- 基于社交网络算法优化的二维最大熵图像分割
智能算法研学社(Jack旭)
智能优化算法应用图像分割算法php开发语言
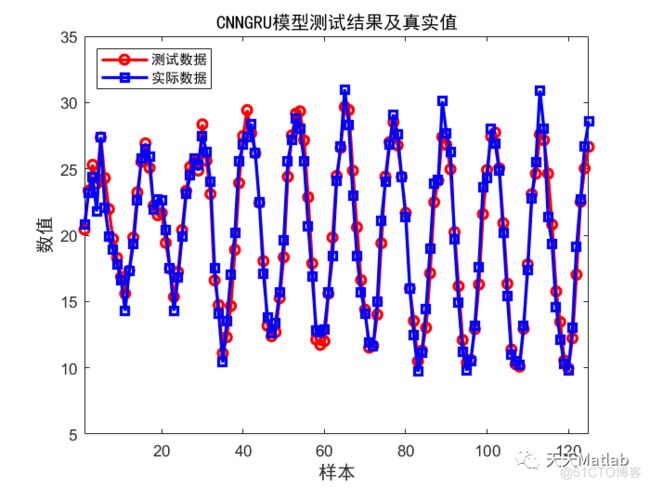
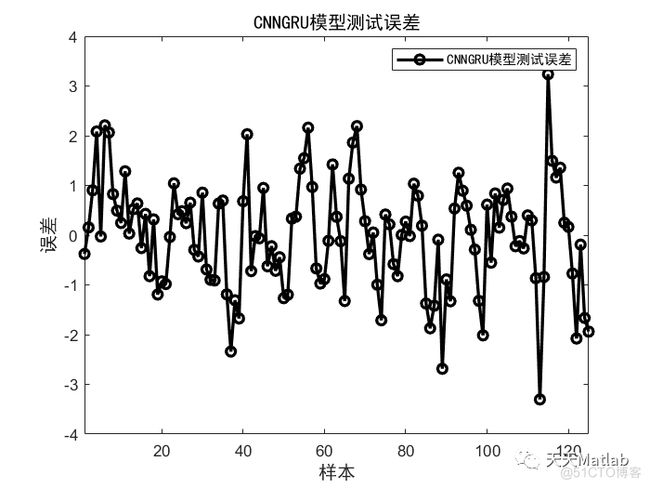
智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码文章目录智能优化算法应用:基于社交网络优化的二维最大熵图像阈值分割-附代码1.前言2.二维最大熵阈值分割原理3.基于社交网络优化的多阈值分割4.算法结果:5.参考文献:6.Matlab代码摘要:本文介绍基于最大熵的图像分割,并且应用社交网络算法进行阈值寻优。1.前言阅读此文章前,请阅读《图像分割:直方图区域划分及信息统计介绍》htt
- 高端密码学院笔记285
柚子_b4b4
高端幸福密码学院(高级班)幸福使者:李华第(598)期《幸福》之回归内在深层生命原动力基础篇——揭秘“激励”成长的喜悦心理案例分析主讲:刘莉一,知识扩充:成功=艰苦劳动+正确方法+少说空话。贪图省力的船夫,目标永远下游。智者的梦再美,也不如愚人实干的脚印。幸福早课堂2020.10.16星期五一笔记:1,重视和珍惜的前提是知道它的价值非常重要,当你珍惜了,你就真正定下来,真正的学到身上。2,大家需要
- 【华为OD技术面试真题 - 技术面】- python八股文真题题库(1)
算法大师
华为od面试python
华为OD面试真题精选专栏:华为OD面试真题精选目录:2024华为OD面试手撕代码真题目录以及八股文真题目录文章目录华为OD面试真题精选1.数据预处理流程数据预处理的主要步骤工具和库2.介绍线性回归、逻辑回归模型线性回归(LinearRegression)模型形式:关键点:逻辑回归(LogisticRegression)模型形式:关键点:参数估计与评估:3.python浅拷贝及深拷贝浅拷贝(Shal
- Python实现简单的机器学习算法
master_chenchengg
pythonpython办公效率python开发IT
Python实现简单的机器学习算法开篇:初探机器学习的奇妙之旅搭建环境:一切从安装开始必备工具箱第一步:安装Anaconda和JupyterNotebook小贴士:如何配置Python环境变量算法初体验:从零开始的Python机器学习线性回归:让数据说话数据准备:从哪里找数据编码实战:Python实现线性回归模型评估:如何判断模型好坏逻辑回归:从分类开始理论入门:什么是逻辑回归代码实现:使用skl
- matlab mle 优化,MLE+: Matlab Toolbox for Integrated Modeling, Control and Optimization for Buildings...
