大数据之几分钟处理完30亿个数据
写在前面
假定现在我们有一个10G的文件,存储的是17~70岁的年龄,每个年龄使用,分割,现需要找出出现次数最多的年龄,以及其出现的次数。
源码 。
1:数据准备
我们首先来准备一个10G大小的存储年龄信息的数据文件,使用如下程序:
public class GenerateData {
private static Random random = new Random();
public static int generateRandomData(int start, int end) {
return random.nextInt(end - start + 1) + start;
}
/**
* 产生10G的 1-1000的数据在D盘
*/
public void generateData() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:\\test\\User.dat");
if (!file.exists()) {
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int start = 18;
int end = 70;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
BufferedWriter bos = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file, true)));
int lineNum = 0;
for (long i = 1; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE * 1.7; i++) {
String data = generateRandomData(start, end) + ",";
bos.write(data);
// 每1百万个数字,一行,每个大小为3个字节,所以一行为3000000字节,大概是3M
// Integer.MAX_VALUE * 1.7 = 3650000000 所以共3650*3M=10G大概
if (i % 1000000 == 0) {
bos.write("\n");
System.out.println(++lineNum + " 写入!");
}
}
System.out.println("写入完成! 共花费时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000 + " s");
bos.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenerateData generateData = new GenerateData();
try {
generateData.generateData();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class WorkCls {
String FILE_NAME = "D:\\test\\User.dat";
@Test
public void readData() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME), "utf-8"));
String line;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 0;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 按行读取
if (count % 1000 == 0 && count > 0) {
// 共3650行
System.out.println("读取1000行,总耗时间: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) / 1000 + " s");
}
count++;
}
System.out.println("共读取 "+ count + "行,读取时间: "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - start) / 1000+" s");
br.close();
}
}
输出如下:
读取1000行,总耗时间: 8 s
读取1000行,总耗时间: 14 s
读取1000行,总耗时间: 32 s
共读取 3651行,读取时间: 42 s
Process finished with exit code 0
可以看到读取3651行数据大概耗时为42s。
2:单线程处理
public class HandleMaxRepeatProblem_v0 {
public static final String FILE_NAME = "D:\\test\\User.dat";
/**
* 统计数量
*/
private static Map<String, AtomicInteger> countMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 按照 "," 分割数据,并写入到countMap里
*/
static class SplitData {
public static void splitLine(String lineData) {
String[] arr = lineData.split(",");
for (String str : arr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str)) {
continue;
}
// 不存在str,则创建new AtomicInteger(0)并put,并返回new AtomicInteger(0)
// .getAndIncrement(); 直接+1,首次不存在则结果为1,否则为原来的值+1,如原来是10,则 变为11
countMap.computeIfAbsent(str, s -> new AtomicInteger(0)).getAndIncrement();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程异步处理
// 非守护线程,不结束jvm不会退出(此时主线程已经结束退出)
new Thread(() -> {
try {
readData();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
private static void readData() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME), "utf-8"));
String line;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 1;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 按行读取,并向map里写入数据
SplitData.splitLine(line);
if (count % 100 == 0) {
System.out.println("读取100行,总耗时间: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) / 1000 + " s");
try {
// 释放CPU,防止CPU资源耗尽
Thread.sleep(1L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
count++;
}
findMostAge();
br.close();
}
private static void findMostAge() {
Integer targetValue = 0;
String targetKey = null;
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger>> entrySetIterator = countMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (entrySetIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger> entry = entrySetIterator.next();
Integer value = entry.getValue().get();
String key = entry.getKey();
if (value > targetValue) {
targetValue = value;
targetKey = key;
}
}
System.out.println("数量最多的年龄为:" + targetKey + "数量为:" + targetValue);
}
}
运行:
读取100行,总耗时间: 6 s
读取100行,总耗时间: 11 s
...
读取100行,总耗时间: 195 s
读取100行,总耗时间: 201 s
数量最多的年龄为:40数量为:68903596
Process finished with exit code 0
总耗时大概是200s,通过前面读取数据行数程序耗时40s,我们可以知道,数据处理的耗时是160s,二者的比例数据读取:数据处理=1:4,所以大部分的时间都消耗在数据处理上了,即单线程处理的主要瓶颈出现在数据处理上,这样的话,我们就可以尝试通过多线程的方式来进行数据处理,提高性能这就需要用到分治。
3:分治
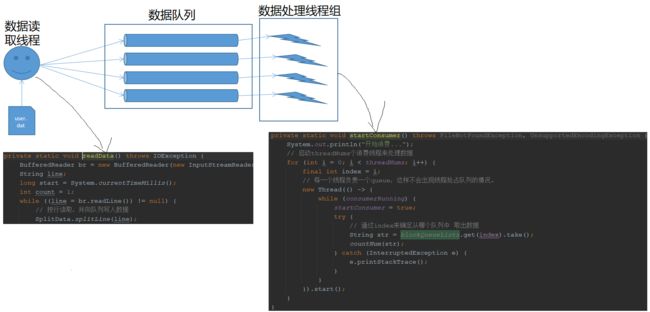
为了能够实现分治,我们需要用到几个队列(使用)来临时存储需要处理的行数据,负责数据读取的线程,向队列里放数据,负责数据处理的线程负责从队列里取数据,即典型的生产-消费模型。这里有几个队列我们就可以创建几个线程来,示意图如下:

可以看到有多个线程从多个队列中获取数据进行处理,程序实现如下:
public class HandleMaxRepeatProblem {
public static final int start = 18;
public static final int end = 70;
public static final String FILE_NAME = "D:\\test\\User.dat";
private static final int threadNums = 20;
/**
* key 为年龄, value为所有的行列表,使用队列
*/
/**
* 存放数据的队列
*/
private static List<LinkedBlockingQueue<String>> blockQueueLists = new LinkedList<>();
/**
* 统计数量
*/
private static Map<String, AtomicInteger> countMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 队列负载均衡
private static AtomicLong count = new AtomicLong(0);
/**
* 开启消费的标志
*/
private static volatile boolean startConsumer = false;
