vue+springboot项目练习(三、引入数据库)
本篇联系引入数据库,通过数据库验证进行访问页面
一、引入数据库
二、使用数据库验证登录
上一篇中我们直接在后端的控制器中用把账号密码进行写死验证

下面可使用数据库验证逻辑如下
1、获得前端发送过来的用户名和密码信息
2、查询数据库中是否存在相通的一堆用户名和密码
3、如果存在返回 Result(400),如果不存在返回 Result(200)
三、使用数据库进行项目配置
在项目中修改 pom.xml来更新Maven库中的依赖
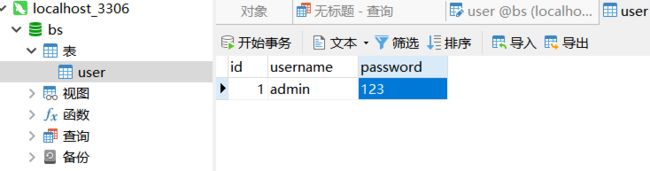
数据库导入mysql
data-jpa下面写user类需要使用
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId>
dependency>
配置完依赖后,还需要配置数据库。打开src\main\resources\application.properties ,在原来的基础上,添加如下语句
spring.datasource.url= jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bs?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username= root
spring.datasource.password= 123456
spring.datasource.driver-class-name= com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = none
mysql8.0 driver-class-name中必须填写cj
四、完善登录控制器
User类
修改 User 类代码如下,以建立对数据库的映射。
package com.example.wei.pojo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
@JsonIgnoreProperties({"handler","hibernateLazyInitializer"})
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
int id;
@Column(name = "username")
String username;
@Column(name = "password")
String password;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
注解说明
@Entity表示这是一个实体类
@Table(name=“user”)表示对应user表
@JsonIgnoreProperties({“handler”,“hibernateLazyInitializer”})简化数据库操作使用了 Java Persistence API(JPA)作用是在 json 序列化时忽略 bean 中的一些不需要转化的属性
前后端分离,而前后端数据交互用的是 json 格式。 那么 User 对象就会被转换为 json 数据。 而本项目使用 jpa 来做实体类的持久化,jpa 默认会使用 hibernate, 在 jpa 工作过程中,就会创造代理类来继承 User ,并添加 handler 和 hibernateLazyInitializer 这两个无须 json 化的属性,所以这里需要用 JsonIgnoreProperties 把这两个属性忽略掉。
UserDao
数据访问对象,DAO,用来操作数据库对象,对象可自己开发可使用框架我们通过继承 JpaRepository来构建Dao层
JpaRepository增删改查博客讲解
新建package包,命名dao,然后创建UserDao接口(Interface)
package com.example.wei.dao;
import com.example.wei.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User,Integer> {
User findByUsername(String username);
User getByUsernameAndPassword(String username,String password);
}
方法名字使用。使用了 JPA,无需手动构建 SQL 语句,而只需要按照规范提供方法的名字即可实现对数据库的增删改查。
如findByUsername,就是通过 username字段查询到对应的行并返回给 User 类。
构建了两个方法,一个是通过用户名查询,一个是通过用户名及密码查询。
UserService
新建package包,命名service然后创建UserService类
package com.example.wei.service;
import com.example.wei.dao.UserDao;
import com.example.wei.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserDao userDao;
public boolean isExist(String username) {
User user = getByName(username);
return null!=user;
}
public User getByName(String username) {
return userDao.findByUsername(username);
}
public User get(String username,String password){
return userDao.getByUsernameAndPassword(username, password);
}
public void add(User user){
userDao.save(user);
}
}
这里对 UserDao 进行了二次封装,一般来讲,我们在 dao 中只定义基础的增删改查操作,而具体的操作,需要由 dao 来完成。
由于我们做的操作原本就比较简单,所以这里看起来只是简单地重命名了一下
比如把 “通过用户名及密码查询并获得对象” 这种方法命名为 get。
LoginController
登录控制器是通过 UserService 提供的 get 方法查询数据库,如果返回的对象为空,则验证失败,否则就验证成功。
package com.example.wei.controller;
import com.example.wei.pojo.User;
import com.example.wei.result.Result;
import com.example.wei.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.util.HtmlUtils;
import java.util.Objects;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
// LoginController loginController;
@PostMapping(value = "/api/login")
@ResponseBody
@CrossOrigin
public Result login(@RequestBody User requsetUser){
String username = requsetUser.getUsername();
username = HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(username);
// if (!Objects.equals("admin",username) || !Objects.equals("123456", requsetUser.getPassword())){
// String message= "账号密码错误";
// System.out.println("test");
// return new Result(400);
// }else{
// return new Result(200);
// }
User user =userService.get(username,requsetUser.getPassword());
if (null == user){
return new Result(400);
}else{
return new Result(200);
}
}
}
三层架构(Dao + Service + Controller)具体说明
- Dao用来与数据库的直接操作,定义增删改查操作
- Service负责业务逻辑,跟功能相关的代码一般写在这里编写、调用各种方法对 DAO 取得的数据进行操作
- Controller负责数据交互,接收前端发送的数据,通过调用 Service 获得处理后的数据并返回
在实践中倾向于让 Controller 显得干净一些,方便代码的阅读者寻找分析功能的入口。(后期重构)
五、测试
同时运行前端和后端项目,访问localhost:8080/#/login ,输入用户名 admin,密码 123