Flink学习笔记(四)
以下笔记基于对尚硅谷Java版Flink(2020版)的学习,Flink版本1.10
目录
Table API 与SQL
基本程序结构
表环境配置
创建表
表的查询
表的输出
读写Kafka
更新模式
输出到 ES
输出到 MySql
表和流的转换
Table转换成DataStream
将DataStream转换成表
创建临时视图(Temporary View)
查看执行计划
动态表和持续查询
流处理和关系代数(表)/SQL的区别
动态表(Dynamic Tables)
持续查询(Continuous Query)
流式表查询的处理过程:
将动态表转换成DataStream
时间特性
定义处理时间(Processing Time)
定义事件时间(Event Time)
窗口
Group Windows
SQL 中的 Group Windows
Over Windows
SQL 中的 Over Windows
函数
系统内置函数
用户自定义函数(UDF)
Table API 与SQL
Table API是流处理和批处理通用的关系型API,Table API可以基于流输入或者批输入来运行而不需要进行任何修改。
Table API是SQL语言的超集,Table API是专门为Apache Flink设计的,Table API是Scala 和Java语言集成式的API。
Table API与常规SQL语言中将查询指定为字符串不同,Table API查询是以Java或Scala中的语言嵌入样式来定义的,具有IDE支持,如:自动完成和语法检测。
基本程序结构
Table API 和 SQL 的程序结构,与流式处理的程序结构十分类似
// 创建表的执行环境
StreamTableEnvironment tableEnv = ...
// 创建一张表,用于读取数据
tableEnv.connect(...).createTemporaryTable("inputTable");
// 注册一张表,用于把计算结果输出
tableEnv.connect(...).createTemporaryTable("outputTable");
// 通过 Table API 查询算子,得到一张结果表
Table result = tableEnv.from("inputTable").select(...);
// 通过 SQL查询语句,得到一张结果表
Table sqlResult = tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT ... FROM inputTable ...");
// 将结果表写入输出表中
result.insertInto("outputTable");表环境配置
TableEnvironment 是 flink 中集成 Table API 和 SQL 的核心概念,所有对 表的操作都基于 TableEnvironment
– 注册 Catalog
– 在 Catalog 中注册表
– 执行 SQL 查询
– 注册用户自定义函数(UDF)
// 默认配置创建表环境(1.10里默认使用老版本planner)
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
StreamTableEnvironment tableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env);
// 基于老版本planner的流处理表环境
EnvironmentSettings oldStreamSettings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useOldPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build();
StreamTableEnvironment oldStreamTableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, oldStreamSettings);
// 基于老版本planner的批处理表环境
ExecutionEnvironment batchEnv = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
BatchTableEnvironment oldBatchTableEnv = BatchTableEnvironment.create(batchEnv);
// 基于Blink的流处理表环境
EnvironmentSettings blinkStreamSettings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useBlinkPlanner()
.inStreamingMode()
.build();
StreamTableEnvironment blinkStreamTableEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env, blinkStreamSettings);
// 基于Blink的批处理表环境
EnvironmentSettings blinkBatchSettings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance()
.useBlinkPlanner()
.inBatchMode()
.build();
TableEnvironment blinkBatchTableEnv = TableEnvironment.create(blinkBatchSettings);创建表
TableEnvironment 可以注册目录 Catalog,并可以基于 Catalog 注册表
表(Table)是由一个“标识符”(identifier)来指定的,由3部分组成: Catalog名、数据库(database)名和对象名
表可以是常规的,也可以是虚拟的(视图,View)
常规表(Table)一般可以用来描述外部数据,比如文件、数据库表或消息队列的数据,也可以直接从 DataStream转换而来
视图(View)可以从现有的表中创建,通常是 table API 或者 SQL 查询的 一个结果集
从外部数据源创建表的基本流程
tableEnv
.connect(...) // 定义表的数据来源,和外部系统建立连接
.withFormat(...) // 定义数据格式化方法
.withSchema(...) // 定义表结构
.createTemporaryTable("MyTable"); // 创建临时表读取文件创建表的示例
tableEnv
