【C++初阶】list的常见使用操作
![]()
个人主页:@Weraphael
✍作者简介:目前学习C++和算法
✈️专栏:C++航路
希望大家多多支持,咱一起进步!
如果文章对你有帮助的话
欢迎 评论 点赞 收藏 加关注✨
目录
- 一、list的基本概念
- 二、list的构造
-
-
- 2.1 默认构造
- 2.2 拷贝构造函数
- 2.3 用n个值为val的元素构造
- 2.4 用迭代区间的元素构造
-
- 三、list的迭代器begin + end
- 四、list的容量操作
-
-
- 4.1 size
- 4.2 empty
-
- 五、list的遍历
-
-
- 5.1 迭代器遍历
- 5.2 范围for
-
- 六、list的获取元素操作
-
-
- 6.1 front
- 6.2 back
- 七、list的对容器修改操作
- 7.1 push_front
- 7.2 pop_front
- 7.3 push_back
- 7.4 pop_back
- 7.5 insert + 迭代器随机访问问题
- 7.6 erase + 迭代器失效问题
- 7.7 swap
- 7.8 clear
-
- 八、其他操作(常见)
-
-
- 8.1 reverse
- 8.2 sort
- 8.3 remove
- 8.4 unique
-
一、list的基本概念
- 功能:将数据进行链式存储。
- 链表(
list)是一种物理存储单元上非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接实现的。 - 链表的组成:链表由一系列结点组成。
- 结点的组成:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
- STL中的链表是一个 双向带头循环链表。这意味着链表中的每个节点都包含指向前一个节点和后一个节点的指针,而头节点和尾节点互相连接形成一个循环。这样的设计使得在链表中插入、删除节点的操作更加高效,同时也提供了双向遍历链表的能力。
list的数据域同样可以存储不同数据类型,因此它同样是一个模板容器。

二、list的构造
2.1 默认构造
list<int> l;
构造空的list对象
2.2 拷贝构造函数
【函数原型】
list (const list& x)
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "l1:";
for (auto x : l1)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
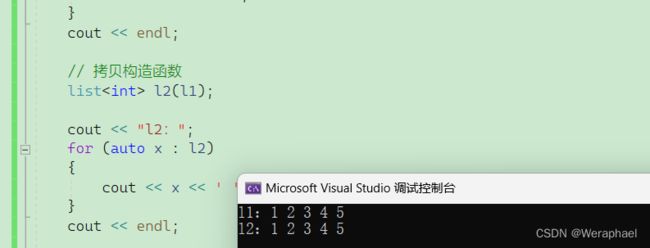
// 拷贝构造函数
list<int> l2(l1);
cout << "l2:";
for (auto x : l2)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
2.3 用n个值为val的元素构造
【函数原型】
list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type())
没有显示给出第二个参数默认为0
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
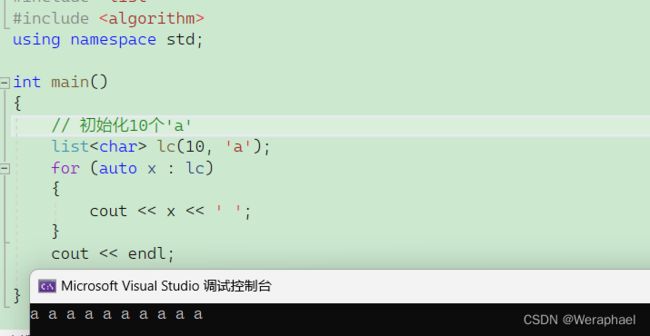
