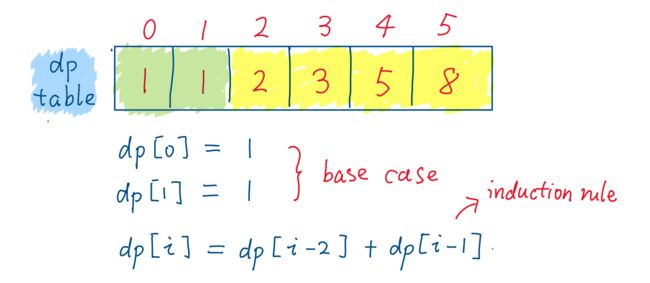Leetcode热题100:简单部分
[001] 合并二叉树
给定两个二叉树,想象当你将它们中的一个覆盖到另一个上时,两个二叉树的一些节点便会重叠。
你需要将他们合并为一个新的二叉树。合并的规则是如果两个节点重叠,那么将他们的值相加作为节点合并后的新值,否则不为 NULL 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
示例 1:
输入:
Tree 1 Tree 2
1 2
/ \ / \
3 2 1 3
/ \ \
5 4 7
输出:
合并后的树:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
5 4 7
注意: 合并必须从两个树的根节点开始。
方法一:深度优先搜索
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null) {
return t2;
}
if (t2 == null) {
return t1;
}
TreeNode merged = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
merged.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
merged.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
return merged;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(min(m,n))
空间复杂度:O(min(m,n))
方法二:广度优先搜索
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null) {
return t2;
}
if (t2 == null) {
return t1;
}
TreeNode merged = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue1 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue2 = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(merged);
queue1.offer(t1);
queue2.offer(t2);
while (!queue1.isEmpty() && !queue2.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll(), node1 = queue1.poll(), node2 = queue2.poll();
TreeNode left1 = node1.left, left2 = node2.left, right1 = node1.right, right2 = node2.right;
if (left1 != null || left2 != null) {
if (left1 != null && left2 != null) {
TreeNode left = new TreeNode(left1.val + left2.val);
node.left = left;
queue.offer(left);
queue1.offer(left1);
queue2.offer(left2);
} else if (left1 != null) {
node.left = left1;
} else if (left2 != null) {
node.left = left2;
}
}
if (right1 != null || right2 != null) {
if (right1 != null && right2 != null) {
TreeNode right = new TreeNode(right1.val + right2.val);
node.right = right;
queue.offer(right);
queue1.offer(right1);
queue2.offer(right2);
} else if (right1 != null) {
node.right = right1;
} else {
node.right = right2;
}
}
}
return merged;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(min(m,n))
空间复杂度:O(min(m,n))
[002] 汉明距离
两个整数之间的汉明距离指的是这两个数字对应二进制位不同的位置的数目。
给出两个整数 x 和 y,计算它们之间的汉明距离。
注意:
0 ≤ x, y < 231.
