LeetCode - 56.Merge Intervals & LeetCode - 57.Insert Interval (贪心、插入排序)
LeetCode - 56.Merge Intervals & LeetCode - 57.Insert Interval (贪心、插入排序)
- LeetCode - 56.Merge Intervals
- LeetCode - 57.Insert Interval
LeetCode - 56.Merge Intervals
题目链接
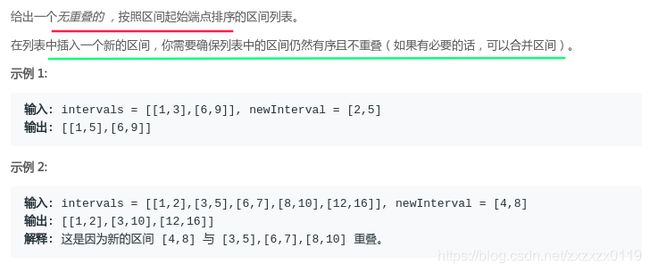
题目
解析
这题一看就是贪心的题目:
- 对这些区间按照
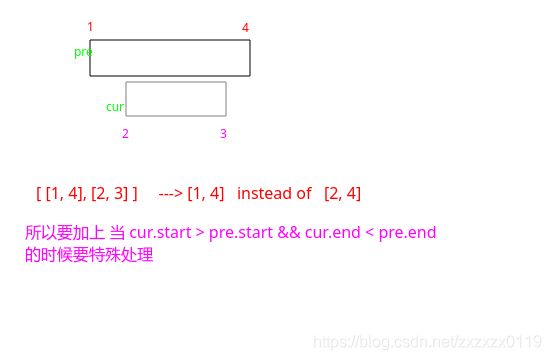
start升序排列(不同于活动安排问题(按照结束时间排序)),然后start相同的按照end排序; - 然后检查前一个的
end和当前的start之间的关系,如果cur.start <= pre.end说明有交集,然后合并即可。但是一定要注意当pre包含cur区间的时候要特殊处理;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Interval {
int start;
int end;
Interval() { start = 0; end = 0; }
Interval(int s, int e) { start = s; end = e; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + start +
", " + end +
']';
}
}
class Solution {
// greedy algorithm
public List<Interval> merge(List<Interval> intervals) {
List<Interval> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(intervals == null || intervals.size() == 0)
return res;
Collections.sort(intervals, (o1, o2) -> {
if(o1.start == o2.start)
return o1.end - o2.end;
return o1.start - o2.start;
});
Interval pre = intervals.get(0);
res.add(pre);
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); i++) {
Interval cur = intervals.get(i);
if (pre.end >= cur.start) {
res.remove(res.size() - 1);
// should consider this special situation, such as [1, 4], [2, 3]
if(cur.start > pre.start && cur.end < pre.end)
res.add(pre);
else
res.add(new Interval(pre.start, intervals.get(i).end));
} else{ // directly add cur
res.add(cur);
}
pre = res.get(res.size() - 1);
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
PrintStream out = System.out;
List<Interval>intervals = Arrays.asList( new Interval(1,4),
new Interval(2,3));
out.println(new Solution().
merge(intervals)
);
}
}
可以将上面的过程写的更加的简洁,每次更新一下pre的end即可,每次res都是添加pre
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Interval {
int start;
int end;
Interval() { start = 0; end = 0; }
Interval(int s, int e) { start = s; end = e; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + start +
", " + end +
']';
}
}
class Solution {
// greedy algorithm
public List<Interval> merge(List<Interval> intervals) {
List<Interval> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(intervals == null || intervals.size() == 0)
return res;
Collections.sort(intervals, (o1, o2) -> {
if(o1.start == o2.start)
return o1.end - o2.end;
return o1.start - o2.start;
});
Interval pre = intervals.get(0);
for(Interval cur : intervals){
if(pre.end >= cur.start)
pre.end = Math.max(pre.end, cur.end); // the same as above special situation, [1, 4]、[2, 3]
else { // no interval
res.add(pre);
pre = cur;
}
}
res.add(pre);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
PrintStream out = System.out;
List<Interval>intervals = Arrays.asList( new Interval(1,4),
new Interval(2,3));
out.println(new Solution().
merge(intervals)
);
}
}
LeetCode - 57.Insert Interval
题目链接
题目
解析
因为已经对所有的区间排过序了,所以只需要在上一题的基础上,先找到newInterval的合适插入位置, 然后调用上一题的merge过程即可。
class Solution {
// greedy algorithm
public List<Interval> insert(List<Interval> intervals, Interval newInterval) {
List<Interval> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(intervals == null) // 注意这里不能加上 intervals.size() == 0
return res;
// find the suitable position that the new interval should insert
int p = 0;
for(p = 0; p < intervals.size() && intervals.get(p).start < newInterval.start; )
p++;
intervals.add(p, newInterval);
// just like leetcode - 56. Merge Intervals
Interval pre = intervals.get(0);
for(Interval cur : intervals){
if(pre.end >= cur.start)
pre.end = Math.max(pre.end, cur.end); // the same as above special situation, [1, 4]、[2, 3]
else { // no interval
res.add(pre);
pre = cur;
}
}
res.add(pre);
return res;
}
}
第二种方法:
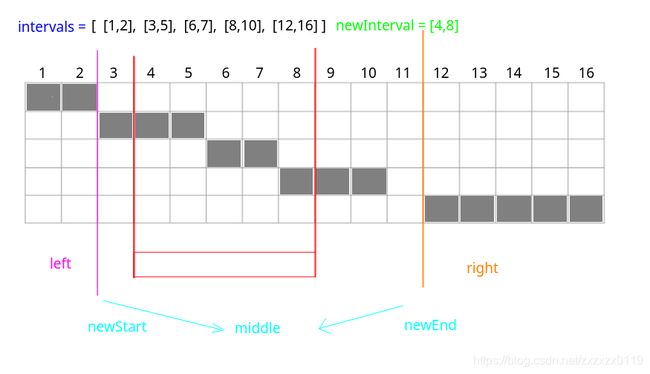
- 就是遍历一遍
intervals,然后如果当前遍历的cur,如果和newInterval没有交集的话,就分别各自加到left、right(都是List集合)中; - 如果有交集的话就需要一直维护一个最左端点
newStart和最右端点newEnd的区间,具体看下面(题目的样例);
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Interval {
int start;
int end;
Interval() { start = 0; end = 0; }
Interval(int s, int e) { start = s; end = e; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + start +
", " + end +
']';
}
}
class Solution {
// greedy algorithm
public List<Interval> insert(List<Interval> intervals, Interval newInterval) {
List<Interval> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(intervals == null)
return res;
int newStart = newInterval.start, newEnd = newInterval.end;
List<Interval> left = new ArrayList<>();
List<Interval> right = new ArrayList<>();
for(Interval cur : intervals){
if(cur.end < newStart) // cur small than newInterval
left.add(cur);
else if(cur.start > newEnd)// cur bigger than newInterval
right.add(cur);
else { // have overlaps(intersect) --> get the final newInterval's left and right position
newStart = Math.min(newStart, cur.start); // the smallest
newEnd = Math.max(newEnd, cur.end); // the biggest
}
}
res.addAll(left);
res.add(new Interval(newStart, newEnd));
res.addAll(right);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
PrintStream out = System.out;
List<Interval>intervals = Arrays.asList( new Interval(1, 2), new Interval(3, 5),
new Interval(6, 7), new Interval(8, 10), new Interval(12, 16));
Interval newInterval = new Interval(4, 8);
out.println(new Solution().
insert(intervals, newInterval)
);
}
}