网易《python全栈工程师》 2.2.1 迭代器和生成器
目录
- 1. 课程目标
- 2. 迭代器
-
- 2.1 名词解释——迭代
-
- 2.1.2 可迭代对象
- 2.1.3 “牛顿法”求根
- 2.1.4 查看列表是否是可迭代对象
- 2.1.5 map()函数的参数iterables为可迭代对象,“*”说明可以有若干个可迭代对象
- 2.2 名词解释——迭代器
-
- 2.2.1 判断列表是否为迭代器
- 2.2.2 创建迭代器
- 2.2.3 读取迭代器中的数据
- 2.2.4 迭代器的执行过程
- 2.2.5 使用for循环读取迭代器中的数据流
- 2.3 例题一
-
- 2.3.1 题目
- 2.3.2 程序源码
-
- 三级目录
1. 课程目标
2. 迭代器
2.1 名词解释——迭代
2.1.2 可迭代对象
>>> lst = [1,2,3]
>>> hasattr(lst, '_next_')
False
>>> iter_lst = iter(lst)
>>> iter_lst
<list_iterator object at 0x0000015F6BB387F0>
>>>
创建迭代器
使用 >>> iter_lst = iter(lst) 创建迭代器
2.1.3 “牛顿法”求根
"""
计算平方根的方法
"""
# 使用牛顿法计算平方根
value = 23 # f(x) = x^2 - 23
epsilon = 0.001
result = value / 2
# 使用while循环进行迭代,abs()用于求绝对值
while abs(result*result - value) >= epsilon:
result = result - ((result*result - value) / (2 * result))
print("The square root of {0} is about {1}".format(value, result))
# 使用内置函数计算平方根
import math
print(math.sqrt(23))
运行结果
C:\Users\邢程\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38\python.exe "D:/Python 项目/入门/2.2.1_000.py"
The square root of 23 is about 4.795837982658063
4.795831523312719
Process finished with exit code 0
2.1.4 查看列表是否是可迭代对象
使用hasattr()函数判断列表中是否含有“_iter_”函数,是则说明列表是可迭代对象
>>> hasattr(list, '__iter__')
True
>>>
判断range()对象是否为可迭代对象
>>> r = range(0, 10)
>>> r
range(0, 10)
>>> hasattr(r, '__iter__')
True
>>>
2.1.5 map()函数的参数iterables为可迭代对象,“*”说明可以有若干个可迭代对象
>>> help(map)
Help on class map in module builtins:
class map(object)
| map(func, *iterables) --> map object
|
| Make an iterator that computes the function using arguments from
| each of the iterables. Stops when the shortest iterable is exhausted.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __iter__(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| __next__(self, /)
| Implement next(self).
|
| __reduce__(...)
| Return state information for pickling.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods defined here:
|
| __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
>>>
2.2 名词解释——迭代器
2.2.1 判断列表是否为迭代器
使用hasattr()函数判断列表中是否含有’_next_'判断列表是否为迭代器,True则为迭代器
>>> lst = [1,2,3]
>>> hasattr(lst, '__next__')
False
>>>
2.2.2 创建迭代器
以列表lst为基础创建迭代器
>>> hasattr(lst, '__next__')
False
>>> iter_lst = iter(lst)
>>> iter_lst
<list_iterator object at 0x0000023756622550>
>>> hasattr(iter_lst, '__next__')
True
>>>
2.2.3 读取迭代器中的数据
>>> iter_lst.__next__()
1
>>> iter_lst.__next__()
2
>>> iter_lst.__next__()
3
>>> iter_lst.__next__()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "" , line 1, in <module>
iter_lst.__next__()
StopIteration
>>>
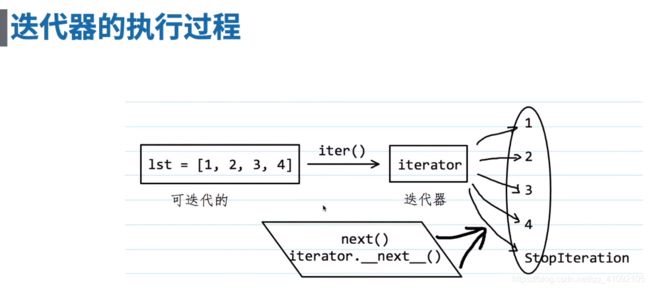
2.2.4 迭代器的执行过程
2.2.5 使用for循环读取迭代器中的数据流
读没有显示数值说明之前的实验已经读取完数据了,没有返回StopIteration异常是因为for循环自动捕获并处理了该异常。
>>> for i in iter_lst:
print(i)
>>>
简单的实现方法,再创建一次迭代器
>>> iter_lst = iter(lst)
>>> for i in iter_lst:
print(i)
1
2
3
>>> iter_lst.__next__()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "" , line 1, in <module>
iter_lst.__next__()
StopIteration
>>>