示例:
输入: x = 1, y = 4
输出: 2
解释:
1 (0 0 0 1)
4 (0 1 0 0)
↑ ↑
上面的箭头指出了对应二进制位不同的位置。
方法一:
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
return Integer.bitCount(x ^ y);
}
}
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
方法二:位移
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int xor = x ^ y;
int distance = 0;
while (xor != 0) {
if (xor % 2 == 1)
distance += 1;
xor = xor >> 1;
}
return distance;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
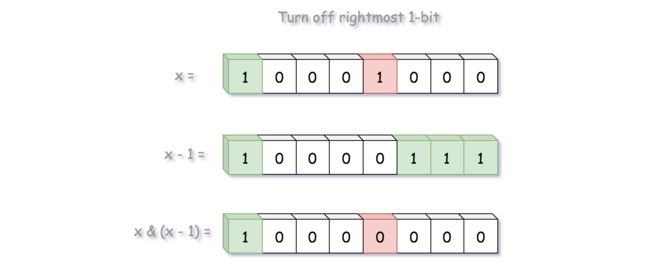
方法三:
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int xor = x ^ y;
int distance = 0;
while (xor != 0) {
distance += 1;
// remove the rightmost bit of '1'
xor = xor & (xor - 1);
}
return distance;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(1)
[003] 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
示例:
输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
方法一:递归-从下到上
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
递归-从上到下
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
//递归函数的终止条件,节点为空时返回
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
//下面三句是将当前节点的左右子树交换
TreeNode tmp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = tmp;
//递归交换当前节点的 左子树
invertTree(root.left);
//递归交换当前节点的 右子树
invertTree(root.right);
//函数返回时就表示当前这个节点,以及它的左右子树
//都已经交换完了
return root;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(N)
方法二:
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
//将二叉树中的节点逐层放入队列中,再迭代处理队列中的元素
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
//每次都从队列中拿一个节点,并交换这个节点的左右子树
TreeNode tmp = queue.poll();
TreeNode left = tmp.left;
tmp.left = tmp.right;
tmp.right = left;
//如果当前节点的左子树不为空,则放入队列等待后续处理
if(tmp.left!=null) {
queue.add(tmp.left);
}
//如果当前节点的右子树不为空,则放入队列等待后续处理
if(tmp.right!=null) {
queue.add(tmp.right);
}
}
//返回处理完的根节点
return root;
}
}
[004] 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
方法一:递归,深度优先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(H),其中 H 表示二叉树的高度。
方法二:广度优先
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);//添加失败返回false。add抛出异常
int ans = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();//记录该层多少个节点
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();//失败返回null,romove异常
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
size--;
}
ans++;//层数加1
}
return ans;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:最坏情况下会达到 O(n)
[005] 反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶:
你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
方法一:递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode p = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return p;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
方法二:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
[006] 只出现一次的数字
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
说明:
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗?
示例 1:
输入: [2,2,1]
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [4,1,2,1,2]
输出: 4
方法一:
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int single = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
single ^= num;
}
return single;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
[007] 多数元素
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3]
输出: 3
示例 2:
输入: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
输出: 2
方法一:摩尔投票法
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int count = 0;
Integer candidate = null;
for (int num : nums) {
if (count == 0) {
candidate = num;
}
count += (num == candidate) ? 1 : -1;
}
return candidate;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
方法二:哈希表
class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Integer> countNums(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counts = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (!counts.containsKey(num)) {
counts.put(num, 1);
} else {
counts.put(num, counts.get(num) + 1);
}
}
return counts;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counts = countNums(nums);
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> majorityEntry = null;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
if (majorityEntry == null || entry.getValue() > majorityEntry.getValue()) {
majorityEntry = entry;
}
}
return majorityEntry.getKey();
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
方法三:排序
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length / 2];
}
}
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
空间复杂度:O(log n)
方法四:随机化
由于一个给定的下标对应的数字很有可能是众数,我们随机挑选一个下标,检查它是否是众数,如果是就返回,否则继续随机挑选。
class Solution {
private int randRange(Random rand, int min, int max) {
return rand.nextInt(max - min) + min;
}
private int countOccurences(int[] nums, int num) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == num) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Random rand = new Random();
int majorityCount = nums.length / 2;
while (true) {
int candidate = nums[randRange(rand, 0, nums.length)];
if (countOccurences(nums, candidate) > majorityCount) {
return candidate;
}
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(∞)
空间复杂度:O(1)
方法五:分治(递归)
分治法解决这个问题:将数组分成左右两部分,分别求出左半部分的众数 a1 以及右半部分的众数 a2,随后在 a1 和 a2 中选出正确的众数。
使用经典的分治算法递归求解,直到所有的子问题都是长度为 1 的数组。长度为 1 的子数组中唯一的数显然是众数,直接返回即可。如果回溯后某区间的长度大于 1,我们必须将左右子区间的值合并。如果它们的众数相同,那么显然这一段区间的众数是它们相同的值。否则,我们需要比较两个众数在整个区间内出现的次数来决定该区间的众数。
class Solution {
private int countInRange(int[] nums, int num, int lo, int hi) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
if (nums[i] == num) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
private int majorityElementRec(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
// base case; the only element in an array of size 1 is the majority
// element.