.connect(
new FileSystem().path(“YOUR_Path/sensor.txt”)
) // 定义到文件系统的连接
.withFormat(new Csv()) // 定义以csv格式进行数据格式化
.withSchema( new Schema()
.field("id", DataTypes.STRING())
.field("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT())
.field("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
) // 定义表结构
.createTemporaryTable("sensorTable"); // 创建临时表表的查询
Table API 是集成在 Scala 和 Java 语言内的查询 API
Table API 基于代表“表”的 Table 类,并提供一整套操作处理的方法 API; 这些方法会返回一个新的 Table 对象,表示对输入表应用转换操作的结果
有些关系型转换操作,可以由多个方法调用组成,构成链式调用结构
Table API查询示例
// 取得Table
Table inputTable = tableEnv.from("inputTable");
// 简单转换
Table resultTable = inputTable
.select("id, temperature")
.filter("id === 'sensor_6'");
// 聚合统计
Table aggTable = inputTable.groupBy("id")
.select("id, id.count as count, temp.avg as avgTemp"); Flink 的 SQL 集成,基于实现 了SQL 标准的 Apache Calcite
在 Flink 中,用常规字符串来定义 SQL 查询语句
SQL 查询的结果,也是一个新的 Table
// 简单转换
Table resultSqlTable = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select id, temperature from inputTable where id ='sensor_6'");
// 聚合统计
Table sqlAggTable = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select id, count(id) as cnt, avg(temp) as avgTemp from inputTable group by id");表的输出
// outputTable为使用tableEnv创建的表
resultTable.insertInto("outputTable");读写Kafka
// 连接Kafka,读取数据
tableEnv.connect(new Kafka()
.version("0.11")
.topic("sensor")
.property("zookeeper.connect", "localhost:2181")
.property("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092")
)
.withFormat(new Csv())
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id", DataTypes.STRING())
.field("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT())
.field("temp", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
)
.createTemporaryTable("inputTable");
// 查询转换
// 简单转换
Table sensorTable = tableEnv.from("inputTable");
Table resultTable = sensorTable.select("id, temp").filter("id === 'sensor_6'");
// 聚合统计
Table aggTable = sensorTable.groupBy("id").select("id, id.count as count, temp.avg as avgTemp");
// 建立kafka连接,输出到不同的topic下
tableEnv.connect(new Kafka()
.version("0.11")
.topic("sinktest")
.property("zookeeper.connect", "localhost:2181")
.property("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092")
)
.withFormat(new Csv())
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id", DataTypes.STRING())
.field("temp", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
)
.createTemporaryTable("outputTable");
// 输出
resultTable.insertInto("outputTable");更新模式
对于流式查询,需要声明如何在表和外部连接器之间执行转换
与外部系统交换的消息类型,由更新模式(Update Mode)指定
追加(Append)模式
表只做插入操作,和外部连接器只交换插入(Insert)消息
撤回(Retract)模式
表和外部连接器交换添加(Add)和撤回(Retract)消息
插入操作(Insert)编码为 Add 消息;删除(Delete)编码为 Retract 消息;更新(Update) 编码为上一条的 Retract 和下一条的 Add 消息
更新插入(Upsert)模式
更新和插入都被编码为 Upsert 消息;删除编码为 Delete 消息
输出到 ES
可以创建 Table 来描述 ES 中的数据,作为输出的 TableSink
tableEnv.connect(
new Elasticsearch()
.version("6")
.host("localhost", 9200, "http")
.index("sensor")
.documentType("temp")
)
.inUpsertMode()
