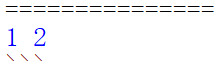python-——notes——third
模块
-
.py就是一个模块(事先定义好的函数和变量的文件)
-
使用关键字import或者from xxx import xxx 引用模块
-
例子:
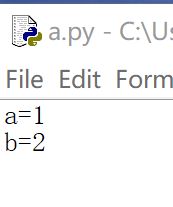
a.py中的内容为:
import a#import 后面加模块的名字
print(a.a,a.b)#a.a代表的是a.py中的a。
运行结果为
from a import hello,a,b
hello()
print(a,b,a+b)
- 包:存放模块的一个文件夹,__init __.py用于做全局的设置。可以为空但必须存在的文件
- 使用包:
#第一种
import bao
bao.a.hello()
#第二种
from bao.a import hello
hello()#一次只引入一个模块
#一次引入多个模块需要在_ _init_ _.py文件加入特殊功能_ _all_ _=["a1",""a2"]
from bao import*#把一个模块的所有内容全都导入到当前的程序
print(a.add(a.a,b.b))
●pyc文件:是经过python编译后得模块文件,用于加快模块的速度
★python内置模块,sys用于设置python解释器得模块
★安装第三方模块:
(1)安装:pip install 模块名
(2)卸载:pip uninstall 模块名
(3)查看所有安装;pip list
sys.path.append("E:\\")#所有e盘内容都添加进入
★nameerror错误指未定义函数或变量
★from…import语句:
(1)from 模块名 import 函数名(或者变量名和类名)
(2)from 模块名 import 函数名 as 别名
(3)from 模块名 import *(把一个模块的所有内容全都导入到当前的程序)
常用内置函数
__ name__属性:被另外一个程序第一次引入时,程序被执行
用__ name__属性来使该程序块自身运行时执行*(__都是两个下划线,两个下划线之间没有空格)*
例:
if __name__="__ main__":
print('程序自身在运行')
else:
print('来自另外一个模块')
print(__name__)
print("welcom my boke")
#运行结果为:
__main__
welcom my boke
[Finished in 0.5s]
#当模块被引用时不执行:
if __name__=="__main__":
print("被引用时不执行")
#运行结果
被引用时不执行
__ name __ python解释器定义好得内置变量直接运行当前模块时,它的值是"__ main __"。当模块被引用执行时,它的值时"模块文件的名字"或"包.模块名"
-
引用模块:
import 模块名:功能是将模块中的代码在当前脚本中执行 -
标准模块(python本身自带一些模块)
| sys | 用于提供对python解释器相关的操作 |
|---|---|
| os | 用于提供系统级别的操作,关机,删文件,创建文件,调用系统命令 |
| time | 时间相关的操作 |
| hashilib | 用于加密相关的操作 |
| random | 用于随机数 |
| re | 用于正则表达式 |
| json | 用于字符串和python基本数据类型间进行转换 |
- sys模块
(1)sys.path属性:
模块位置,list类型可以修改
例:
import sys
print(sys.path)
#运行结果:
['D:\\python', 'D:\\python\\python39.zip', 'D:\\python\\DLLs', 'D:\\python\\lib', 'D:\\python', 'D:\\python\\lib\\site-packages']
(2) sys.version属性:
显示python编辑器的版本
例:
import sys
print(sys.version)
#运行结果:
3.9.0 (tags/v3.9.0:9cf6752, Oct 5 2020, 15:34:40) [MSC v.1927 64 bit (AMD64)]
import sys
print(sys.version[:5])#去前五个字符
#运行结果:
3.9.0
[Finished in 0.2s]
(3)sys.argv属性:
例:
import sys
print(sys.argv)
#运行结果:
['D:\\python\\x.py']
(4)sys.exit属性:
sys.exit()强制终止程序
- os模块
1、功能:os模块调用系统的功能
2、 例:
>>> os.system("ipconfig")#ip地址
>>> os.system("mspaint")#画图工具
>>> os.system("ping 192.168.10.1")#ping 所连接的ip
>>>
3、os模块常用方法:
(1)os.name 字符串指示当前使用平台。win->‘nt’;linux->‘posix’
例:
>>> print(os.name)
nt
(2)os.system(“command”)运行系统命令,直接显示。
os.environ 获取环境变量
例:
>>> print(os.environ)