// 初始化10个'a'
list<char> lc(10, 'a');
for (auto x : lc)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
2.4 用迭代区间的元素构造
【函数原型】
list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
注意:迭代区间的范围通常是左闭右开的[first, last)
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
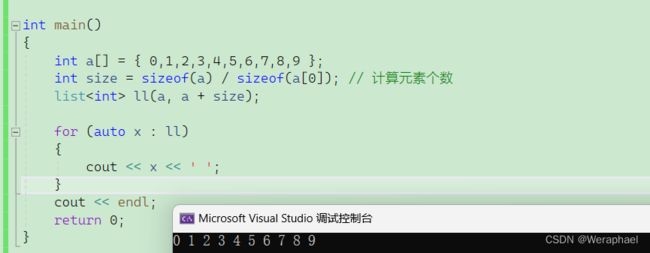
int a[] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
int size = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); // 计算元素个数
list<int> ll(a, a + size);
for (auto x : ll)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
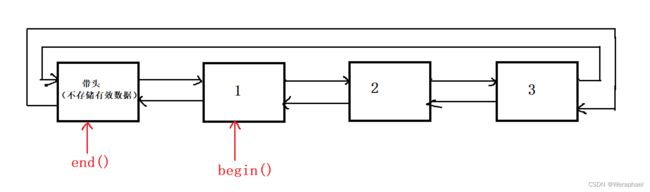
三、list的迭代器begin + end
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
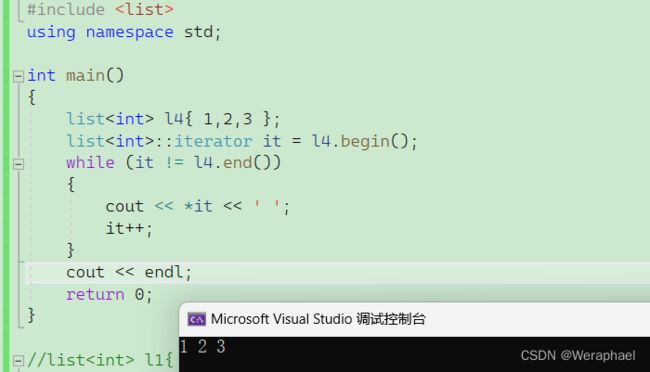
list<int> l4{ 1,2,3 };
list<int>::iterator it = l4.begin();
while (it != l4.end())
{
cout << *it << ' ';
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
四、list的容量操作
4.1 size
功能:返回
list中有效节点的个数
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
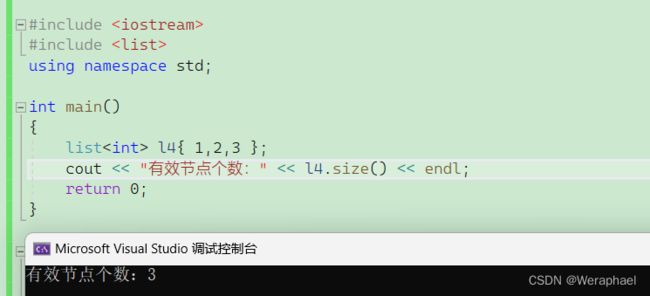
list<int> l4{ 1,2,3 };
cout << "有效节点个数:" << l4.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
4.2 empty
功能:检测
list是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l4;
if (l4.empty())
{
cout << "l4是空结点" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "l4不是空结点" << endl;
cout << "l4的有效结点" << l4.size() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
五、list的遍历
list本质是链表,不是用连续性空间存储数据的。因此,list是不支持下标访问[]
5.1 迭代器遍历
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<char> lc;
