板的掌握。
C++代码
#includeJava代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int N = 200010;
static class Point {
double x, y;
Point() {}
Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; }
Point add(Point b) { return new Point(x + b.x, y + b.y); }
Point subtract(Point b) { return new Point(x - b.x, y - b.y); }
Point multiply(double k) {return new Point(k * x, k * y); }
}
static double cross(Point A, Point B) {return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x;}
static double area(Point A, Point B, Point C) {return 0.5 * cross(B.subtract(A), C.subtract(A));}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
Point[] p = new Point[N];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
p[i] = new Point(scan.nextDouble(), scan.nextDouble());
double s = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n - 1; i++)
s += area(p[1], p[i], p[i + 1]);
s *= 0.5;
double a = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n - 1; i++) {
double b = a + area(p[1], p[i], p[i + 1]);
if (a <= s && b >= s) {
double t = (s - a) / (b - a);
Point delta = p[i + 1].subtract(p[i]).multiply(t);
Point ans = p[i].add(delta);
System.out.printf("%.9f %.9f\n", ans.x, ans.y);
break;
}
a = b;
}
scan.close();
}
}
Python代码
N = 200010
class Point:
def __init__(self, x=0, y=0): self.x = x; self.y = y
def __add__(self, B): return Point(self.x + B.x, self.y + B.y)
def __sub__(self, B): return Point(self.x - B.x, self.y - B.y)
def __mul__(self, k): return Point(self.x * k, self.y * k)
def cross(A, B): return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x
def area(A, B, C): return 0.5 * cross(B - A, C - A)
n = int(input())
p = [None] * (N)
for i in range(1, n + 1):
x, y = map(float, input().split())
p[i] = Point(x, y)
s = 0
for i in range(2, n): s += area(p[1], p[i], p[i + 1])
s *= 0.5
a = 0
for i in range(2, n):
b = a + area(p[1], p[i], p[i + 1])
if a <= s and b >= s:
t = (s - a) / (b - a)
delta = (p[i + 1] - p[i]) * t
ans = p[i] + delta
print("%.9f %.9f" % (ans.x, ans.y))
break
a = b