if (lo == hi) {
return nums[lo];
}
// recurse on left and right halves of this slice.
int mid = (hi - lo) / 2 + lo;
int left = majorityElementRec(nums, lo, mid);
int right = majorityElementRec(nums, mid + 1, hi);
// if the two halves agree on the majority element, return it.
if (left == right) {
return left;
}
// otherwise, count each element and return the "winner".
int leftCount = countInRange(nums, left, lo, hi);
int rightCount = countInRange(nums, right, lo, hi);
return leftCount > rightCount ? left : right;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
return majorityElementRec(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
}
时间复杂度:O(nlog n)
空间复杂度:O(log n)
[008] 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
方法一:递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
} else if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
} else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n + m)
空间复杂度:O(n + m)
方法二:迭代
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = prehead;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n + m)
空间复杂度:O(1)
[009] 移动零
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
示例:
输入: [0,1,0,3,12]
输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
说明:
必须在原数组上操作,不能拷贝额外的数组。
尽量减少操作次数。
方法一:两次遍历
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null) {
return;
}
//第一次遍历的时候,j指针记录非0的个数,只要是非0的统统都赋给nums[j]
int j = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;++i) {
if(nums[i]!=0) {
nums[j++] = nums[i];
}
}
//非0元素统计完了,剩下的都是0了
//所以第二次遍历把末尾的元素都赋为0即可
for(int i=j;i<nums.length;++i) {
nums[i] = 0;
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
方法二:一次遍历
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null) {
return;
}
//两个指针i和j
int j = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++) {
//当前元素!=0,就把其交换到左边,等于0的交换到右边
if (nums[i] != 0) {
if (i > j) {// #1
nums[j] = nums[i];
nums[i] = 0;
}
j++;
}
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
[010] 找到所有数组中消失的数字
给定一个范围在 1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n ( n = 数组大小 ) 的 整型数组,数组中的元素一些出现了两次,另一些只出现一次。
找到所有在 [1, n] 范围之间没有出现在数组中的数字。
您能在不使用额外空间且时间复杂度为O(n)的情况下完成这个任务吗? 你可以假定返回的数组不算在额外空间内。
示例:
输入:
[4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
输出:
[5,6]
方法一:HashMap(复杂度为O(n),不符合题目要求)
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
HashMap<Integer, Boolean> hashTable = new HashMap<Integer, Boolean>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
hashTable.put(nums[i], true);
}
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for (int i = 1; i <= nums.length; i++) {
if (!hashTable.containsKey(i)) {
result.add(i);
}
}
return result;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(N)
方法二:
- 遍历每个元素,对索引进行标记,将对应索引位置的值变为负数;
- 遍历下索引,看看哪些索引位置上的数不是负数的,位置上不是负数的索引,对应的元素就是不存在的。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
//用来存放结果
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
//1. 遍历下数组的元素,对对应的索引位置的元素作标记
int len = nums.length;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
int num = Math.abs(nums[i]); //由于数组的元素有可能被*-1,所以取绝对值
int index = num - 1;
if(nums[index] > 0){
nums[index] *= -1;
}
}
// 寻找没有标记的索引位置
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
if(nums[i] > 0){
int num = i + 1; //将索引转化为对应的元素
res.add(num);
}
}
return res;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
[011] 相交链表
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
![]()
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
![]()
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
![]()
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
![]()
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
- 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
方法一: 暴力法
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode flagA=headA;
do {
ListNode flagB=headB;
do {
if(flagA==flagB) {
return flagA;
}else {
flagB=flagB.next;
}
}while(flagB!=null);
flagA=flagA.next;
}while(flagA!=null);
return null;
}//暴力法
- 时间复杂度 : (mn)
- 空间复杂度 : O(1)
方法二: 哈希表法
public ListNode getIntersectionNode1(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null) {
return null;
}
HashMap<ListNode, Integer> nodeOfHeadA=new HashMap<ListNode, Integer>();
ListNode pA=headA;
while(pA!=null) {
if(!nodeOfHeadA.containsKey(pA)) {
nodeOfHeadA.put(pA,pA.val);
}
pA=pA.next;
}
ListNode pB=headB;
while(pB!=null) {
if(nodeOfHeadA.containsKey(pB)) {
return pB;
}
pB=pB.next;
}
return null;
}//哈希表法
- 时间复杂度 : O(m+n)
- 空间复杂度 : O(m) 或 O(n)。
方法三:双指针法,消除长度差,拼接两链表
pA:1->2->3->4->5->6->null->9->5->6->null
pB:9->5->6->null->1->2->3->4->5->6->null
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
- 时间复杂度 : O(m+n)
- 空间复杂度 : O(1)
[012] 最小栈
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x) —— 将元素 x 推入栈中。
pop() —— 删除栈顶的元素。
top() —— 获取栈顶元素。
getMin() —— 检索栈中的最小元素。
示例:
输入:
["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"]
[[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]]
输出:
[null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]
解释:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> 返回 0.