// 尾插
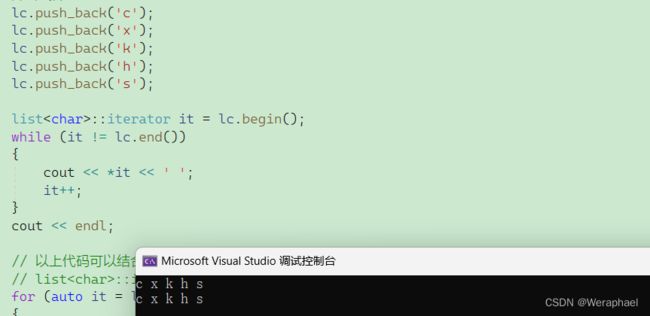
lc.push_back('c');
lc.push_back('x');
lc.push_back('k');
lc.push_back('h');
lc.push_back('s');
list<char>::iterator it = lc.begin();
while (it != lc.end())
{
cout << *it << ' ';
it++;
}
cout << endl;
// 以上代码可以结合成for循环的形式
// list::iterator太长可使用auto
for (auto it = lc.begin(); it != lc.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
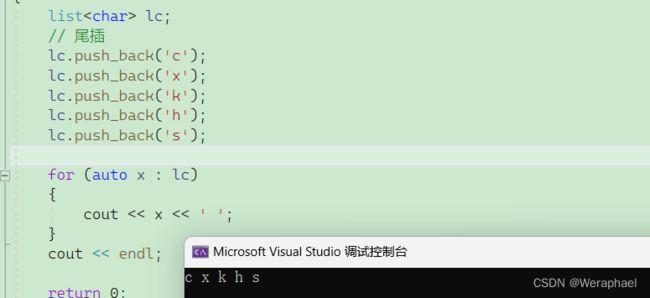
5.2 范围for
由于list支持迭代器,那么就一定支范围for。因为范围for的底层就是迭代器实现的
【代码实现】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<char> lc;
// 尾插
lc.push_back('c');
lc.push_back('x');
lc.push_back('k');
lc.push_back('h');
lc.push_back('s');
for (auto x : lc)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
六、list的获取元素操作
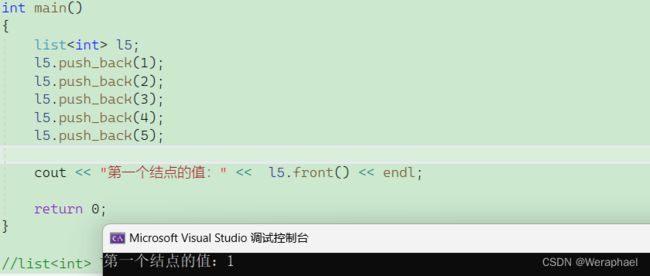
6.1 front
功能:返回
list的第一个节点中值的引用。
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l5;
l5.push_back(1);
l5.push_back(2);
l5.push_back(3);
l5.push_back(4);
l5.push_back(5);
cout << "第一个结点的值:" << l5.front() << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
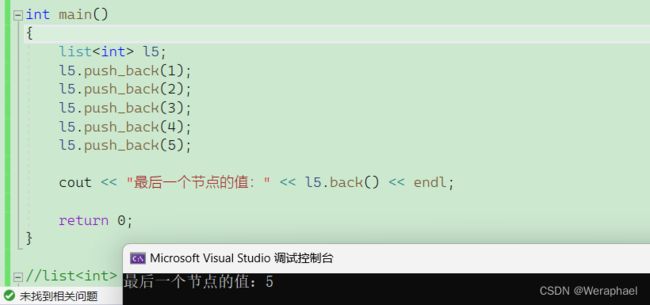
6.2 back
功能:返回
list的最后一个节点中值的引用。
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l5;
l5.push_back(1);
l5.push_back(2);
l5.push_back(3);
l5.push_back(4);
l5.push_back(5);
cout << "最后一个节点的值:" << l5.back() << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
七、list的对容器修改操作
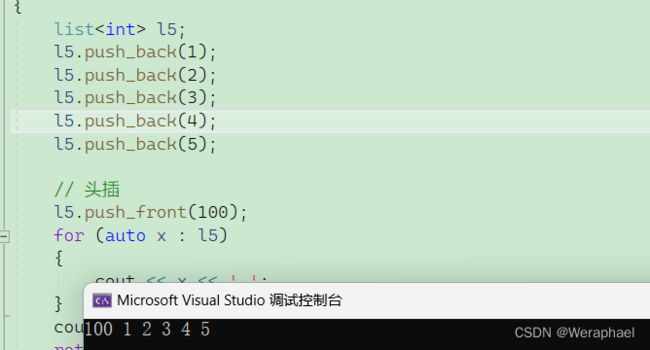
7.1 push_front
功能:头插
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l5;