/**
* 消费者运行保证
*/
private static volatile boolean consumerRunning = true;
/**
* 按照 "," 分割数据,并写入到文件里
*/
static class SplitData {
public static void splitLine(String lineData) {
String[] arr = lineData.split("\n");
for (String str : arr) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str)) {
continue;
}
long index = count.get() % threadNums;
try {
// 如果满了就阻塞
blockQueueLists.get((int) index).put(str);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count.getAndIncrement();
}
}
/**
* 按照 x坐标 来分割 字符串,如果切到的字符不为“,”, 那么把坐标向前或者向后移动一位。
*
* @param line
* @param arr 存放x1,x2坐标
* @return
*/
public static String splitStr(String line, int[] arr) {
int startIndex = arr[0];
int endIndex = arr[1];
char start = line.charAt(startIndex);
char end = line.charAt(endIndex);
if ((startIndex == 0 || start == ',') && end == ',') {
arr[0] = endIndex + 1;
arr[1] = arr[0] + line.length() / 3;
if (arr[1] >= line.length()) {
arr[1] = line.length() - 1;
}
return line.substring(startIndex, endIndex);
}
if (startIndex != 0 && start != ',') {
startIndex = startIndex - 1;
}
if (end != ',') {
endIndex = endIndex + 1;
}
arr[0] = startIndex;
arr[1] = endIndex;
if (arr[1] >= line.length()) {
arr[1] = line.length() - 1;
}
return splitStr(line, arr);
}
}
/**
* init map
*/
static {
// 创建threadNums个阻塞队列,每个 队列长度为256
for (int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
blockQueueLists.add(new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(256));
}
// 初始化 统计信息map
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
countMap.computeIfAbsent(i + "", integer -> new AtomicInteger(0));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 读取数据
readData();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 开始消费
startConsumer();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
// 监控
monitor();
}).start();
}
/**
* 每隔60s去检查栈是否为空
*/
private static void monitor() {
AtomicInteger emptyNum = new AtomicInteger(0);
while (consumerRunning) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (startConsumer) {
// 如果所有栈的大小都为0,那么终止进程
AtomicInteger emptyCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
for (int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
if (blockQueueLists.get(i).size() == 0) {
emptyCount.getAndIncrement();
}
}
if (emptyCount.get() == threadNums) {
emptyNum.getAndIncrement();
// 如果连续检查指定次数都为空,那么就停止消费
if (emptyNum.get() > 12) {
consumerRunning = false;
System.out.println("消费结束...");
try {
// 可能消费还没有真正结束,休眠一会
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
try {
clearTask();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getCause());
} finally {
System.exit(-1);
}
}
}
}
}
}
private static void readData() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME), "utf-8"));
String line;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 1;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// 按行读取,并向队列写入数据
SplitData.splitLine(line);
if (count % 100 == 0) {
System.out.println("读取100行,总耗时间: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) / 1000 + " s");
try {
Thread.sleep(10L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
count++;
}
br.close();
}
private static void clearTask() {
// 清理,同时找出出现字符最大的数
Integer targetValue = 0;
String targetKey = null;
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger>> entrySetIterator = countMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (entrySetIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, AtomicInteger> entry = entrySetIterator.next();
Integer value = entry.getValue().get();
String key = entry.getKey();
if (value > targetValue) {
targetValue = value;
targetKey = key;
}
}
System.out.println("数量最多的年龄为:" + targetKey + "数量为:" + targetValue);
System.exit(-1);
}
/**
* 使用linkedBlockQueue
*
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws UnsupportedEncodingException
*/
private static void startConsumer() throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
System.out.println("开始消费...");
// 启动threadNums个消费线程来处理数据
for (int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
final int index = i;
// 每一个线程负责一个queue,这样不会出现线程抢占队列的情况。
new Thread(() -> {
while (consumerRunning) {
startConsumer = true;
try {
// 通过index来确定从哪个队列中 取出数据
String str = blockQueueLists.get(index).take();
countNum(str);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
// 按照arr的大小,运用多线程分割字符串
private static void countNum(String str) {
int[] arr = new int[2];
arr[1] = str.length() / 3;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
final String innerStr = SplitData.splitStr(str, arr);
new Thread(() -> {
String[] strArray = innerStr.split(",");
for (String s : strArray) {
countMap.computeIfAbsent(s, s1 -> new AtomicInteger(0)).getAndIncrement();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
运行:
开始消费...
读取100行,总耗时间: 4 s
...
读取100行,总耗时间: 101 s
读取100行,总耗时间: 104 s
消费结束...
数量最多的年龄为:40数量为:68903596
Process finished with exit code -1
时长从单线程版本的201s优化为104秒,优化效果还是比较明显的。另,程序和示意图对应关系参考下图:
写在后面
总结
了解分治的思想,当一个人干不完的时候,就多找几个人一起干,不要一股脑死干。
参考文章列表
海量数据问题: 如何用JAVA几分钟处理完30亿个数据? 。