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
提示:
pop、top 和 getMin 操作总是在 非空栈 上调用。
方法一
class MinStack {
Deque<Integer> xStack;
Deque<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
xStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
minStack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
minStack.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int x) {
xStack.push(x);
minStack.push(Math.min(minStack.peek(), x));
}
public void pop() {
xStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return xStack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(x);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
时间复杂度:对于题目中的所有操作,时间复杂度均为 O(1)
空间复杂度:O(n)
[013] 买卖股票的最佳时机
给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
如果你最多只允许完成一笔交易(即买入和卖出一支股票一次),设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
注意:你不能在买入股票前卖出股票。
示例 1:
输入: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出: 5
解释: 在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
示例 2:
输入: [7,6,4,3,1]
输出: 0
解释: 在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
题解
方法一:暴力法
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int prices[]) {
int maxprofit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < prices.length; j++) {
int profit = prices[j] - prices[i];
if (profit > maxprofit) {
maxprofit = profit;
}
}
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
方法二:一次遍历
我们需要遍历价格数组一遍,记录历史最低点,然后在每一天考虑这么一个问题:如果我是在历史最低点买进的,那么我今天卖出能赚多少钱?当考虑完所有天数之时,我们就得到了最好的答案。
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int prices[]) {
int minprice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxprofit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] < minprice) {
minprice = prices[i];
} else if (prices[i] - minprice > maxprofit) {
maxprofit = prices[i] - minprice;
}
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
[014] 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
但是下面这个 [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
进阶:
你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
方法一:递归
递归函数,通过「同步移动」两个指针的方法来遍历这棵树,p 指针和 q 指针一开始都指向这棵树的根,随后 p 右移时,q 左移,p 左移时,q 右移。每次检查当前 p 和 q 节点的值是否相等,如果相等再判断左右子树是否对称。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root, root);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
}
return p.val == q.val && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);
}
}
- 时间复杂度:这里遍历了这棵树,渐进时间复杂度为 O(n)
- 空间复杂度:这里的空间复杂度和递归使用的栈空间有关,这里递归层数不超过 n,故渐进空间复杂度为 O(n)
方法二:迭代
首先我们引入一个队列,这是把递归程序改写成迭代程序的常用方法。初始化时我们把根节点入队两次。每次提取两个结点并比较它们的值(队列中每两个连续的结点应该是相等的,而且它们的子树互为镜像),然后将两个结点的左右子结点按相反的顺序插入队列中。当队列为空时,或者我们检测到树不对称(即从队列中取出两个不相等的连续结点)时,该算法结束。
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root, root);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode u, TreeNode v) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q.offer(u);
q.offer(v);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
u = q.poll();
v = q.poll();
if (u == null && v == null) {