Simon Zhong
matlabmle优化
摘要:FollowingunilateralopticnervesectioninadultPVGhoodedrat,theaxonguidancecueephrin-A2isup-regulatedincaudalbutnotrostralsuperiorcolliculus(SC)andtheEphA5receptorisdown-regulatedinaxotomisedretinalgan
- 如何用matlab灵活控制feko的求解
NingrLi
matlab开发语言
https://bbs.rfeda.cn/read.php?tid=3778Feko中的模型和求解设置等都可以通过editfeko进行设置,其文件存储为.pre文件,该文件可以用文本打开,因此,我们可以通过VB、VC、matlab等工具对.pre文件进行读写操作,以达到更灵活的使用feko。同样,对于.out文件,我们也可以进行读操作。熟练使用对.pre文件和.out文件的操作后,我们可以方便的计
- matlab delsat = setdiff(1:69,unique(Eph(30,:))); 语句含义
黄卷青灯77
matlab开发语言setdiff
这行MATLAB代码用于计算在范围1:69中不包含在Eph矩阵第30行的唯一值集合中的所有元素。具体解释如下:delsat=setdiff(1:69,unique(Eph(30,:)));解释Eph(30,:)Eph(30,:)提取矩阵Eph的第30行的所有列元素。这是一个行向量,包含了第30行的所有值。unique(Eph(30,:))unique函数返回Eph(30,:)中的唯一元素。这意味着
- 100天持续行动—Day01
Richard_DL
今天开始站着学习,发现效率大幅提升。把fast.ai的Lesson1的后半部分和Lesson2看完了。由于Keras版本和视频中的不一致,运行notebook时经常出现莫名其妙的错误,导致自己只动手实践了视频中的一小部分内容。为了赶时间,我打算先把与CNN相关的视频过一遍。然后尽快开始做自己的项目。明天继续加油,争取把Lesson3和Lesson4看完。
- yolov5>onnx>ncnn>apk
图像处理大大大大大牛啊
opencv实战代码讲解yoloonnxncnn安卓
一.yolov5pt模型转onnx条件:colabnotebookyolov51.安装环境!pipinstallonnx>=1.7.0#forONNXexport!pipinstallcoremltools==4.0#forCoreMLexport!pipinstallonnx-simplifier2.修改common.py在classFocus下面
- [实践应用] 深度学习之模型性能评估指标
YuanDaima2048
深度学习工具使用深度学习人工智能损失函数性能评估pytorchpython机器学习
文章总览:YuanDaiMa2048博客文章总览深度学习之模型性能评估指标分类任务回归任务排序任务聚类任务生成任务其他介绍在机器学习和深度学习领域,评估模型性能是一项至关重要的任务。不同的学习任务需要不同的性能指标来衡量模型的有效性。以下是对一些常见任务及其相应的性能评估指标的详细解释和总结。分类任务分类任务是指模型需要将输入数据分配到预定义的类别或标签中。以下是分类任务中常用的性能指标:准确率(
- 做事一定要认真
地上的垚
大脑突然被惊醒,我猛然起身,接着发了下呆,灵魂回归后意识到:啊,今天上班要迟到了!我按了按手机发现手机已关机,略微一看,原来是昨晚充电器没插上。一件微不足道的事折射出我的粗心大意,反映了我对待事情漠不关心,草草了事的态度。许许多多的事情都需要认认真真的对待才能做好,认真是自我努力的表现。工作中,我总是不停的犯错误,我谴责自己:连这点小事都要犯错,你有什么用啊。同时也安慰自己:不过是一点小错误而已,
- 计算机视觉中,Pooling的作用
Wils0nEdwards
计算机视觉人工智能
在计算机视觉中,Pooling(池化)是一种常见的操作,主要用于卷积神经网络(CNN)中。它通过对特征图进行下采样,减少数据的空间维度,同时保留重要的特征信息。Pooling的作用可以归纳为以下几个方面:1.降低计算复杂度与内存需求Pooling操作通过对特征图进行下采样,减少了特征图的空间分辨率(例如,高度和宽度)。这意味着网络需要处理的数据量会减少,从而降低了计算量和内存需求。这对大型神经网络
- 神经网络-损失函数
红米煮粥
神经网络人工智能深度学习
文章目录一、回归问题的损失函数1.均方误差(MeanSquaredError,MSE)2.平均绝对误差(MeanAbsoluteError,MAE)二、分类问题的损失函数1.0-1损失函数(Zero-OneLossFunction)2.交叉熵损失(Cross-EntropyLoss)3.合页损失(HingeLoss)三、总结在神经网络中,损失函数(LossFunction)扮演着至关重要的角色,它
- 无人值守模式,自习室创业,真的那么赚钱吗?