.withFormat(new Json())
.withSchema( new Schema()
.field("id", DataTypes.STRING())
.field("count", DataTypes.BIGINT())
)
.createTemporaryTable("esOutputTable");
aggResultTable.insertInto("esOutputTable");输出到 MySql
可以创建 Table 来描述 MySql 中的数据,作为输入和输出
String sinkDDL=
"create table jdbcOutputTable (" +
" id varchar(20) not null, " +
" cnt bigint not null " +
") with (" +
" 'connector.type' = 'jdbc', " +
" 'connector.url' = 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test', " +
" 'connector.table' = 'sensor_count', " +
" 'connector.driver' = 'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver', " +
" 'connector.username' = 'root', " +
" 'connector.password' = '123456' )";
// 执行 DDL创建表
tableEnv.sqlUpdate(sinkDDL);
aggResultSqlTable.insertInto("jdbcOutputTable");表和流的转换
Table转换成DataStream
表可以转换为 DataStream 或 DataSet ,这样自定义流处理或批处理程序就可以继续在 Table API 或 SQL 查询的结果上运行了
将表转换为 DataStream 或 DataSet 时,需要指定生成的数据类型,即要将表的每一行转换成的数据类型
表作为流式查询的结果,是动态更新的
转换有两种转换模式:追加(Append)模式和撤回(Retract)模式
追加模式(Append Mode)
– 用于表只会被插入(Insert)操作更改的场景
DataStream resultStream = tableEnv.toAppendStream(resultTable, Row.class);
撤回模式(Retract Mode)
– 用于任何场景。有些类似于更新模式中 Retract 模式,它只有 Insert 和 Delete 两类操作。
– 得到的数据会增加一个 Boolean 类型的标识位(返回的第一个字段),用它来表示到底是
新增的数据(Insert),还是被删除的数据(Delete)
DataStream> aggResultStream = tableEnv.toRetractStream(aggResultTable , Row.class);
将DataStream转换成表
对于一个 DataStream,可以直接转换成 Table,进而方便地调用 Table API 做转换操作
DataStream dataStream = ...
Table sensorTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream);
默认转换后的 Table schema 和 DataStream 中的字段定义一一对应,也可以单独指定出来
DataStream dataStream = ...
Table sensorTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream, "id, timestamp as ts, temperature");
创建临时视图(Temporary View)
基于 DataStream 创建临时视图
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensorView", dataStream);
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensorView", dataStream, "id, temperature, timestamp as ts");
基于 Table 创建临时视图
tableEnv.createTemporaryView("sensorView", sensorTable);
查看执行计划
Table API 提供了一种机制来解释计算表的逻辑和优化查询计划
查看执行计划,可以通过 TableEnvironment.explain(table) 方法或TableEnvironment.explain() 方法完成,返回一个字符串,描述三个计划
优化的逻辑查询计划
优化后的逻辑查询计划
实际执行计划
String explaination = tableEnv.explain(resultTable);
System.out.println(explaination);动态表和持续查询
流处理和关系代数(表)/SQL的区别
| 关系代数(表)/SQL | 流处理 | |
|---|---|---|
| 处理的对象 | 字段元组的有界集合 | 字段元组的无序序列 |
| 查询(Query)对数据的访问 | 可以访问到完整的数据输入 | 无法访问所有数据,必须持续"等待"流式输入 |
| 查询终止条件 | 生成固定大小的结果集后终止 | 永不停止,根据持续收到的数据不断更新查询结果 |
动态表(Dynamic Tables)
动态表是 Flink 对流数据的 Table API 和 SQL 支持的核心概念
与表示批处理数据的静态表不同,动态表是随时间变化的
持续查询(Continuous Query)
动态表可以像静态的批处理表一样进行查询,查询一个动态表会产生持续查询(Continuous Query)
连续查询永远不会终止,并会生成另一个动态表
查询会不断更新其动态结果表,以反映其动态输入表上的更改
流式表查询的处理过程:
流被转换为动态表
为了处理带有关系查询的流,必须先将其转换为表
从概念上讲,流的每个数据记录,都被解释为对结果表的插入 (Insert)修改操作
对动态表计算连续查询,生成新的动态表
持续查询会在动态表上做计算处理,并作为结果生成新的动态表
生成的动态表被转换回流
将动态表转换成DataStream
与常规的数据库表一样,动态表可以通过插入(Insert)、更新(Update)和删除(Delete)更改,进行持续的修改
将动态表转换为流或将其写入外部系统时,需要对这些更改进行编码