continue;
}
if ((u == null || v == null) || (u.val != v.val)) {
return false;
}
q.offer(u.left);
q.offer(v.right);
q.offer(u.right);
q.offer(v.left);
}
return true;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:这里需要用一个队列来维护节点,每个节点最多进队一次,出队一次,队列中最多不会超过 n 个点,故渐进空间复杂度为 O(n)
[015] 最大子序和
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
示例:
输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
输出: 6
解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
进阶:
如果你已经实现复杂度为 O(n) 的解法,尝试使用更为精妙的分治法求解。
题解
方法一:动态规划
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int pre = 0, maxAns = nums[0];
for (int x : nums) {
pre = Math.max(pre + x, x);
maxAns = Math.max(maxAns, pre);
}
return maxAns;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
方法二:分治 ★
class Solution {
public class Status {
public int lSum, rSum, mSum, iSum;
public Status(int lSum, int rSum, int mSum, int iSum) {
this.lSum = lSum;
this.rSum = rSum;
this.mSum = mSum;
this.iSum = iSum;
}
}
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
return getInfo(nums, 0, nums.length - 1).mSum;
}
public Status getInfo(int[] a, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return new Status(a[l], a[l], a[l], a[l]);
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
Status lSub = getInfo(a, l, m);
Status rSub = getInfo(a, m + 1, r);
return pushUp(lSub, rSub);
}
public Status pushUp(Status l, Status r) {
int iSum = l.iSum + r.iSum;
int lSum = Math.max(l.lSum, l.iSum + r.lSum);
int rSum = Math.max(r.rSum, r.iSum + l.rSum);
int mSum = Math.max(Math.max(l.mSum, r.mSum), l.rSum + r.lSum);
return new Status(lSum, rSum, mSum, iSum);
}
}
[016] 二叉树的直径
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
示例 :
给定二叉树
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]。
一条路径的长度为该路径经过的节点数减一,所以求直径(即求路径长度的最大值)等效于求路径经过节点数的最大值减一。
而任意一条路径均可以被看作由某个节点为起点,从其左儿子和右儿子向下遍历的路径拼接得到。
方法一:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int maxd=0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
depth(root);
return maxd;
}
public int depth(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return 0;
}
int Left = depth(node.left);
int Right = depth(node.right);
maxd=Math.max(Left+Right,maxd);//将每个节点最大直径(左子树深度+右子树深度)当前最大值比较并取大者
return Math.max(Left,Right)+1;//返回节点深度
}
}
[017] 爬楼梯
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
示例 1:
输入: 2
输出: 2
解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 2 阶
示例 2:
输入: 3
输出: 3
解释: 有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 1 阶 + 2 阶
3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
题解
我们用 f(x) 表示爬到第 x 级台阶的方案数,考虑最后一步可能跨了一级台阶,也可能跨了两级台阶,所以我们可以列出如下式子:
f ( x ) = f ( x − 1 ) + f ( x − 2 ) f(x)=f(x−1)+f(x−2) f(x)=f(x−1)+f(x−2)
它意味着爬到第 x 级台阶的方案数是爬到第 x - 1 级台阶的方案数和爬到第 x - 2 级台阶的方案数的和。很好理解,因为每次只能爬 1 级或 2 级,所以 f(x) 只能从 f(x - 1) 和 f(x - 2) 转移过来,而这里要统计方案总数,我们就需要对这两项的贡献求和。
假设 n = 5,有5级楼梯要爬
-
每次都有2种选择:爬1级,或爬2级。
- 如果爬1级,则剩下4级要爬。
- 如果爬2级,则剩下3级要爬。
-
这拆分出了2个子问题:
- 爬4级楼梯有几种方式?
- 爬3级楼梯有几种方式?