森屿旅人
“创业是一条不归路,不要拿自己亏不起的钱当赌注!”在和大家分享无人自习室创业经历前,先和大家强调上面这一句话,创过业的朋友,应该深有体会。因为,我们要深刻的认知市场规律,一个行业,如果利润很高,那必然趋之若鹜得涌入,所以在市场充分博弈以后,市场会回归价值本身,这个是市场的客观规律。因此,不要抓风口,抓风口,说实在的,和赌博无异,那些和你鼓吹风口的人,永远是把你当成一根韭菜,诚然,真正赚钱的项目,不
- 损失函数与反向传播
Star_.
PyTorchpytorch深度学习python
损失函数定义与作用损失函数(lossfunction)在深度学习领域是用来计算搭建模型预测的输出值和真实值之间的误差。1.损失函数越小越好2.计算实际输出与目标之间的差距3.为更新输出提供依据(反向传播)常见的损失函数回归常见的损失函数有:均方差(MeanSquaredError,MSE)、平均绝对误差(MeanAbsoluteErrorLoss,MAE)、HuberLoss是一种将MSE与MAE
- 七.正则化
愿风去了
吴恩达机器学习之正则化(Regularization)http://www.cnblogs.com/jianxinzhou/p/4083921.html从数学公式上理解L1和L2https://blog.csdn.net/b876144622/article/details/81276818虽然在线性回归中加入基函数会使模型更加灵活,但是很容易引起数据的过拟合。例如将数据投影到30维的基函数上,模
- 探索创新科技: Lite-Mono - 简约高效的小型化Mono框架
杭律沛Meris
探索创新科技:Lite-Mono-简约高效的小型化Mono框架Lite-Mono[CVPR2023]Lite-Mono:ALightweightCNNandTransformerArchitectureforSelf-SupervisedMonocularDepthEstimation项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/li/Lite-Mono如果你在寻找一个轻
- Github 2024-09-12 Go开源项目日报Top10
老孙正经胡说
githubgolang开源Github趋势分析开源项目PythonGolang
根据GithubTrendings的统计,今日(2024-09-12统计)共有10个项目上榜。根据开发语言中项目的数量,汇总情况如下:开发语言项目数量Go项目10C项目1Terraform:基础设施即代码的开源工具创建周期:3626天开发语言:Go协议类型:OtherStar数量:40393个Fork数量:9397次关注人数:40393人贡献人数:358人OpenIssues数量:1943个Git
- matlab设置图像窗口大小,matlab 图形窗口大小的设置
weixin_39534002
matlab设置图像窗口大小
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%常用选项和小技巧%%%%%%画等值线[cchh]=contour(peaks(30),'LINESPEC','b-')clabel(cc,hh,'manual')%写文本text(5,10,'\bfmath\slmath\itmath\rmmath\alpha','color',[0.10.10.9],'fonts
- Matlab在工业机器人中的运用,基于MATLAB的工业机器人建模与仿真.docx
weixin_34518801
摘要:机器人运动系统作为机器人系统中最重要的组成部分之一,其重要性不言而喻,因为它影响着机器人的主要性能,因此为了提高机器人的质量,对机器人进行运动学分析和仿真是不可或缺的。本次毕业设计主要对KUKA机器人的三维仿真进行了一系列的分析,主要是以下几个内容:(1)研究了机器人运动学仿真的背景意义及发展趋势。(2)通过对齐次坐标变换理论的研究,说明了KUKA机器人结构及参数,并且建立了相应的D-H参数
- matlab游标标注移动,matlab实现图形窗口的数据游标
莫白想
matlab游标标注移动