environ({'ALLUSERSPROFILE': 'C:\\ProgramData', 'APPDATA': 'C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\AppData\\Roaming', 'COMMONPROGRAMFILES': 'C:\\Program Files\\Common Files', 'COMMONPROGRAMFILES(X86)': 'C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Common Files', 'COMMONPROGRAMW6432': 'C:\\Program Files\\Common Files', 'COMPUTERNAME': 'LAPTOP-4VB56GGS', 'COMSPEC': 'C:\\Windows\\system32\\cmd.exe', 'DRIVERDATA': 'C:\\Windows\\System32\\Drivers\\DriverData', 'FPS_BROWSER_APP_PROFILE_STRING': 'Internet Explorer', 'FPS_BROWSER_USER_PROFILE_STRING': 'Default', 'HOME': 'C:\\Users\\Sunshine', 'HOMEDRIVE': 'C:', 'HOMEPATH': '\\Users\\Sunshine', 'JAVA-HOME': 'C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk-13.0.2\\bin', 'LOCALAPPDATA': 'C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\AppData\\Local', 'LOGONSERVER': '\\\\LAPTOP-4VB56GGS', 'NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS': '8', 'ONEDRIVE': 'C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\OneDrive', 'ONEDRIVECONSUMER': 'C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\OneDrive', 'OS': 'Windows_NT', 'PATH': 'C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk-13.0.2\\bin;D:\\python\\Scripts\\;D:\\python\\;C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\AppData\\Local\\Programs\\Python\\Python38-32\\Scripts\\;C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\AppData\\Local\\Programs\\Python\\Python38-32\\;C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\AppData\\Local\\Microsoft\\WindowsApps;C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk-13.0.2\\bin;', 'PATHEXT': '.COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD;.VBS;.VBE;.JS;.JSE;.WSF;.WSH;.MSC', 'PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE': 'AMD64', 'PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER': 'AMD64 Family 23 Model 24 Stepping 1, AuthenticAMD', 'PROCESSOR_LEVEL': '23', 'PROCESSOR_REVISION': '1801', 'PROGRAMDATA': 'C:\\ProgramData', 'PROGRAMFILES': 'C:\\Program Files', 'PROGRAMFILES(X86)': 'C:\\Program Files (x86)', 'PROGRAMW6432': 'C:\\Program Files', 'PSMODULEPATH': 'C:\\Program Files\\WindowsPowerShell\\Modules;C:\\Windows\\system32\\WindowsPowerShell\\v1.0\\Modules', 'PUBLIC': 'C:\\Users\\Public', 'SESSIONNAME': 'Console', 'SYSTEMDRIVE': 'C:', 'SYSTEMROOT': 'C:\\Windows', 'TEMP': 'C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\AppData\\Local\\Temp', 'TMP': 'C:\\Users\\Sunshine\\AppData\\Local\\Temp', 'USERDOMAIN': 'LAPTOP-4VB56GGS', 'USERDOMAIN_ROAMINGPROFILE': 'LAPTOP-4VB56GGS', 'USERNAME': 'Sunshine', 'USERPROFILE': 'C:\\Users\\Sunshine', 'VBOX_MSI_INSTALL_PATH': 'D:\\Program Files\\Oracle\\VirtualBox\\', 'WINDIR': 'C:\\Windows'})
>>>
os.makedir创建多层目录(mkdir -p)
(3)os模块文件操作方法:
- os.getcwd()获取当前工作目录,即当前脚本工作的目录路径。
- os.chdir(“dirname”)改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd。 os.curdir返回当前目录:(’.’)
