未经许可请勿转载。
Please do not reprint this article without permission.
Introduction 引言
Due to its performance in non-euclidean spatial data, GNN methods are gradually appealing to the attention of researchers. Traditional deep neural networks take Euclidean-structured data as input, which is one of the reasons for its excellent performance in computer vision and other fields. However, in real life, there are many non-euclidean data, such as social network, retail network and biological network. In the field of brain neuroinformatics where the author focuses, one of the most commonly used methods of brain image analysis is voxel-based morphology, but different areas of the human brain are usually correlated and interacting, the brain network constructed based on which can reveal the higher-level brain activity mechanism. Similar to other topological network data, brain network is usually represented in the form of connection matrices, which cannot be directly vectorized and fed into machine learning models. However, the emergence of graph network analysis method breaks the deadlock.
得益于其在非欧几里得空间数据中的表现,图网络研究方法正逐渐吸引着研究人员的关注。传统的深度神经网络将欧几里得空间结构化数据作为输入,这也是其在计算机视觉等领域有着优异表现的原因之一。但现实生活中往往存在着各种非欧几里得结构的数据,例如社交网络数据、零售网络数据以及生物网络数据等。以笔者所处的脑神经信息学领域来说,目前常用的脑神经影像分析手段都是基于体素的形态学分析,但人脑的不同区域往往存在着相互关联和影响,以此为基础构建出的脑网络往往能反映出更深层次的大脑活动机理。而正如其他网络拓扑结构数据,脑网络通常以连接矩阵的形式表示,无法通过直观的手段将其向量化,作为机器学习模型的输入。而图网络分析方法的出现打破了这种僵局。
Theory 基础理论
What is GRAPH? 什么是图?
Graphs are a kind of common data structure used to represent objects and the interactions among them. Objects are expressed by nodes or vertices, and their interactions or connections are described by edges. A graph is mathematically expressed by , where is the set of nodes, is the set of edges, is a matrix with size of used to describe the relationships between nodes. If , then . Moreover, is the feature matrix with size of , where means the attributes or features of the th node, and is the dimension of the attributes.
图是一种常见的数据结构,用于表示对象及其之间的关系。其中,对象又称节点(node)或顶点(vertex),关系用边(edge)来描述。在数学上一般用 来表示,其中 是节点集合, 表示边的集合, 是大小为的邻接矩阵,用于表示节点之间的连接关系,如果 ,则 , 是大小为 的特征矩阵, 的第 行 表示第 个节点的属性特征,其中 是属性的维度。
Reference: 从数据结构到算法:图网络方法初探
Simply put, a graph is an abstract and irregular data structure that can be used to describe and model complex systems. Different from Euclidean spatial data, graphs in real world usually have complex topological structure and huge data size. Using traditional graph analysis methods would be difficult to achieve the same level of performance as applications of machine learning like computer vision, while existing machine learning algorithms cannot be applied to graph data straightforward. In view of this, how to combine machine learning with graph data analysis method, capture the interactions between data nodes in graphs and mine the information therein, has become a hot trend in the field of machine learning.
简单来说,图是一种抽象而不规则的数据结构,可以用于描述和建模复杂的系统。不同于欧几里得空间数据,现实中的图往往具有复杂的拓扑结构和庞大的数据量,传统的图分析方法难以实现与计算机视觉领域相当的应用水平和模型性能,而现有的机器学习算法不能直接应用于图数据中。鉴于此,如何将机器学习与图数据分析方法结合起来,捕捉图结构中数据之间的依赖关系,挖掘其中的信息,成为了机器学习领域的一股热潮。
Notations of GNN 图网络中的符号表示
Theory of GCN 图卷积网络原理
Generally, before data is fed into machine learning algorithm models, it needs to be processed to extract valuable features, which can not only improve the quality of input data, but also greatly improve the reliability and performance of the model. This process is called feature engineering. Since the quality of feature engineering methods directly determines the performance of models, the research of data mining focuses on the handcrafted design and extraction of valuable features for specific data. For example, neuroimaging data often contains a lot of noise and has very high resolution, which is not suitable for direct input to machine learning models. Therefore, we preprocess the data and calculate the corresponding feature vectors, which are fed into the analysis model.
通常,在将数据输入到强大的机器学习算法模型中之前,需要将其进行一定的处理,提取出有价值的特征,这样不仅可以提高数据的质量,更能大大提升模型的可靠性和性能,这一处理过程被称作特征工程。正因为特征工程方法的好坏直接决定着模型的性能,数据挖掘的研究都将重心放在了针对特定的数据人工设计有价值的特征上。举例来说,神经影像数据通常作为包含着多种噪音,并且分辨率极高,不适合直接作为机器学习模型的输入。因此笔者将数据进行一定的预处理并计算出相应的特征向量,在输入到分析模型中。
Deep learning is essentially a kind of "feature engineering", or mostly called "feature learning". This is because the general idea of deep learning is to transform the original data into higher-level features through the nonlinear transformation model of neural network, and these features are usually a vector that can be used as the input of classifiers. The graph convolutional neural network mentioned in this section is a method that can represent the nodes and edges in the graph using feature vectors to serve as the input of high-performance machine learning algorithm model. This method of embedding graph nodes into low-dimensional Euclidean space is also called graph embedding method.