DatacursorsforfigurewindowSeveralrelatedfunctions:CreateCursorsetsupaverticalcursoronallaxesinafigure.Thecursorscanbemovedaroundusingthemouse.MultiplecursorsaresupportedineachfigureGetCursorLocationre
- 只生欢喜不生愁
花间星事
《只生欢喜不生愁》是我很喜欢的一本书,挺适合当下的环境阅读。作者林曦老师是位水墨画家,设计师。她1983年生于重庆,毕业于中央美术学院,年少成名,以手艺人自居。在她的这本艺术生活随笔集里,用自己的切身实践解析艺术美育的本质内涵。分享了艺术学习,写字的乐趣,专注心力的法门与修炼,用中式文人的视角观照当代生活的审美情趣及路径,讨论艺术之道与无用之美,让传统美学回归到现实生活践行中。林曦少年时办过不少画
- MATLAB语言基础教程、 小项目1:简单的计算器、 小项目2:有页面的计算器、使用App Designer创建GUI计算器
azuredragonz
学习教程matlab开发语言
MATLABMATLAB语言基础教程1.MATLAB简介2.基本语法变量与赋值向量与矩阵矩阵运算数学函数控制流3.函数4.绘图案例:简单方程求解小项目1:简单的科学计算器功能代码项目说明小项目2:有页面的计算器使用AppDesigner创建GUI计算器主要步骤:完整代码(使用MATLAB编写)说明:如何运行:小项目总结MATLAB语言基础教程1.MATLAB简介MATLAB(矩阵实验室)是一种用于
- MATLAB在无线通信系统测试和验证中的应用
2401_85812053
matlab开发语言
在无线通信系统的开发过程中,测试和验证是确保系统性能满足设计要求的关键步骤。MATLAB提供了一系列的工具和功能,这些工具在无线通信系统的测试和验证中发挥着重要作用。本文将详细介绍MATLAB在无线通信系统测试和验证中的应用,包括信道建模、调制解调、射频(RF)链路分析以及硬件验证等方面。1.信道建模信道建模是无线通信系统设计中的关键环节,它影响着信号的传输质量和系统的整体性能。MATLAB提供了
- MATLAB中的函数编写有哪些最佳实践
2401_85812053
matlab算法人工智能
在MATLAB中,函数是执行特定任务的代码块,可以通过自定义函数来提高代码的可重用性和模块化。以下是一些关于MATLAB函数编写的最佳实践:函数结构和语法:MATLAB函数由函数名、参数列表和函数体组成。函数名必须以字母开头,后面可以跟字母、数字或下划线。参数列表包含函数接收的输入变量,用逗号分隔。函数体包含要执行的代码。functiony=my_function(x)%函数体y=x^2;end参
- Python和R均方根误差平均绝对误差算法模型
亚图跨际
Python交叉知识R回归模型误差指标归一化均方根误差生态状态指标神经网络成本误差气体排放气候模型多项式拟合
要点回归模型误差评估指标归一化均方根误差生态状态指标神经网络成本误差计算气体排放气候算法模型Python误差指标均方根误差和平均绝对误差均方根偏差或均方根误差是两个密切相关且经常使用的度量值之一,用于衡量真实值或预测值与观测值或估计值之间的差异。估计器θ^\hat{\theta}θ^相对于估计参数θ\thetaθ的RMSD定义为均方误差的平方根:RMSD(θ^)=MSE(θ^)=E((θ^−θ
- Python和MATLAB及C++信噪比导图(算法模型)
亚图跨际
算法交叉知识Python视频图像修复模数转换信号链噪音频谱计算量化周期性视觉刺激高斯噪声的矩形脉冲心率失常检测算法
要点视频图像修复模数转换中混合信号链噪音测量频谱计算和量化周期性视觉刺激脑电图高斯噪声的矩形脉冲总谐波失真周期图功率谱密度各种心率失常检测算法胶体悬浮液跟踪检测计算交通监控摄像头图像噪音计算Python信噪比信噪比是科学和工程中使用的一种测量方法,用于比较所需信号水平与背景噪声水平。信噪比定义为信号功率与噪声功率之比,通常以分贝表示。高于1:1(大于0dB)的比率表示信号大于噪声。信噪比是影响处理
- Python(PyTorch)和MATLAB及Rust和C++结构相似度指数测量导图
亚图跨际