l5.push_back(1);
l5.push_back(2);
l5.push_back(3);
l5.push_back(4);
l5.push_back(5);
// 头插
l5.push_front(100);
for (auto x : l5)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
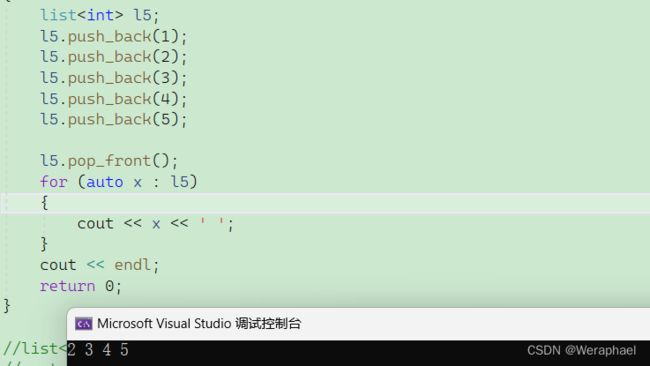
7.2 pop_front
功能:头删
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l5;
l5.push_back(1);
l5.push_back(2);
l5.push_back(3);
l5.push_back(4);
l5.push_back(5);
l5.pop_front();
for (auto x : l5)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
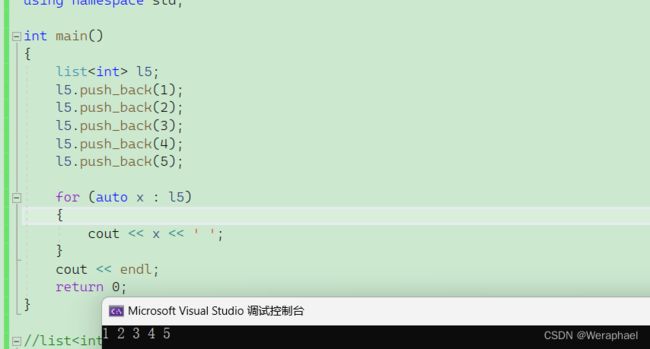
7.3 push_back
功能:尾插
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l5;
l5.push_back(1);
l5.push_back(2);
l5.push_back(3);
l5.push_back(4);
l5.push_back(5);
for (auto x : l5)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
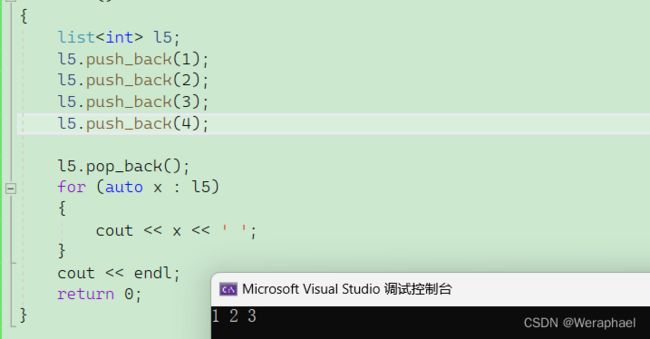
7.4 pop_back
功能:尾删
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l5;
l5.push_back(1);
l5.push_back(2);
l5.push_back(3);
l5.push_back(4);
l5.pop_back();
for (auto x : l5)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
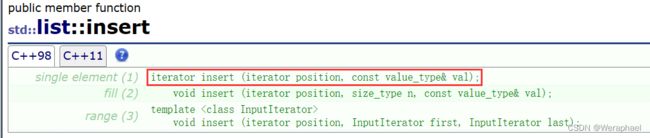
7.5 insert + 迭代器随机访问问题
从vector开始insert都是使用迭代器来访问的
假设已有数据:1 2 3 4,现要在2后插入100。根据以往所学知识不难可以写出以下代码:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l5;
l5.push_back(1);
l5.push_back(2);
l5.push_back(3);
l5.push_back(4);
l5.insert(l5.begin() + 2, 100);
for (auto x : l5)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
可惜报错了。
原因是:list本质是链表,不是用连续性空间存储数据的,迭代器也是不支持随机访问的,只能支持++和--操作(支持双向遍历)
那可能就有人想,++的底层就是+1,那么为什么+1不行,而++可以?