仅追加(Append-only)流
– 仅通过插入(Insert)更改来修改的动态表,可以直接转换为仅追加流
撤回(Retract)流
– 撤回流是包含两类消息的流:添加(Add)消息和撤回(Retract)消息
Upsert(更新插入)流
– Upsert 流也包含两种类型的消息:Upsert 消息和删除(Delete)消息。
时间特性
基于时间的操作(比如 Table API 和 SQL 中窗口操作),需要定义相关的时间语义和时间数据来源的信息
Table 可以提供一个逻辑上的时间字段,用于在表处理程序中,指示时间和访问相应的时间戳
时间属性,可以是每个表schema的一部分。一旦定义了时间属性,它就可以作为一个字段引用,并且可以在基于时间的操作中使用
时间属性的行为类似于常规时间戳,可以访问,并且进行计算
定义处理时间(Processing Time)
处理时间语义下,允许表处理程序根据机器的本地时间生成结果。它是时间的最简单概念。它既不需要提取时间戳,也不需要生成 watermark
由DataStream 转换成表时指定
在定义Schema期间,可以使用.proctime,指定字段名定义处理时间字段
这个proctime属性只能通过附加逻辑字段,来扩展物理schema。因此,只能在schema定义的末尾定义它
Table sensorTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream, "id, temperature, timestamp, pt.proctime");
定义Table Schema时指定
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id", DataTypes.STRING())
.field("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT())
.field("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
.field("pt", DataTypes.TIMESTAMP(3))
.proctime()
)
在创建表的 DDL 中定义
String sinkDDL =
"create table dataTable (" +
" id varchar(20) not null, " +
" ts bigint, " +
" temperature double, " +
" pt AS PROCTIME() " +
") with (" +
" 'connector.type' = 'filesystem', " +
" 'connector.path' = '/sensor.txt', " +
" 'format.type' = 'csv')";
tableEnv.sqlUpdate(sinkDDL);定义事件时间(Event Time)
事件时间语义,允许表处理程序根据每个记录中包含的时间生成结果。这样即使在有乱序事件或者延迟事件时,也可以获得正确的结果。
为了处理无序事件,并区分流中的准时和迟到事件;Flink 需要从事件数据中,提取时间戳,并用来推进事件时间的进展
由DataStream转换成表时指定
在 DataStream 转换成 Table,使用 .rowtime 可以定义事件时间属性
// 将 DataStream转换为 Table,并指定时间字段
Table sensorTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream, "id, timestamp.rowtime, temperature");
// 字段的类型会变成时间戳类型
// 或者,直接追加时间字段
Table sensorTable = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream, "id, temperature, timestamp, rt.rowtime");定义 Table Schema 时指定
.withSchema(new Schema()
.field("id", DataTypes.STRING())
.field("timestamp", DataTypes.BIGINT())
.rowtime(
new Rowtime()
.timestampsFromField("timestamp") // 从字段中提取时间戳
.watermarksPeriodicBounded(1000) // watermark延迟1秒
)
.field("temperature", DataTypes.DOUBLE())
)
在创建表的 DDL 中定义
String sinkDDL=
"create table dataTable (" +
" id varchar(20) not null, " +
" ts bigint, " +
" temperature double, " +
" rt AS TO_TIMESTAMP( FROM_UNIXTIME(ts) ), " +
" watermark for rt as rt - interval '1' second" +
") with (" +
" 'connector.type' = 'filesystem', " +
" 'connector.path' = '/sensor.txt', " +
" 'format.type' = 'csv')";
tableEnv.sqlUpdate(sinkDDL);窗口
时间语义,要配合窗口操作才能发挥作用
在 Table API 和 SQL 中,主要有两种窗口
Group Windows(分组窗口)
– 根据时间或行计数间隔,将行聚合到有限的组(Group)中,并对每个组的数据执行一次聚合函数
Over Windows
– 针对每个输入行,计算相邻行范围内的聚合
Group Windows
Group Windows 是使用 window(w:GroupWindow)子句定义的,并且必须由as子句指定一个别名。
为了按窗口对表进行分组,窗口的别名必须在 group by 子句中,像常规的分组字段一样引用
Table table = input.window([w: GroupWindow] as "w") // 定义窗口,别名为w
.groupBy("w, a") // 按照字段 a和窗口w分组
.select("a, b.sum"); // 聚合
Table API 提供了一组具有特定语义的预定义 Window 类,这些类会被转换 为底层 DataStream 或 DataSet 的窗口操作
滚动窗口(Tumbling windows)
// Tumbling Event-time Window