深度学习本质上就是一种“特征工程”,更多地被称为“特征学习”。这是由于深度学习的思想就是将原始数据通过神经网络这一非线性变换模型转变为更高层次的特征,而这些特征通常是一个向量,可以作为分类器的输入。本节提到的图卷积神经网络就是一种能够将图中的节点和边使用特征向量表示出来,以作为高性能机器学习算法模型的输入的方法,这种将图节点嵌入到低维欧几里得空间中的方法也称作图嵌入方法。
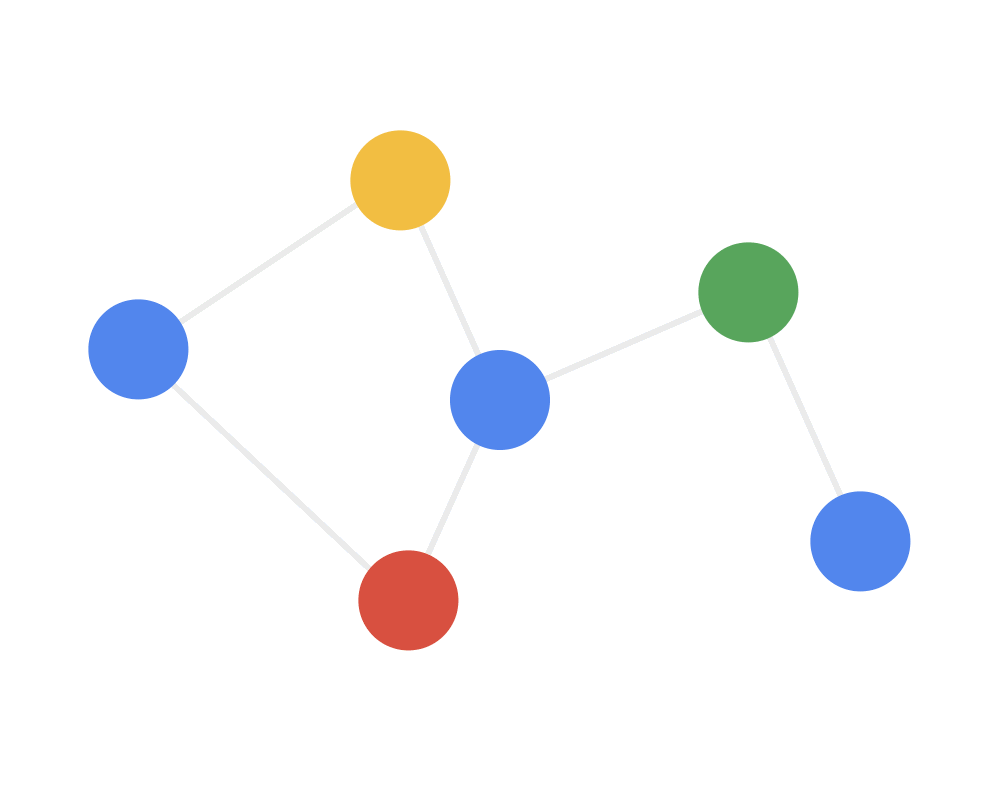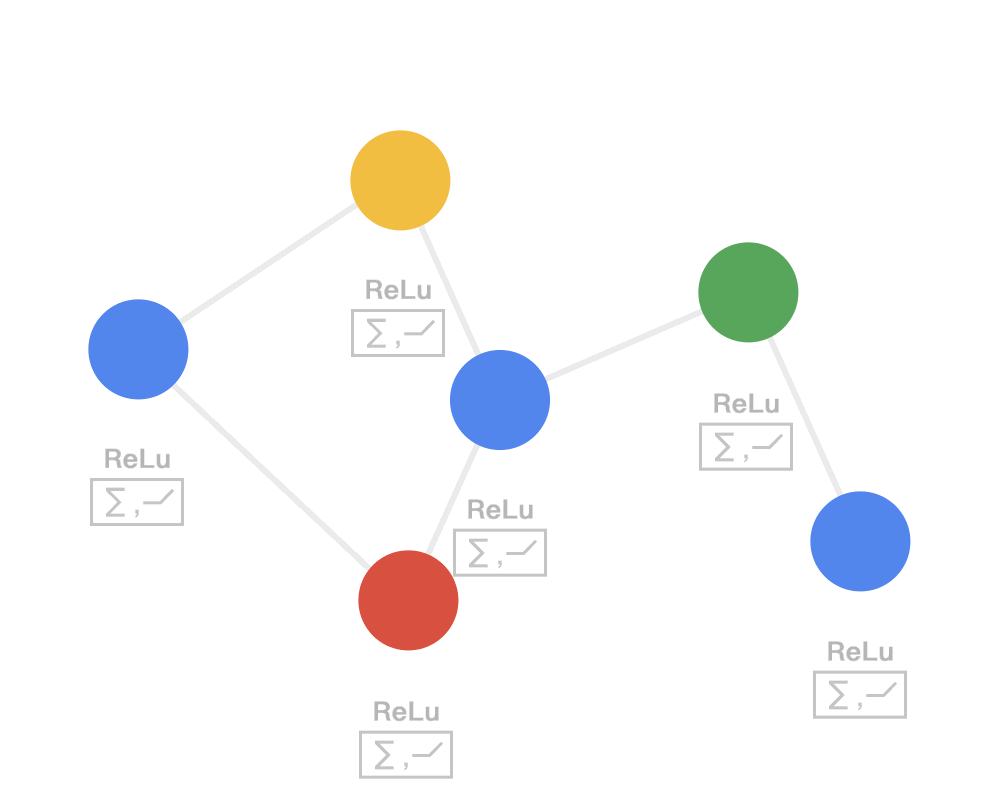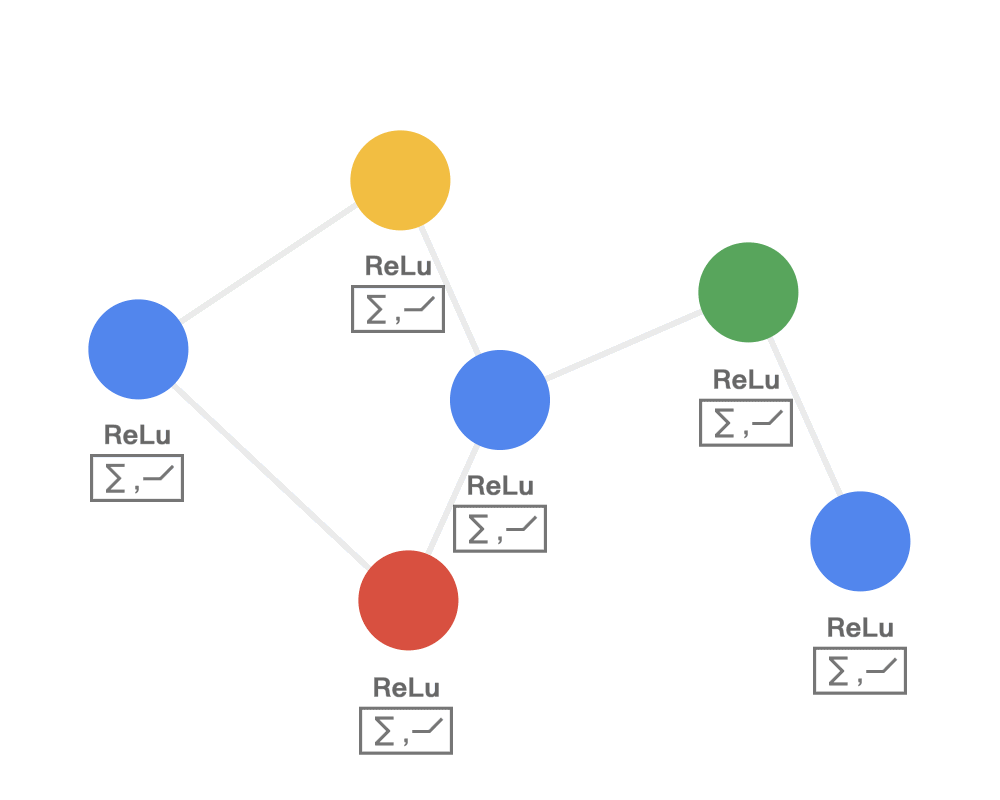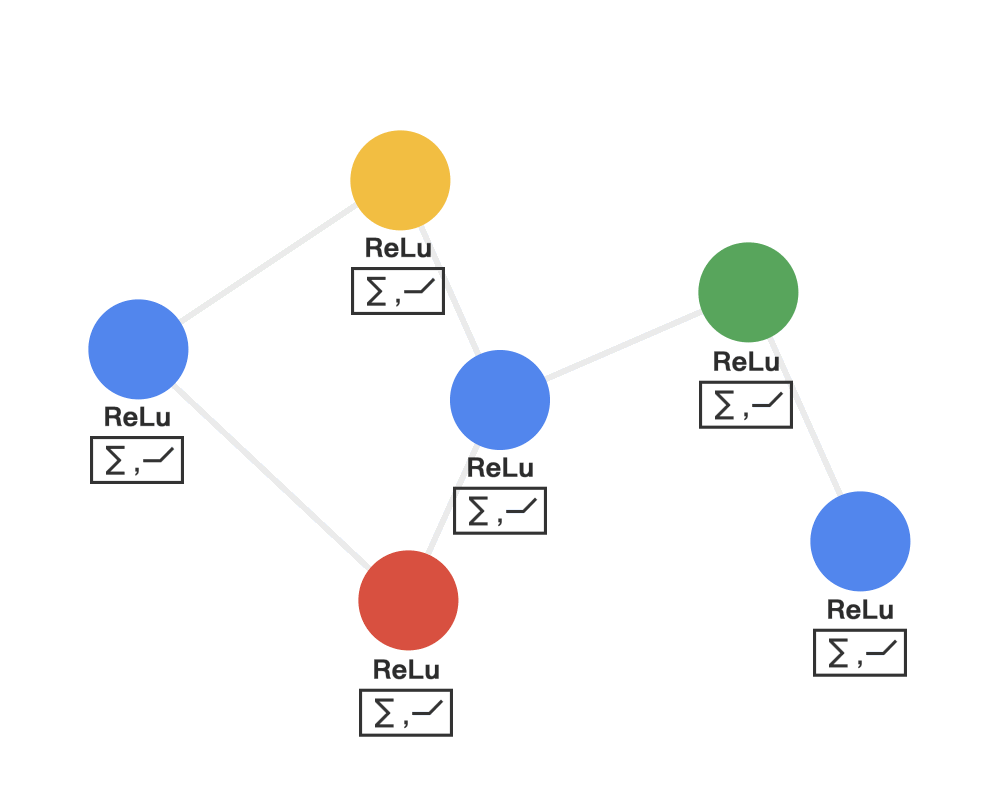
通常用邻居聚合或消息传递来表示卷积算法在不规则数据上的泛化,用动图来理解就是:
第一步:发射(send)每一个节点将自身的特征信息经过变换后发送给邻居节点。这一步是在对节点的特征信息进行抽取变换。
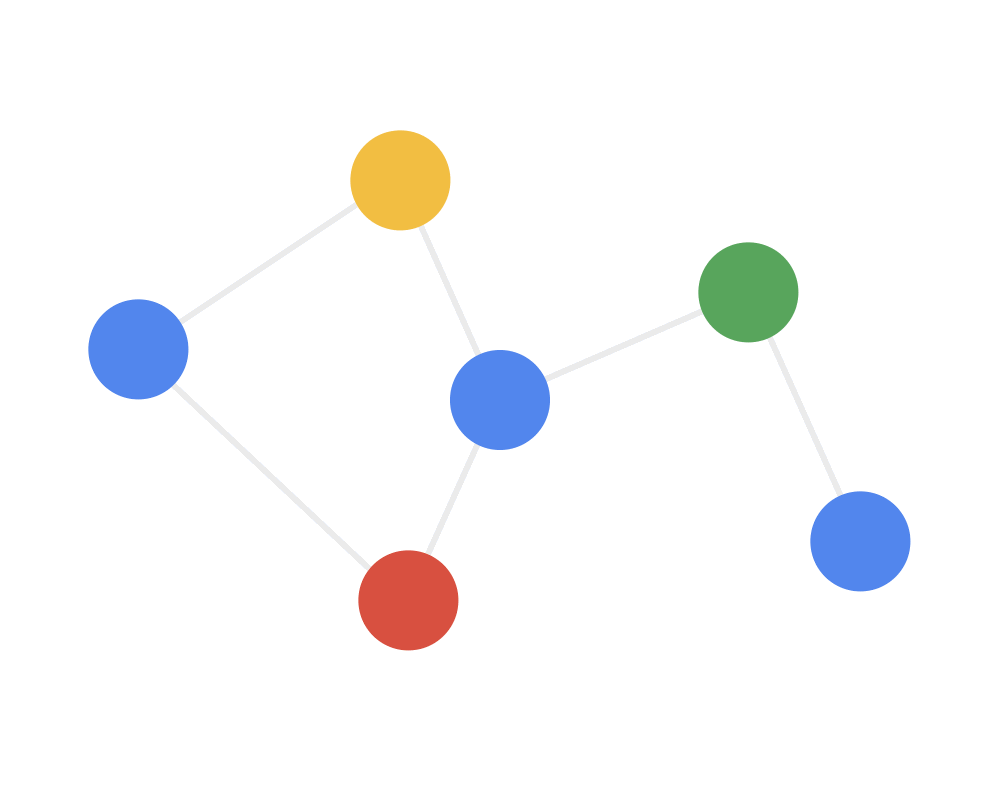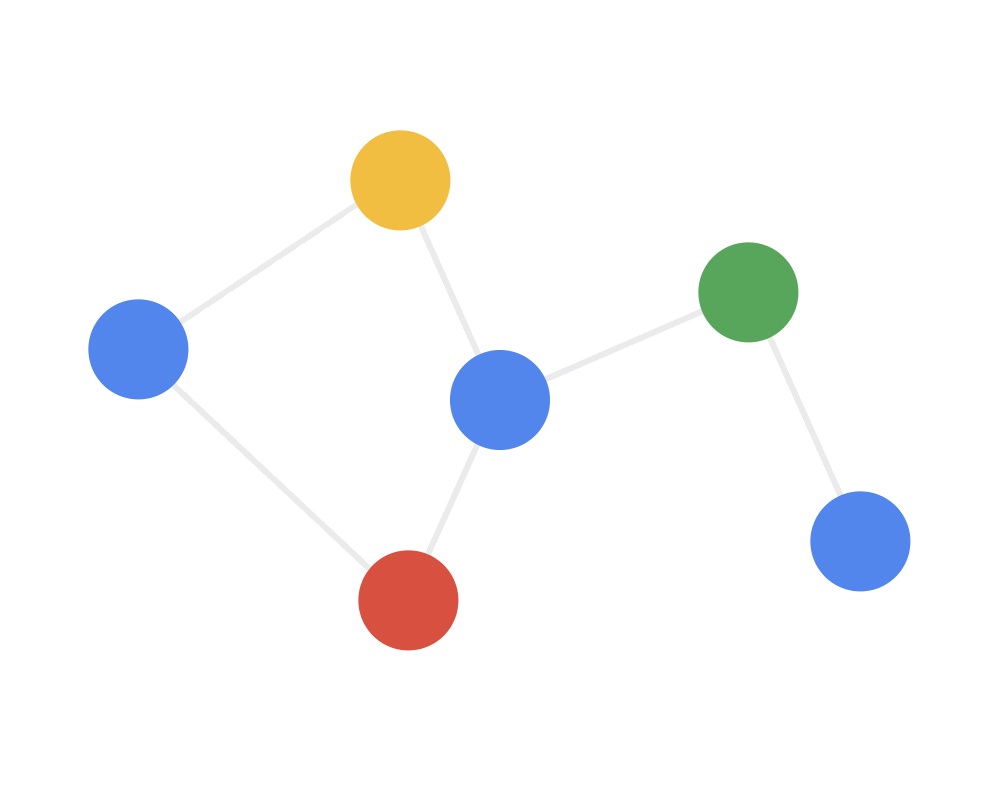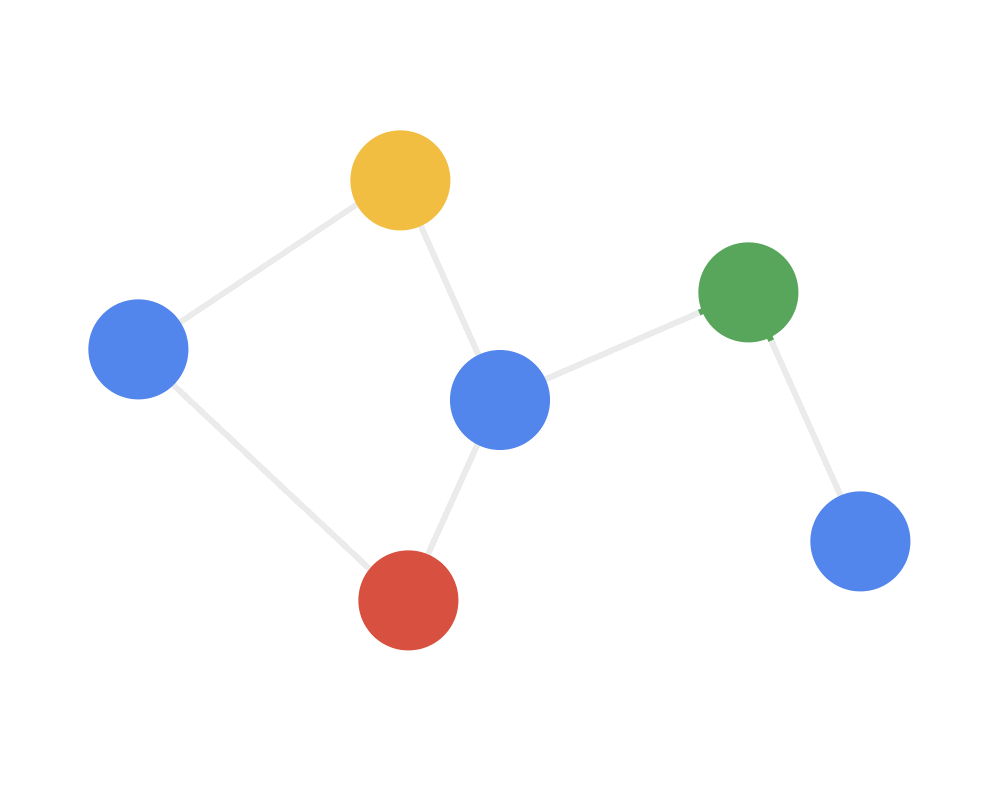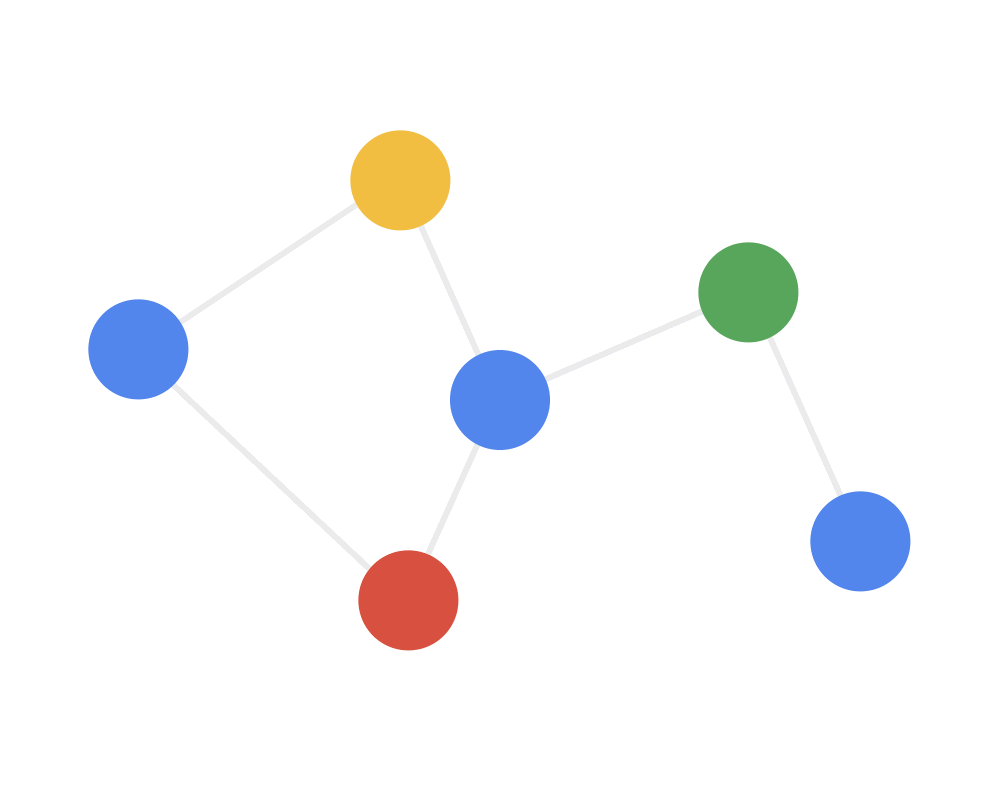 Step 1 SEND