于是,爬 5 级楼梯的方式数 = 爬 4 级楼梯的方式数 + 爬 3 级楼梯的方式数
方法一:递归
调用栈的深度是楼梯数 n ,时间复杂度最坏是 O(2^n),所有节点都遍历到,空间复杂度是O(n)
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n == 1)
return 1;
if (n == 2)
return n;
return climbStairs(n - 1) + climbStairs(n - 2);
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(2^n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
方法二:递归优化
如下图,黄色阴影部分,蓝色阴影部分,就是相同的子树,即相同的子问题。
- 计算过的子问题的结果可以哈希表存起来,也可以用数组,下次遇到就不用再次计算。
- 去除重复的计算后的子树如下,时间复杂度降到了O(n),空间复杂度O(n)。
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int memo[] = new int[n+1];
return climbStairsMemo(n, memo);
}
public int climbStairsMemo(int n, int memo[]){
if (memo[n] > 0)
return memo[n];
if (n == 1)
memo[1] = 1;
if (n == 2)
memo[2] = 2;
if (n > 2)
memo[n] = climbStairsMemo(n - 1, memo) + climbStairsMemo(n - 2, memo);
return memo[n];
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
方法三:动态规划
用一个数组存放中间子问题的结果,dp[i]:爬 i 级楼梯的方式数。从dp[0]、dp[1]出发,顺序计算直到算出 dp[i]。
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[n];
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
方法四:动态规划空间优化
dp[i] 只与过去的两项:dp[i-1] 和 dp[i-2] 有关,没有必要存下所有计算过的 dp 项。用两个变量去存这两个过去的状态就好。
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int p = 0, q = 0, r = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
p = q; //dp[i-2]
q = r; //dp[i-1]
r = p + q; //dp[i]
}
return r;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
方法五:通项公式
public class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
double sqrt5 = Math.sqrt(5);
double fibn = Math.pow((1 + sqrt5) / 2, n + 1) - Math.pow((1 - sqrt5) / 2, n + 1);
return (int)(fibn / sqrt5);
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(log n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
方法六:矩阵
public class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[][] q = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
int[][] res = pow(q, n);
return res[0][0];
}
public int[][] pow(int[][] a, int n) {
int[][] ret = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}};
while (n > 0) {
if ((n & 1) == 1) {
ret = multiply(ret, a);
}
n >>= 1;
a = multiply(a, a);
}
return ret;
}
public int[][] multiply(int[][] a, int[][] b) {
int[][] c = new int[2][2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
c[i][j] = a[i][0] * b[0][j] + a[i][1] * b[1][j];
}
}
return c;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(log n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
[018] 环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
示例 1:
![]()
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
![]()
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
![]()
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 10^4]
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
- pos 为 -1 或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
方法一:哈希表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (!seen.add(head)) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(N)
-
空间复杂度:O(N)
方法二:快慢指针
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(N)
-
空间复杂度:O(1)
[019] 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素不能使用两遍。
示例:
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
方法一:暴力枚举
枚举数组中的每一个数 x,寻找数组中是否存在 target - x。
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
return new int[0];
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(N^2)
-
空间复杂度:O(1)
方法二:哈希表
对于每一个 x,我们首先查询哈希表中是否存在 target - x,然后将 x 插入到哈希表中,可保证不会让 x 和自己匹配
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> hashtable = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (hashtable.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{hashtable.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
hashtable.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(N)
-
空间复杂度:O(N)
[020] 打家劫舍
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。
给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你 不触动警报装置的情况下 ,一夜之内能够偷窃到的最高金额。
示例 1:
输入:[1,2,3,1]
输出:4
解释:偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 1) ,然后偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 3)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 1 + 3 = 4 。
示例 2:
输入:[2,7,9,3,1]
输出:12
解释:偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 2), 偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 9),接着偷窃 5 号房屋 (金额 = 1)。