table.window(Tumble.over("10.minutes").on("rowtime").as("w"))
// Tumbling Processing-time Window
table.window(Tumble.over("10.minutes").on("proctime").as("w"))
// Tumbling Row-count Window
table.window(Tumble.over("10.rows").on("proctime").as("w"))滑动窗口(Sliding windows)
// Sliding Event-time Window
table.window(Slide.over("10.minutes").every("5.minutes").on("rowtime").as("w"))
// Sliding Processing-time window
table.window(Slide.over("10.minutes").every("5.minutes").on("proctime").as("w"))
// Sliding Row-count window
table.window(Slide.over("10.rows").every("5.rows").on("proctime").as("w"))会话窗口(Session windows)
// Session Event-time Window
table.window(Session.withGap("10.minutes").on("rowtime").as("w"))
// Session Processing-time Window
table.window(Session.withGap("10.minutes").on(“proctime").as("w"))SQL 中的 Group Windows
Group Windows 定义在 SQL 查询的 Group By 子句中
TUMBLE(time_attr, interval)
定义一个滚动窗口,第一个参数是时间字段,第二个参数是窗口长度
Table resultSqlTable = tableEnv.sqlQuery(
"select id, count(id) as cnt, avg(temp) as avgTemp, tumble_end(rt, interval '10' second) " +
"from sensor group by id, tumble(rt, interval '10' second)");
HOP(time_attr, interval, interval)
定义一个滑动窗口,第一个参数是时间字段,第二个参数是窗口滑动步长,第三个是窗口长度
SESSION(time_attr, interval)
定义一个会话窗口,第一个参数是时间字段,第二个参数是窗口间隔
Over Windows
Over window 聚合是标准 SQL 中已有的(over 子句),可以在查询的SELECT 子句中定义
Over window 聚合,会针对每个输入行,计算相邻行范围内的聚合
Over windows 使用 window(w:overwindows)子句定义,并在 select()方法中通过别名来引用
Table table = input.window([w: OverWindow] as "w")
.select("a, b.sum over w, c.min over w");
Table API 提供了 Over 类,来配置 Over 窗口的属性
无界 Over Windows
可以在事件时间或处理时间,以及指定为时间间隔、或行计数的范围内,定义 Over windows
无界的 over window 是使用常量指定的
// 无界的事件时间 over window
table.window(Over.partitionBy("a").orderBy("rowtime").preceding(UNBOUNDED_RANGE).as("w"))
// 无界的处理时间 over window
table.window(Over.partitionBy("a").orderBy("proctime").preceding(UNBOUNDED_RANGE).as("w"))
// 无界的事件时间 Row-count over window
table.window(Over.partitionBy("a").orderBy("rowtime").preceding(UNBOUNDED_ROW).as("w"))
// 无界的处理时间 Row-count over window
table.window(Over.partitionBy("a").orderBy("proctime").preceding(UNBOUNDED_ROW).as("w")) 有界 Over Windows
有界的 over window 是用间隔的大小指定的
// 有界的事件时间 over window
table.window(Over.partitionBy("a").orderBy("rowtime").preceding("1.minutes").as("w"))
// 有界的处理时间 over window
table.window(Over.partitionBy("a").orderBy("proctime").preceding("1.minutes").as("w"))
// 有界的事件时间 Row-count over window
table.window(Over.partitionBy("a").orderBy("rowtime").preceding("10.rows").as("w"))
// 有界的处理时间 Row-count over window
table.window(Over.partitionBy("a").orderBy("procime").preceding("10.rows").as("w"))
Table overResult = table.window(Over.partitionBy("id").orderBy("rt").preceding("2.rows").as("ow"))
.select("id, rt, id.count over ow, temp.avg over ow");SQL 中的 Over Windows
用 Over 做窗口聚合时,所有聚合必须在同一窗口上定义,也就是说必须是相同的分区、排序和范围
目前仅支持在当前行范围之前的窗口
ORDER BY 必须在单一的时间属性上指定
SELECT COUNT(amount) OVER (
PARTITION BY user
ORDER BY proctime
ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW)
FROM Orders
Table overSqlResult = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select id, rt, count(id) over ow, avg(temp) over ow " +
" from sensor " +
" window ow as (partition by id order by rt rows between 2 preceding and current row)");函数
系统内置函数
Flink Table API 和 SQL 为用户提供了一组用于数据转换的内置函数
SQL 中支持的很多函数,Table API 和 SQL 都已经做了实现,以下仅为部分函数:
比较函数
SQL:
value1 = value2
value1 > value2
Table API:
any1 === any2
any1 > any2
逻辑函数
SQL:
boolean1 OR boolean2
boolean1 IS FALSE
NOT boolean
Table API:
boolean1 || boolean2
boolean.isFalse
!boolean
算术函数
SQL:
numeric1 + numeric2
POWER(numeric1 ,numeric2)
Table API:
numeric1 + numeric2
numeric1.power(numeric2)
字符串函数
SQL:
string1 || string2
UPPER(string)
CHAR_LENGTH(string)
Table API:
string1 + string2
string.upperCase()
string.charLength()
时间函数
SQL:
DATE string
TIMESTAMP string
CURRENT_TIME
INTERVAL string range
Table API:
string.toDate
string.toTimestamp
currentTime()
numeric.days
numeric.minutes
聚合函数
SQL:
COUNT(*)
SUM(expression)
RANK()
ROW_NUMBER()
Table API:
filed.count
filed.sum0
用户自定义函数(UDF)
用户定义函数(User-defined Functions,UDF)是一个重要的特性,它们显著地扩展了查询的表达能力
在大多数情况下,用户定义的函数必须先注册,然后才能在查询中使用
函数通过调用 registerFunction()方法在 TableEnvironment 中注册。当用户定义的函数被注册时,它被插入到 TableEnvironment 的函数目录中,这样Table API 或 SQL 解析器就可以识别并正确地解释它
标量函数(Scalar Functions)
用户定义的标量函数,可以将0、1或多个标量值,映射到新的标量值
为了定义标量函数,必须在 org.apache.flink.table.functions 中扩展基类Scalar Function,并实现(一个或多个)求值(eval)方法
标量函数的行为由求值方法决定,求值方法必须公开声明并命名为 eval
// 实现自定义的ScalarFunction
public static class HashCode extends ScalarFunction{
private int factor = 13;
public HashCode(int factor) {
this.factor = factor;
}
public int eval(String str){
return str.hashCode() * factor;
}
}
// 创建函数类对象
HashCode hashCode = new HashCode(23);
// 需要在环境中注册UDF
tableEnv.registerFunction("hashCode", hashCode);
// Table API调用
Table resultTable = sensorTable.select("id, ts, hashCode(id)");
// SQL调用
Table resultSqlTable = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select id, ts, hashCode(id) from sensor"); 表函数(Table Functions)
用户定义的表函数,也可以将0、1或多个标量值作为输入参数;与标量函数不同的是,它可以返回任意数量的行作为输出,而不是单个值
为了定义一个表函数,必须扩展 org.apache.flink.table.functions 中的基类TableFunction 并实现(一个或多个)求值方法
表函数的行为由其求值方法决定,求值方法必须是 public 的,并命名为 eval
// 实现自定义TableFunction
public static class Split extends TableFunction>{
// 定义属性,分隔符
private String separator = ",";
public Split(String separator) {
this.separator = separator;
}
// 必须实现一个eval方法,没有返回值
public void eval( String str ){
for( String s: str.split(separator) ){
collect(new Tuple2<>(s, s.length()));
}
}
}
// 创建函数类对象
Split split = new Split("_");
// 需要在环境中注册UDF
tableEnv.registerFunction("split", split);
// Table API调用
Table resultTable = sensorTable
.joinLateral("split(id) as (word, length)")
.select("id, ts, word, length");
// SQL调用
Table resultSqlTable = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select id, ts, word, length " +
" from sensor, lateral table(split(id)) as splitid(word, length)"); 聚合函数(Aggregate Functions)