Step 1 SEND
第二步:接收(receive)每个节点将邻居节点的特征信息聚集起来。这一步是在对节点的局部结构信息进行融合。
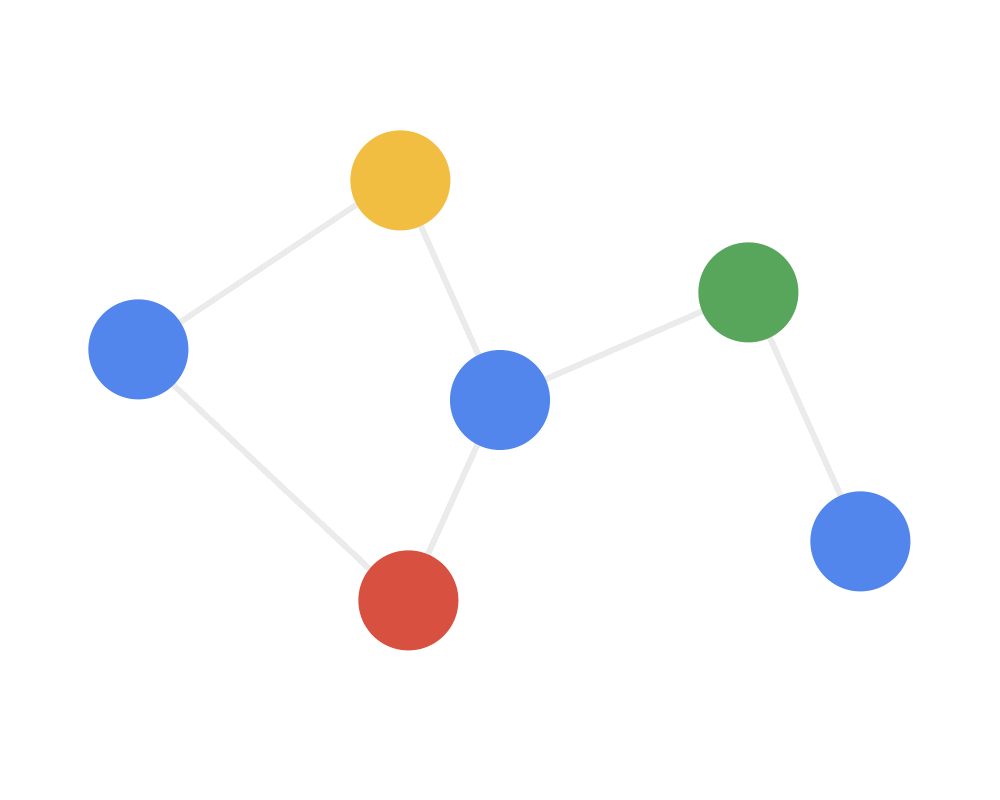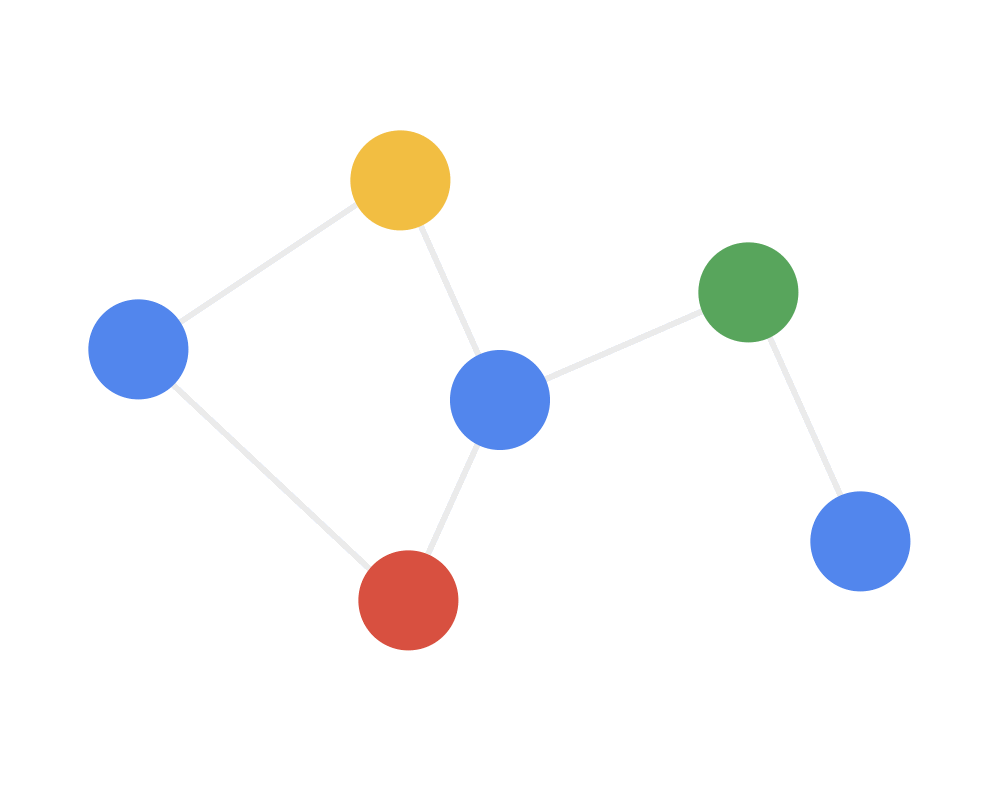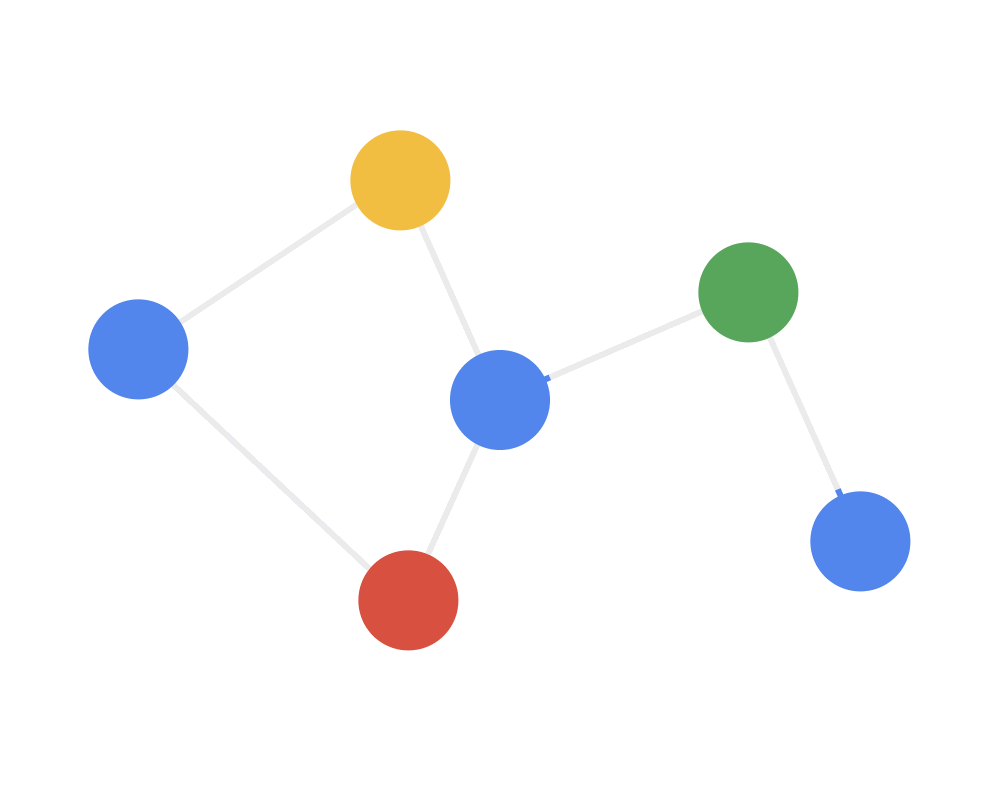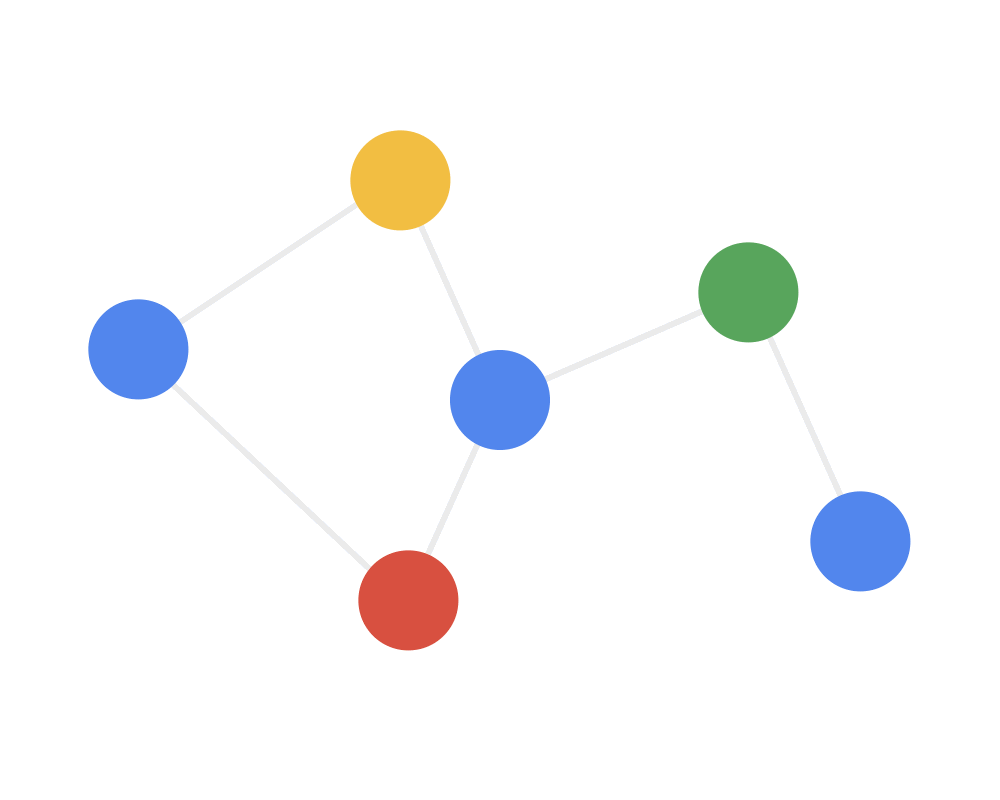 Step 2 RECEIVE
Step 2 RECEIVE
第三步:变换(transform)把前面的信息聚集之后做非线性变换,增加模型的表达能力。
 Step 3 TRANSFORM
Step 3 TRANSFORM
Reference: 浅析图卷积神经网络
上面给出的是图卷积算子的计算公式,设中心节点为,是节点在第层的特征表达,是归一化因子,如取节点度的倒数,是节点的邻节点,包含自身,是节点的类型,表示类型节点的变换权重参数,表示激活函数。
Applications and Open-Source Implementations 应用和开源实现