Python交叉知识算法量化检查图像压缩质量低分辨率多光谱峰值信噪比端到端优化图像压缩手术机器人三维实景实时可微分渲染重建三维可视化
要点量化检查图像压缩质量低分辨率多光谱和高分辨率图像实现超分辨率分析图像质量图像索引/多尺度结构相似度指数和光谱角映射器及视觉信息保真度多种指标峰值信噪比和结构相似度指数测量结构相似性图像分类PNG和JPEG图像相似性近似算法图像压缩,视频压缩、端到端优化图像压缩、神经图像压缩、GPU变速图像压缩手术机器人深度估计算法重建三维可视化推理图像超分辨率算法模型三维实景实时可微分渲染算法MATLAB结构
- 数据仓库介绍
阿龙的代码在报错
数据分析数据仓库数据库
数据仓库数据仓库的概念数据仓库的主要特征数据仓库的主流开发语言-sql结构化数据sql语句数据仓库的概念数据仓库(英语:DataWarehouse,简称数仓、DW),是一个用于存储、分析、报告的数据系统。数据仓库的目的是构建面向分析的集成化数据环境,分析结果为企业提供决策支持(DecisionSupport)。就是数据仓库只分析数据并不产生数据数据仓库的主要特征1、面向主题主题是一个抽象的概念,是
- 外卖霸王餐返利外卖会员卡小程序开发
闹小艾
good506070微信小程序小程序
外卖霸王餐返利外卖会员卡小程序开发"社交电商赋能下的外卖返利小程序"是专为商家与用户双赢而设计的创新平台。以下是其开发方案的详细步骤:一、需求梳理:首先,我们需要明确小程序的核心功能和特色。包括设定活动类型、返利策略,以及用户体验友好的界面设计。二、技术决策:技术选型是关键。我们采用小程序的开发框架,利用JavaScript作为前端开发语言,并结合微信提供的API进行后端接口调用与数据处理。三、账
- apache ftpserver-CentOS config
gengzg
apache
<server xmlns="http://mina.apache.org/ftpserver/spring/v1"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://mina.apache.o
- 优化MySQL数据库性能的八种方法
AILIKES
sqlmysql
1、选取最适用的字段属性 MySQL可以很好的支持大数据量的存取,但是一般说来,数据库中的表越小,在它上面执行的查询也就会越快。因此,在创建表的时候,为了获得更好的 性能,我们可以将表中字段的宽度设得尽可能小。例如,在定义邮政编码这个字段时,如果将其设置为CHAR(255),显然给数据库增加了不必要的空间,甚至使用VARCHAR这种类型也是多余的,因为CHAR(6)就可以很
- JeeSite 企业信息化快速开发平台
Kai_Ge
JeeSite
JeeSite 企业信息化快速开发平台
平台简介
JeeSite是基于多个优秀的开源项目,高度整合封装而成的高效,高性能,强安全性的开源Java EE快速开发平台。
JeeSite本身是以Spring Framework为核心容器,Spring MVC为模型视图控制器,MyBatis为数据访问层, Apache Shiro为权限授权层,Ehcahe对常用数据进行缓存,Activit为工作流
- 通过Spring Mail Api发送邮件
120153216
邮件main
原文地址:http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1346857871615.html
使用Java Mail API来发送邮件也很容易实现,但是最近公司一个同事封装的邮件API实在让我无法接受,于是便打算改用Spring Mail API来发送邮件,顺便记录下这篇文章。 【Spring Mail API】
Spring Mail API都在org.spri
- Pysvn 程序员使用指南
2002wmj
SVN
源文件:http://ju.outofmemory.cn/entry/35762
这是一篇关于pysvn模块的指南.
完整和详细的API请参考 http://pysvn.tigris.org/docs/pysvn_prog_ref.html.
pysvn是操作Subversion版本控制的Python接口模块. 这个API接口可以管理一个工作副本, 查询档案库, 和同步两个.