这都归功于类的封装,在对迭代器封装的时候,重新的定义了这些符号的意义,也就是符号的重载。这才使得我们能就像使用指针一样去使用迭代器。下面是list的源代码(部分)
self& operator++()
{
node = (link_type)((*node).next);
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
++*this;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
node = (link_type)((*node).prev);
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
--*this;
return tmp;
}
【正确写法】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l5;
l5.push_back(1);
l5.push_back(2);
l5.push_back(3);
l5.push_back(4);
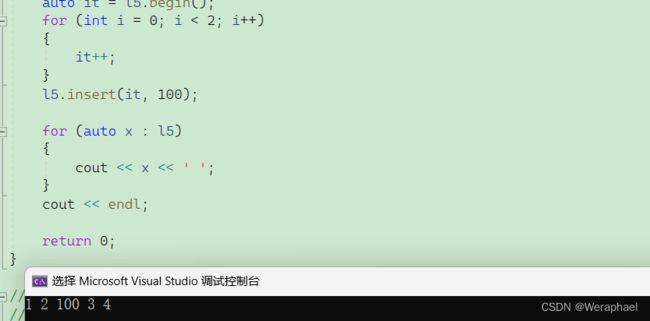
auto it = l5.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
it++;
}
l5.insert(it, 100);
for (auto x : l5)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
接下来我们想,对于insert,list会和vector一样有迭代器失效的问题吗?
答案是没有。原因是:vector在插入时,如果遇到扩容才会存在迭代器失效,而list不存在扩容。
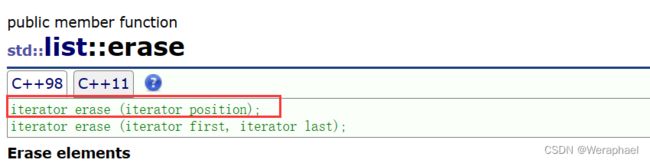
7.6 erase + 迭代器失效问题
功能:删除
list position位置的元素
【代码示例】
目的:删除所有元素
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
cout << "删除前:";
for (auto x : l)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
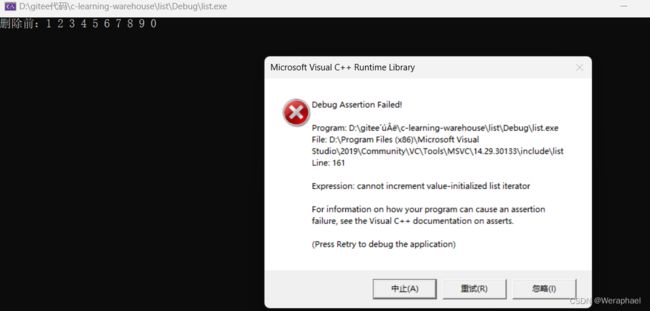
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
l.erase(it);
++it;
}
cout << "删除后:";
for (auto x : l)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
程序崩了!