According to problems in the field of neuro-informatics, the application of graph neural network in which is mainly graph classification, namely after the construction of brain function network and features are added in the corresponding nodes, using GCN to learn the high-level features of brain networks, using full connection layer to extract vectorized features or directly using global average pooling (GAP) to output the class confidence, which can be gender (e.g. Graph Saliency Maps through Spectral Convolutional Networks: Application to Sex Classification with Brain Connectivity) or disease group. Currently open source deep learning frameworks based on graph mostly focus link classification and node classification, support for Graph Classification is relatively lacked, and pytorch_geometric is a Deep Learning framework supporting multiple GNN applications, including the support of this article, An End - to - End Deep Learning Architecture for Graph Classification, which makes it qualified to perform graph convolution operations and output feature vectors ready for learning and classification.
根据笔者所处研究领域的痛点,目前图神经网络在其中的应用主要为图分类,即在构建脑功能网络并在相应节点添加特征后,使用GCN对脑网络进行高层特征学习,使用全连接层提取向量化的特征或直接使用全局平均池化(GAP)输出类别置信度,这一类别可为性别(如: Graph Saliency Maps through Spectral Convolutional Networks: Application to Sex Classification with Brain Connectivity),亦可为疾病。目前基于图的深度学习开源框架大多注重边分类和节点分类,对图分类的支持相对较少,而pytorch_geometric是一个支持多种图深度学习应用的框架,其中对An End-to-End Deep Learning Architecture for Graph Classification这篇文章的支持使其能够胜任图卷积操作并输出特征向量这一工作,以便之后对该特征进行学习和分类。
- Graph Saliency Maps provides the implementation of an activation-based visual attribution method for irregular graphs, which works integrated with graph convolutional neural networks (GCNs). The method has been validated via a sex classification task using functional brain connectivity networks (paper);
- SGCN is a Siamese Graph Convolution Network for learning multi-view brain network embedding;
- pytorch_geometric is a geometric deep learning extension library for PyTorch. It consists of various methods for deep learning on graphs and other irregular structures, also known as geometric deep learning, from a variety of published papers. In addition, it consists of an easy-to-use mini-batch loader for many small and single giant graphs, multi gpu-support, a large number of common benchmark datasets (based on simple interfaces to create your own), and helpful transforms, both for learning on arbitrary graphs as well as on 3D meshes or point clouds;
References 参考文献
- [1] 从数据结构到算法:图网络方法初探
- [2] 深度学习时代的图模型,清华发文综述图网络
- [3] 图神经网络概述第三弹:来自IEEE Fellow的GNN综述 (原文: A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks)
- [4] 浅析图卷积神经网络
- [5] An End-to-End Deep Learning Architecture for Graph Classification (AAAI 2018)
- [6] Graph Saliency Maps through Spectral Convolutional Networks: Application to Sex Classification with Brain Connectivity (MICCAI 2018)
- [7] Global average pooling (GAP)
- [8] CAM(Class Activation Mapping)通俗篇