该
- 在SQLSERVER中查找被阻塞和正在被阻塞的SQL
357029540
SQL Server
SELECT R.session_id AS BlockedSessionID ,
S.session_id AS BlockingSessionID ,
Q1.text AS Block
- Intent 常用的用法备忘
7454103
.netandroidGoogleBlogF#
Intent
应该算是Android中特有的东西。你可以在Intent中指定程序 要执行的动作(比如:view,edit,dial),以及程序执行到该动作时所需要的资料 。都指定好后,只要调用startActivity(),Android系统 会自动寻找最符合你指定要求的应用 程序,并执行该程序。
下面列出几种Intent 的用法
显示网页:
- Spring定时器时间配置
adminjun
spring时间配置定时器
红圈中的值由6个数字组成,中间用空格分隔。第一个数字表示定时任务执行时间的秒,第二个数字表示分钟,第三个数字表示小时,后面三个数字表示日,月,年,< xmlnamespace prefix ="o" ns ="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" />
测试的时候,由于是每天定时执行,所以后面三个数
- POJ 2421 Constructing Roads 最小生成树
aijuans
最小生成树
来源:http://poj.org/problem?id=2421
题意:还是给你n个点,然后求最小生成树。特殊之处在于有一些点之间已经连上了边。
思路:对于已经有边的点,特殊标记一下,加边的时候把这些边的权值赋值为0即可。这样就可以既保证这些边一定存在,又保证了所求的结果正确。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
- 重构笔记——提取方法(Extract Method)
ayaoxinchao
java重构提炼函数局部变量提取方法
提取方法(Extract Method)是最常用的重构手法之一。当看到一个方法过长或者方法很难让人理解其意图的时候,这时候就可以用提取方法这种重构手法。
下面是我学习这个重构手法的笔记:
提取方法看起来好像仅仅是将被提取方法中的一段代码,放到目标方法中。其实,当方法足够复杂的时候,提取方法也会变得复杂。当然,如果提取方法这种重构手法无法进行时,就可能需要选择其他
- 为UILabel添加点击事件
bewithme
UILabel
默认情况下UILabel是不支持点击事件的,网上查了查居然没有一个是完整的答案,现在我提供一个完整的代码。
UILabel *l = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(60, 0, listV.frame.size.width - 60, listV.frame.size.height)]
- NoSQL数据库之Redis数据库管理(PHP-REDIS实例)
bijian1013
redis数据库NoSQL
一.redis.php
<?php
//实例化
$redis = new Redis();
//连接服务器
$redis->connect("localhost");
//授权
$redis->auth("lamplijie");
//相关操
- SecureCRT使用备注
bingyingao
secureCRT每页行数
SecureCRT日志和卷屏行数设置
一、使用securecrt时,设置自动日志记录功能。
1、在C:\Program Files\SecureCRT\下新建一个文件夹(也就是你的CRT可执行文件的路径),命名为Logs;
2、点击Options -> Global Options -> Default Session -> Edite Default Sett
- 【Scala九】Scala核心三:泛型
bit1129
scala
泛型类
package spark.examples.scala.generics
class GenericClass[K, V](val k: K, val v: V) {
def print() {
println(k + "," + v)
}
}
object GenericClass {
def main(args: Arr
- 素数与音乐
bookjovi
素数数学haskell
由于一直在看haskell,不可避免的接触到了很多数学知识,其中数论最多,如素数,斐波那契数列等,很多在学生时代无法理解的数学现在似乎也能领悟到那么一点。
闲暇之余,从图书馆找了<<The music of primes>>和<<世界数学通史>>读了几遍。其中素数的音乐这本书与软件界熟知的&l
- Java-Collections Framework学习与总结-IdentityHashMap
BrokenDreams
Collections
这篇总结一下java.util.IdentityHashMap。从类名上可以猜到,这个类本质应该还是一个散列表,只是前面有Identity修饰,是一种特殊的HashMap。
简单的说,IdentityHashMap和HashM
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-享元模式-Flyweight
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java
- PS人像润饰&调色教程集锦
cherishLC
PS
1、仿制图章沿轮廓润饰——柔化图像,凸显轮廓
http://www.howzhi.com/course/retouching/
新建一个透明图层,使用仿制图章不断Alt+鼠标左键选点,设置透明度为21%,大小为修饰区域的1/3左右(比如胳膊宽度的1/3),再沿纹理方向(比如胳膊方向)进行修饰。
所有修饰完成后,对该润饰图层添加噪声,噪声大小应该和
- 更新多个字段的UPDATE语句
crabdave
update
更新多个字段的UPDATE语句
update tableA a
set (a.v1, a.v2, a.v3, a.v4) = --使用括号确定更新的字段范围
- hive实例讲解实现in和not in子句
daizj
hivenot inin
本文转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ggjucheng/archive/2013/01/03/2842855.html
当前hive不支持 in或not in 中包含查询子句的语法,所以只能通过left join实现。
假设有一个登陆表login(当天登陆记录,只有一个uid),和一个用户注册表regusers(当天注册用户,字段只有一个uid),这两个表都包含
- 一道24点的10+种非人类解法(2,3,10,10)
dsjt
算法
这是人类算24点的方法?!!!
