JDK19 - 虚拟线程如何进行业务代码的改造
JDK19 - 虚拟线程如何进行业务代码的改造
- 一. 线程池的改造
- 二. for 循环同步代码块改造
-
- 2.1 自动关闭资源会等待所有异步任务执行完毕吗?
一. 线程池的改造
假设我们的代码中,原本是这样使用线程池的:
public static ExecutorService getThreadPoolExecutor(String threadName) {
// 自定义线程名称
ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat(threadName).build();
// 初始化线程池
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,
4,
3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(100),
threadFactory,
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
}
那么为了让业务代码更少的改动,我们就针对这类我们自己封装好的函数进行改造:
/**
* 获取线程池,默认使用虚拟线程,不使用线程池
*
* @param threadName
* @return
*/
public static ExecutorService getThreadPoolExecutor(String threadName) {
return getThreadPoolExecutor(threadName, true);
}
public static ExecutorService getThreadPoolExecutor(String threadName, boolean isVirtualThread) {
return getExecutorService(threadName, isVirtualThread, false);
}
/**
- 获取线程池
- 3. @param threadName 线程名称
- @param isVirtualThread 是否虚拟线程
- @param useThreadPool 是否使用线程池
- @return 线程池
*/
private static ExecutorService getExecutorService(String threadName, boolean isVirtualThread, boolean useThreadPool) {
ThreadFactory factory = isVirtualThread ? Thread.ofVirtual().name(threadName).factory()
: Thread.ofPlatform().name(threadName).factory();
// 如果使用线程池
if (useThreadPool) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,
4,
3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(100),
factory,
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
} else {
// 否则不限制线程池大小
return Executors.newThreadPerTaskExecutor(factory);
}
}
那么我们只用改一处地方,外部甚至无感,我们就完成了虚拟线程池的代码改造了。另外还需要注意:
- 如果改造虚拟线程,依旧使用虚拟线程池。若你的相关参数设置的很低。比如最大线程数。那么你的虚拟线程改造基本上是没啥意义的。
- 使用虚拟线程,在确定好相关业务代码的
QPS情况下,建议使用Executors.newThreadPerTaskExecutor()的方式来构建虚拟线程池。
二. for 循环同步代码块改造
我们依旧给一个案例代码:
@org.junit.Test
public void testForTest() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("********************Start********************");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("hello");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
long finish = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("********************finish********************");
System.out.println(finish - start);
}
结果如下:

那么针对这类for循环执行同步代码块的,我们如何进行虚拟线程的改造?
首先我们可以利用try-with-resources语法块来完成,如下:
@org.junit.Test
public void testTryWithResource() {
Instant start = Instant.now();
System.out.println("********************Start********************");
try (ExecutorService executorService = ThreadPoolExecutorService.getThreadPoolExecutor("test")) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executorService.submit(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("hello");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
}
}
Instant finish = Instant.now();
System.out.println("********************finish********************");
System.out.println(Duration.between(start, finish).toMillis());
}
来解释下啥意思:
try-with-resources语法块时候Java 9中引入的一种新的try语法。可以更方便地管理资源的关闭,无需显式地编写finally块。- 它针对的是一个实现了
AutoCloseable接口的对象,它在try语句块执行完毕后会自动关闭。try () {}小括号里面的内容就是相关的资源,用var修饰。
很巧的是,我们的ExecutorService接口就实现了AutoCloseable接口,因此它可以被自动关闭。
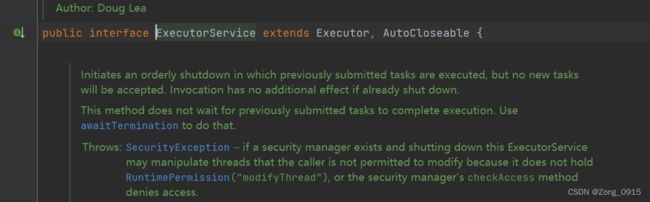
而AutoCloseable接口里面只定义了一个方法:clsoe()

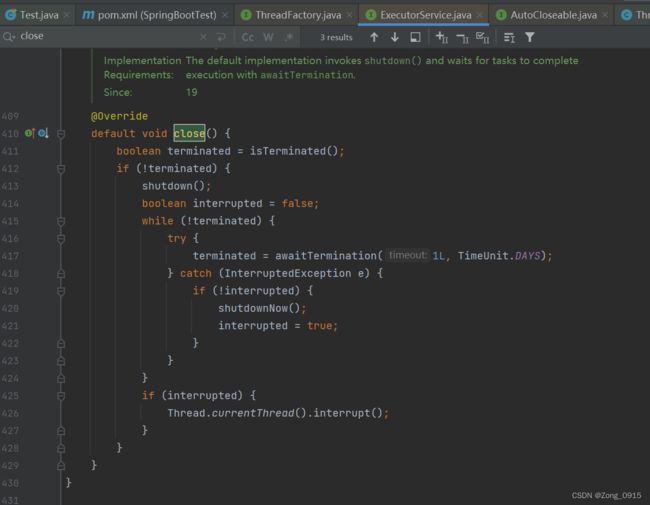
2.1 自动关闭资源会等待所有异步任务执行完毕吗?
先说本文的案例,答案是可以的,因为从本文案例来看,虚拟线程的改造案例中,相关的信息输出都是在finish之前:

让我们再看一下ExecutorService里面对close方法的具体实现:如果发现线程池还没执行完毕,就会一直处于while循环当中。直到所有的异步任务执行完毕才会关闭线程池。