用户自定义聚合函数(User-Defined Aggregate Functions,UDAGGs) 可以把一个表中的数据,聚合成一个标量值
用户定义的聚合函数,是通过继承 AggregateFunction 抽象类实现的
AggregationFunction要求必须实现的方法:
– createAccumulator()
– accumulate()
– getValue()
AggregateFunction 的工作原理如下:
首先,它需要一个累加器(Accumulator),用来保存聚合中间结果的数据结构;可以通过调用 createAccumulator() 方法创建空累加器
随后,对每个输入行调用函数的 accumulate() 方法来更新累加器
处理完所有行后,将调用函数的 getValue() 方法来计算并返回最终结果
// 实现自定义的AggregateFunction
public static class AvgTemp extends AggregateFunction>{
@Override
public Double getValue(Tuple2 accumulator) {
return accumulator.f0 / accumulator.f1;
}
@Override
public Tuple2 createAccumulator() {
return new Tuple2<>(0.0, 0);
}
// 必须实现一个accumulate方法,来数据之后更新状态
public void accumulate( Tuple2 accumulator, Double temp ){
accumulator.f0 += temp;
accumulator.f1 += 1;
}
}
// 创建函数类对象
AvgTemp avgTemp = new AvgTemp();
// 需要在环境中注册UDF
tableEnv.registerFunction("avgTemp", avgTemp);
// Table API调用
Table resultTable = sensorTable
.groupBy("id")
.aggregate( "avgTemp(temp) as avgtemp" )
.select("id, avgtemp");
// SQL调用
Table resultSqlTable = tableEnv.sqlQuery("select id, avgTemp(temp) " +
" from sensor group by id"); 表聚合函数(Table Aggregate Functions)
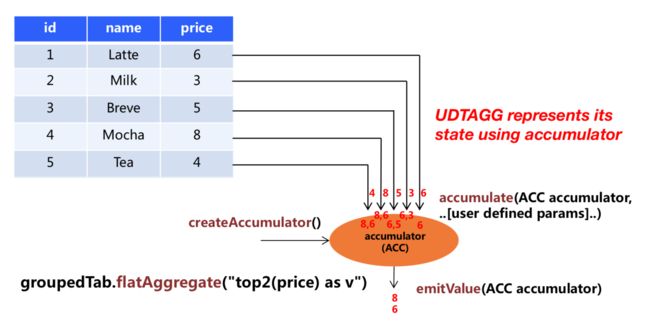
用户定义的表聚合函数(User-Defined Table Aggregate Functions, UDTAGGs),可以把一个表中数据,聚合为具有多行和多列的结果表
用户定义表聚合函数,是通过继承 TableAggregateFunction 抽象类来实现的
TableAggregateFunction 要求必须实现的方法:
– createAccumulator()
– accumulate()
– emitValue()
TableAggregateFunction 的工作原理如下:
首先,它同样需要一个累加器(Accumulator),它是保存聚合中间结果的数据结构。通过调用 createAccumulator() 方法可以创建空累加器。
随后,对每个输入行调用函数的 accumulate() 方法来更新累加器。
处理完所有行后,将调用函数的 emitValue() 方法来计算并返回最终结果。
/**
* Accumulator for Top2.
*/
public class Top2Accum {
public Integer first;
public Integer second;
}
/**
* The top2 user-defined table aggregate function.
*/
public static class Top2 extends TableAggregateFunction, Top2Accum> {
@Override
public Top2Accum createAccumulator() {
Top2Accum acc = new Top2Accum();
acc.first = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
acc.second = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
return acc;
}
public void accumulate(Top2Accum acc, Integer v) {
if (v > acc.first) {
acc.second = acc.first;
acc.first = v;
} else if (v > acc.second) {
acc.second = v;
}
}
public void merge(Top2Accum acc, java.lang.Iterable iterable) {
for (Top2Accum otherAcc : iterable) {
accumulate(acc, otherAcc.first);
accumulate(acc, otherAcc.second);
}
}
public void emitValue(Top2Accum acc, Collector> out) {
// emit the value and rank
if (acc.first != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
out.collect(Tuple2.of(acc.first, 1));
}
if (acc.second != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
out.collect(Tuple2.of(acc.second, 2));
}
}
}
// register function
StreamTableEnvironment tEnv = ...
tEnv.registerFunction("top2", new Top2());
// init table
Table tab = ...;
// use function
tab.groupBy("key")
.flatAggregate("top2(a) as (v, rank)")
.select("key, v, rank");