偷窃到的最高金额 = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12 。
提示:
- 0 <= nums.length <= 100
- 0 <= nums[i] <= 400
题解
对于第 k (k>2) 间房屋,有两个选项:
-
偷窃第 k 间房屋,那么就不能偷窃第 k-1 间房屋,偷窃总金额为前 k-2 间房屋的最高总金额与第 k 间房屋的金额之和。
-
不偷窃第 k 间房屋,偷窃总金额为前 k-1 间房屋的最高总金额。
在两个选项中选择偷窃总金额较大的选项,该选项对应的偷窃总金额即为前 k 间房屋能偷窃到的最高总金额。
用 dp[i] 表示前 i 间房屋能偷窃到的最高总金额,那么就有如下的状态转移方程:
d p [ i ] = m a x ( d p [ i − 2 ] + n u m s [ i ] , d p [ i − 1 ] ) dp[i]=max(dp[i−2]+nums[i],dp[i−1]) dp[i]=max(dp[i−2]+nums[i],dp[i−1])
边界条件为:
d p [ 0 ] = n u m s [ 0 ] 只 有 一 间 房 屋 , 则 偷 窃 该 房 屋 dp[0]=nums[0] 只有一间房屋,则偷窃该房屋 dp[0]=nums[0]只有一间房屋,则偷窃该房屋
d p [ 1 ] = m a x ( n u m s [ 0 ] , n u m s [ 1 ] ) 只 有 两 间 房 屋 , 选 择 其 中 金 额 较 高 的 房 屋 进 行 偷 窃 dp[1]=max(nums[0],nums[1]) 只有两间房屋,选择其中金额较高的房屋进行偷窃 dp[1]=max(nums[0],nums[1])只有两间房屋,选择其中金额较高的房屋进行偷窃
最终的答案即为 dp[n−1],其中 n 是数组的长度。
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int length = nums.length;
if (length == 1) {
return nums[0];
}
int[] dp = new int[length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 2] + nums[i], dp[i - 1]);
}
return dp[length - 1];
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
[021] 回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
进阶:
你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
反转以后和以前一样的就是回文结构,例如 1->2->3->2->1,我们将它反转之后还是与原链表一样,我们就称这种链表结构为回文结构。
方法一:将值复制到数组中后用双指针法
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> vals = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 将链表的值复制到数组中
ListNode currentNode = head;
while (currentNode != null) {
vals.add(currentNode.val);
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 使用双指针判断是否回文
int front = 0;
int back = vals.size() - 1;
while (front < back) {
if (!vals.get(front).equals(vals.get(back))) {
return false;
}
front++;
back--;
}
return true;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(n)
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
方法二:递归
如果使用递归反向迭代节点,同时使用递归函数外的变量向前迭代,就可以判断链表是否为回文。
class Solution {
private ListNode frontPointer;
private boolean recursivelyCheck(ListNode currentNode) {
if (currentNode != null) {
if (!recursivelyCheck(currentNode.next)) {
return false;
}
if (currentNode.val != frontPointer.val) {
return false;
}
frontPointer = frontPointer.next;
}
return true;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
frontPointer = head;
return recursivelyCheck(head);
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(n)
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
方法三:快慢指针
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
// 找到前半部分链表的尾节点并反转后半部分链表
ListNode firstHalfEnd = endOfFirstHalf(head);
ListNode secondHalfStart = reverseList(firstHalfEnd.next);
// 判断是否回文
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = secondHalfStart;
boolean result = true;
while (result && p2 != null) {
if (p1.val != p2.val) {
result = false;
}
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
// 还原链表并返回结果
firstHalfEnd.next = reverseList(secondHalfStart);
return result;
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
private ListNode endOfFirstHalf(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(n)
-
空间复杂度:O(1)
[022] 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
注意空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
示例 1:
输入: "()"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: "()[]{}"
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: "(]"
输出: false
示例 4:
输入: "([)]"
输出: false
示例 5:
输入: "{[]}"
输出: true
方法一:栈
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int n = s.length();
if (n % 2 == 1) {
return false;
}
Map<Character, Character> pairs = new HashMap<Character, Character>() {{
put(')', '(');
put(']', '[');
put('}', '{');
}};
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (pairs.containsKey(ch)) {
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != pairs.get(ch)) {
return false;
}
stack.pop();
} else {
stack.push(ch);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O*(*n+∣Σ∣) 其中 Σ 表示字符集,本题中字符串只包含 6 种括号,∣Σ∣=6
巧妙,扩展性若
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
LinkedList<Character> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == '[') stack.push(']');
else if (c == '(') stack.push(')');
else if (c == '{') stack.push('}');
else if (stack.isEmpty() || c != stack.pop()) return false;
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}