事件缘由:今天晚上突然看到一条24点状态,当时惊为天人,这NM叫人啊?以下是那条状态
朱明西 : 24点,算2 3 10 10,我LX炮狗等面对四张牌痛不欲生,结果跑跑同学扫了一眼说,算出来了,2的10次方减10的3次方。。我草这是人类的算24点啊。。
然后么。。。我就在深夜很得瑟的问室友求室友算
刚出完题,文哥的暴走之旅开始了
5秒后
- 关于YII的菜单插件 CMenu和面包末breadcrumbs路径管理插件的一些使用问题
dcj3sjt126com
yiiframework
在使用 YIi的路径管理工具时,发现了一个问题。 <?php
- 对象与关系之间的矛盾:“阻抗失配”效应[转]
come_for_dream
对象
概述
“阻抗失配”这一词组通常用来描述面向对象应用向传统的关系数据库(RDBMS)存放数据时所遇到的数据表述不一致问题。C++程序员已经被这个问题困扰了好多年,而现在的Java程序员和其它面向对象开发人员也对这个问题深感头痛。
“阻抗失配”产生的原因是因为对象模型与关系模型之间缺乏固有的亲合力。“阻抗失配”所带来的问题包括:类的层次关系必须绑定为关系模式(将对象
- 学习编程那点事
gcq511120594
编程互联网
一年前的夏天,我还在纠结要不要改行,要不要去学php?能学到真本事吗?改行能成功吗?太多的问题,我终于不顾一切,下定决心,辞去了工作,来到传说中的帝都。老师给的乘车方式还算有效,很顺利的就到了学校,赶巧了,正好学校搬到了新校区。先安顿了下来,过了个轻松的周末,第一次到帝都,逛逛吧!
接下来的周一,是我噩梦的开始,学习内容对我这个零基础的人来说,除了勉强完成老师布置的作业外,我已经没有时间和精力去
- Reverse Linked List II
hcx2013
list
Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in-place and in one-pass.
For example:Given 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2 and n = 4,
return
- Spring4.1新特性——页面自动化测试框架Spring MVC Test HtmlUnit简介
jinnianshilongnian
spring 4.1
目录
Spring4.1新特性——综述
Spring4.1新特性——Spring核心部分及其他
Spring4.1新特性——Spring缓存框架增强
Spring4.1新特性——异步调用和事件机制的异常处理
Spring4.1新特性——数据库集成测试脚本初始化
Spring4.1新特性——Spring MVC增强
Spring4.1新特性——页面自动化测试框架Spring MVC T
- Hadoop集群工具distcp
liyonghui160com
1. 环境描述
两个集群:rock 和 stone
rock无kerberos权限认证,stone有要求认证。
1. 从rock复制到stone,采用hdfs
Hadoop distcp -i hdfs://rock-nn:8020/user/cxz/input hdfs://stone-nn:8020/user/cxz/运行在rock端,即源端问题:报版本
- 一个备份MySQL数据库的简单Shell脚本
pda158
mysql脚本
主脚本(用于备份mysql数据库): 该Shell脚本可以自动备份
数据库。只要复制粘贴本脚本到文本编辑器中,输入数据库用户名、密码以及数据库名即可。我备份数据库使用的是mysqlump 命令。后面会对每行脚本命令进行说明。
1. 分别建立目录“backup”和“oldbackup” #mkdir /backup #mkdir /oldbackup
- 300个涵盖IT各方面的免费资源(中)——设计与编码篇
shoothao
IT资源图标库图片库色彩板字体
A. 免费的设计资源
Freebbble:来自于Dribbble的免费的高质量作品。
Dribbble:Dribbble上“免费”的搜索结果——这是巨大的宝藏。
Graphic Burger:每个像素点都做得很细的绝佳的设计资源。
Pixel Buddha:免费和优质资源的专业社区。
Premium Pixels:为那些有创意的人提供免费的素材。
- thrift总结 - 跨语言服务开发
uule
thrift
官网
官网JAVA例子
thrift入门介绍
IBM-Apache Thrift - 可伸缩的跨语言服务开发框架
Thrift入门及Java实例演示
thrift的使用介绍
RPC
POM:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.thrift</groupId>