一篇文章带你实现栈的接口
一,什么是栈
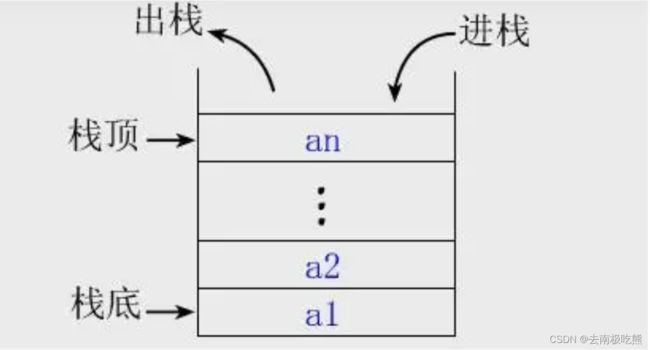
栈(Stacks)是限定在一端插入和删除的线性表。允许插入和删除的一端称为栈顶(Top),另一端称为栈底(Bottom)。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出(Last In First Out)的原则。因此,栈又称为后进先出(先进后出)线性表。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈、压栈、入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
如图所示:
二,栈的实现
栈的实现一般有两种存储方法,顺序栈(数组)和链栈(链表)。
这里我们采用顺序栈。
2.1,栈的结构
这里采用支持动态增长的栈,用a来指向空间中对应数组的地址。用top来表示栈顶,用capcity表示容量,到后面容量不够扩容用。
typedef int SDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
SDataType* a;//数组存储数据
int top;//栈顶
int capcity;//容量
}ST;2.2,栈的接口
void STInit(ST* p);//栈的初始化
void STPush(ST* p, SDataType x);//压栈
bool STEmpty(ST* p);//判断数据是否为空
void STPop(ST* p);//出栈
SDataType STTop(ST* p); //取栈顶数据
void STDestroy(ST* p);//栈的销毁
int STSize(ST* p);//栈的大小三,接口的实现。
3.1,栈的初始化
这里先申请一个4个字节的空间。容量为4。top可以是0,也可以是1。
void STInit(ST* p)//栈的初始化
{
assert(p);
p->a = (SDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SDataType)*4);
p->top = -1;//top = 0 时是栈顶的下一个位置。top =-1 是栈顶的位置。
p->capcity = 4;
}3.2,栈的插入(压栈)
这里插入数据前判断一下容量是否充足,如果不足,就用realloc扩容成原来容量的2倍。最后将x插入到栈顶中。注意:p->top++;//这里加加后,访问栈顶的元素直接可以用a[p->top]
void STPush(ST* p, SDataType x)//压栈
{
assert(p);
if (p->capcity == p->top + 1)
{
SDataType* tmp = (SDataType*)realloc(p->a, sizeof(SDataType) * p->capcity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
}
p->a = tmp;
p->capcity *= 2;
}
p->a[p->top + 1] = x;
p->top++;//这里加加后,访问栈顶的元素直接可以用a[p->top]
}3.3,出栈
这里在top减一之前需要判断一下栈是否为空的情况。
void STPop(ST* p)//出栈
{
assert(p);
assert(!STEmpty(p));//判断是否为空
p->top--;
}栈为空的实现
这里bool(布尔值)的头文件为:stdbool.h,如果为空返回1,不为空等号不成立,返回0;
bool STEmpty(ST* p)
{
assert(p);
return p->top + 1 == 0;
}3.4,获取栈顶元素
这里还是判断一下是否为空,然后返回栈顶元素。
SDataType STTop(ST* p) //取栈顶数据
{
assert(p);
assert(!STEmpty(p));
return p->a[p->top];
}3.5,栈的大小
这里判断完非空后,直接返回top+1(看完上面的压栈程序中,这里可以把top理解成数组下标,加一是总大小)。
int STSize(ST* p)//栈的大小
{
assert(p);
assert(!STEmpty(p));
return p->top + 1;
}3.6,栈的销毁
把申请的空间释放,再置为空。其余赋值为0;
void STDestroy(ST* p)//栈的销毁
{
assert(p);
free(p->a);
p->a = NULL;
p->capcity = 0;
p->top = 0;
}四,总代码
//test.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef int SDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
SDataType* a;//数组存储数据
int top;//栈顶
int capcity;//容量
}ST;
void STInit(ST* p);//栈的初始化
void STPush(ST* p, SDataType x);//压栈
bool STEmpty(ST* p);//判断数据是否为空
void STPop(ST* p);//出栈
SDataType STTop(ST* p); //取栈顶数据
void STDestroy(ST* p);//栈的销毁
int STSize(ST* p);//栈的大小
//stack.c接口的实现
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"test.h"
void STInit(ST* p)//栈的初始化
{
assert(p);
p->a = (SDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SDataType)*4);
p->top = -1;//top = 0 时是栈顶的下一个位置。top =-1 是栈顶的位置。
p->capcity = 4;
}
void STPush(ST* p, SDataType x)//压栈
{
assert(p);
if (p->capcity == p->top + 1)
{
SDataType* tmp = (SDataType*)realloc(p->a, sizeof(SDataType) * p->capcity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
}
p->a = tmp;
p->capcity *= 2;
}
p->a[p->top + 1] = x;
p->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* p)//出栈
{
assert(p);
assert(!STEmpty(p));
p->top--;
}
SDataType STTop(ST* p) //取栈顶数据
{
assert(p);
assert(!STEmpty(p));
return p->a[p->top];
}
void STDestroy(ST* p)//栈的销毁
{
assert(p);
free(p->a);
p->a = NULL;
p->capcity = 0;
p->top = 0;
}
int STSize(ST* p)//栈的大小
{
assert(p);
assert(!STEmpty(p));
return p->top + 1;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* p)
{
assert(p);
return p->top + 1 == 0;
}
//test.c接口的测试
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"test.h"
int main()//测试
{
ST s;
STInit(&s);
STPush(&s, 0);
printf("%d\n", STTop(&s));
STPush(&s, 1);
printf("%d\n", STTop(&s));
STPush(&s, 2);
printf("%d\n", STTop(&s));
STPush(&s, 3);
printf("%d\n", STTop(&s));
STPop(&s);
STPop(&s);
printf("%d\n", STTop(&s));
printf("%d\n", STSize(&s));
return 0;
} 好了,到这里就该结束了。希望对大家有所帮助!