这和vector的情况类似,erase()函数执行后,it所指向的节点已被删除,因此it无效。
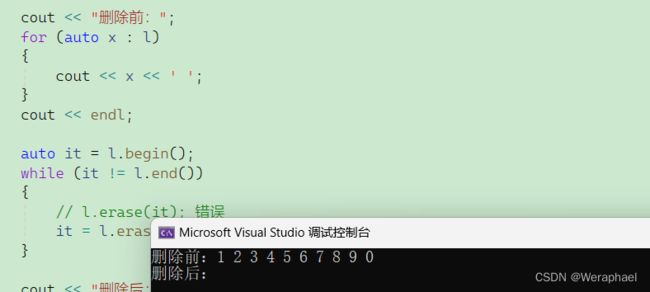
解决方法:在下一次使用it时,必须先给其赋值
【正确代码】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
cout << "删除前:";
for (auto x : l)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
// l.erase(it); 错误
it = l.erase(it);
}
cout << "删除后:";
for (auto x : l)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
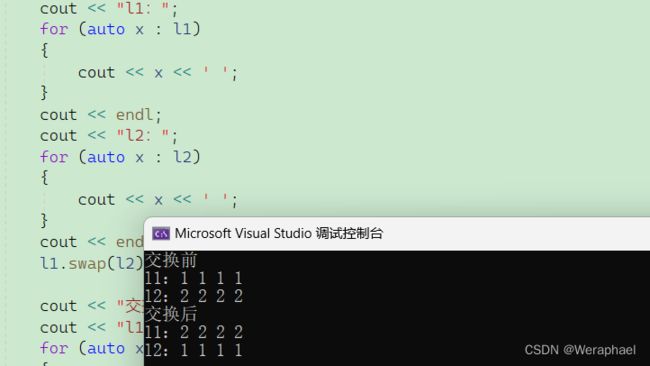
7.7 swap
功能:交换两个
list中的元素
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(1);
list<int> l2;
l2.push_back(2);
l2.push_back(2);
l2.push_back(2);
l2.push_back(2);
cout << "交换前" << endl;
cout << "l1:";
for (auto x : l1)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
cout << "l2:";
for (auto x : l2)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
l1.swap(l2);
cout << "交换后" << endl;
cout << "l1:";
for (auto x : l1)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
cout << "l2:";
for (auto x : l2)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
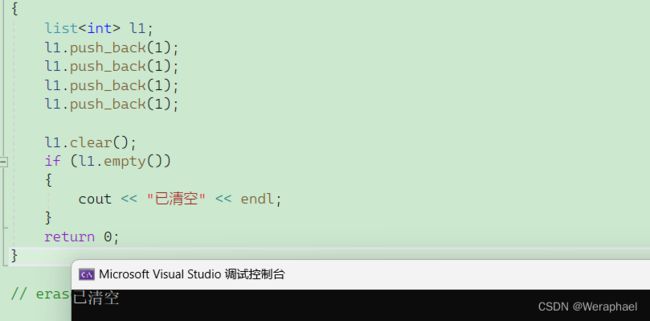
7.8 clear
功能:清空
list中所有的有效元素
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(1);
l1.clear();
if (l1.empty())
{
cout << "已清空" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
八、其他操作(常见)
主要讲解画方括号的,剩下的自行了解即可~
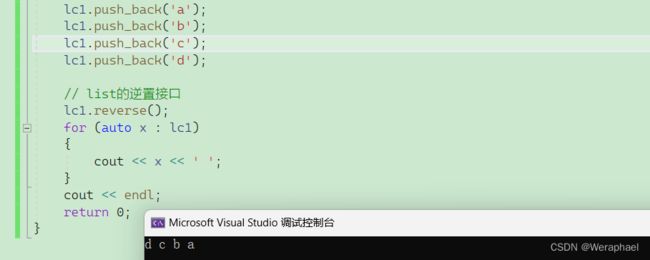
8.1 reverse
功能:逆置
list
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<char> lc1;
lc1.push_back('a');
lc1.push_back('b');
lc1.push_back('c');
lc1.push_back('d');
// list的逆置接口
lc1.reverse();
for (auto x : lc1)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
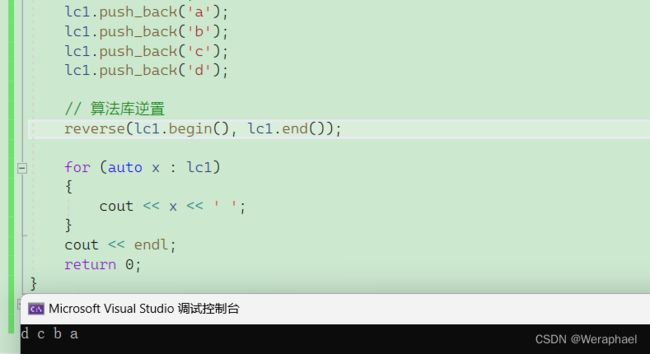
其实list设计这个接口没有必要,因为算法库(algorithm)也设计了reverse算法
【代码示例】
#include
#include 【输出结果】
8.2 sort
功能:排序
list。注意:list底层的sort是归并算法
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> ll;
ll.push_back(5);
ll.push_back(4);
ll.push_back(1);
ll.push_back(2);
ll.push_back(6);
ll.push_back(3);
ll.sort();
for (auto x : ll)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
但是算法库里面也设计了一个sort,但注意:算法库里面的sort对于list是用不了的。
首先从模板参数上就能发现名字有所不同
事实上,这是因为迭代器从功能上进行了分类。
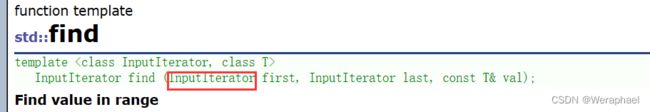
InputIterator就是所有迭代器都可以用。
bidirectional这种迭代器就适合双向的迭代器用。
因此,由于list适合双向迭代器,所以用不了库里的sort(RadomAccessIterator)
那我们怎么知道一个容器是什么类型的迭代器呢?很简单,查文档就行:点击跳转
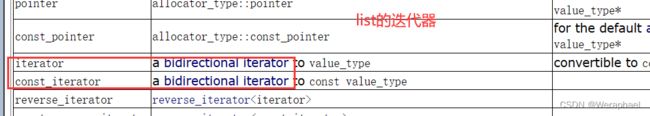
这里我为大家总结了一些常见容器的迭代器:
因此,list接口中实现sort还是有点意义的。我只是说“有点”。
在排序中,vector的排序速度要比list快。这是因为vector是一个连续存储的容器,它的元素在内存中是相邻的,可以利用局部性原理进行高效的排序算法,如快速排序。
相比之下,list是一个链表结构,其元素在内存中是分散存储的,无法直接利用局部性原理,因此排序操作的性能通常较慢。
在某些特定情况下,list可能更适合进行插入和删除操作,因为它对于这些操作的开销较小。因此,在选择容器时,应该根据具体的需求来决定使用哪种容器。
8.3 remove
功能:删除
list某个有效数据
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lit;
lit.push_back(1);
lit.push_back(2);
lit.push_back(3);
lit.push_back(4);
for (auto x : lit)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
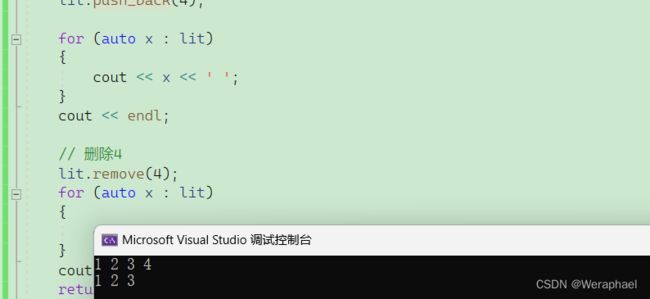
// 删除4
lit.remove(4);
for (auto x : lit)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】
8.4 unique
功能:去重。但是要注意首先得先进行排序,才能进行去重。否则效率极低
【代码示例】
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lit;
lit.push_back(3);
lit.push_back(4);
lit.push_back(1);
lit.push_back(2);
lit.push_back(4);
for (auto x : lit)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
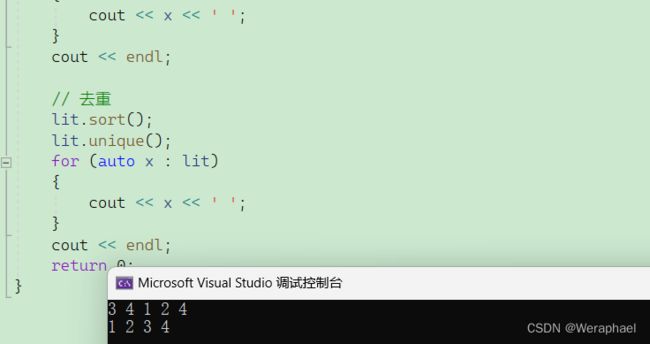
// 去重
lit.sort();
lit.unique();
for (auto x : lit)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【输出结果】