- os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:(’…’) os.makedirs(“dir1/dir2”)可生成多层递归目录
- os.remove()删除一个文件 只能删除
- os.removedirs(‘dirname1’)若目录为空则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如果亦为空则删除,依此类推。
- os.removedirs(‘test’)只能删除空目录rmdir
- os.removedirs(从里到外删除"test"/“table”)
- os.rmdir(‘dirname’)删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错相当于shell中rmdir dirname
- 创建文件:
with open("hello.py","w") as f:
f.writelines(["print(hello)\n","input()"])
- os.rename(“oldname”,“new”)重命名文件/目录
- os.listdir(‘dirname’)列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印。
- os.stat(‘path/filename’)获取文件/目录信息
- os.sep操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\",linux下为"/"
- os.linesep当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",linux下为"\n" os.pathsep用于分割文件路径的字符串
- os模块路径操作方法: os.path.abspath(path)返回path规范化的绝对路径
- os.path.split(path)将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回
- os.path.dirname(path)返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素
- os.basename(path)返回path最后文件名。如path以/或者\结尾,那么就会返回空值,即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素。
- os.path.exists(path)如果path存在,返回True,如果path不存在,返False
- os.path.isabs(path)如果path是绝对路径,返回True
- os.path.isfile(path)如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True,否则返回False
- os.path.isdir(path)如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True,否则返回False
- os.path.jion(path1[,path2[,…]])将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前将被忽略
os.path.getatime(path)返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间 - os.path.getmtime(path)返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
- time模块: 时间戳
- time.time() 1970年1月1日之后的秒 格式化的字符串time.strftime(’%Y-%m-%d’)2020-11-14
11:12 时间元组:time.localtime()年、日、星期等 休眠时间:time.sleep(t)t–推迟执行的秒数。 - datatime日期输出格式化 datatime=>string now =datetime.datetime.now()
- now.strftime(’%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S’) strftime是datetime类的实例方法。 返回当前系统时间;
- import datetime datatime.datetime.now() datetime日期字符串转为日期对象:
string=>datetime t_str=‘2020-11-14 19:28;26’
d=datetime.datetime.strptime(t_str,%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S) - strptime是datetime类的静态方法。 datetime时间运算
- 日期比较操作:timedelta类的实例,支持加、减、乘、除等操作,所得的结果也是timedelta类的实例。 year
=timedelta(days=365) ten_years=year*10 nine_years=ten_years-year 同时,date、time和datetime类也支持与timedelta的加、减运算。 - datetime1=datetime2+/-timedelta timedelta=datetime1-datetime2
- 两个日期相差多少天。
- 今天的n天后的日期
now=datetime.datetime.now()
delta=datetime.timedelta(days=3)
n_days=now +delta
print(n_days.strftime(%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S))
★random随机数模块
例:
>>> import random
>>> print(random.random())
0.7528877116927849
>>> print(random.randint(1,2))
2
>>> print(random.randrange(1,10))
6
>>> print(random.choice([1,10,11,33,55,90]))
33
★位验证码:
>>> import random
>>> code=''
>>> for i in range(4):
cur=random.randrange(0,4)
if cur!=i:
temp=chr(random.randint(65,90))#chr函数会把整数转换成字符
else:
temp=random.randint(0,9)
code+=str(temp)
print(code)
8
★hashlib加密模块
- 用于加密相关的操作,代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供SHA1,SHA224,SHA384,SHA512,MD5算法。
- 摘要算法又称哈希算法、散列算法。它通过一函数,把任意长度的数据转换位一个长度固定的数据串(通常16进制的字符串表示)。
- SHA1的结果是160bit字节,通常用一个40位的16进制字符串表示。
- 比SHA1更安全的算法是SHA256和SHA512,不过越安全的算法越慢,而且摘要长度更长。
>>> import hashlib
>>> md5=hashlib.md5()
>>>print(md5.hexdigest())
d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
★
dir()函数
语法:dir([ 对象or变量or类型])
获取当前模块属性列表:
>>> dir() # 获得当前模块的属性列表
['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__']
★
查看列表的方法
>>> dir([ ]) # 查看列表的方法
['__add__', '__class__', '__class_getitem__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort']
>>>
★
例子:
>>> import sys
>>> print(dir(sys))#显示模块中所有的函数名和变量名
['__breakpointhook__', '__displayhook__', '__doc__', '__excepthook__', '__interactivehook__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', '__stderr__', '__stdin__', '__stdout__', '__unraisablehook__', '_base_executable', '_clear_type_cache', '_current_frames', '_debugmallocstats', '_enablelegacywindowsfsencoding', '_framework', '_getframe', '_git', '_home', '_xoptions', 'addaudithook', 'api_version', 'argv', 'audit', 'base_exec_prefix', 'base_prefix', 'breakpointhook', 'builtin_module_names', 'byteorder', 'call_tracing', 'copyright', 'displayhook', 'dllhandle', 'dont_write_bytecode', 'exc_info', 'excepthook', 'exec_prefix', 'executable', 'exit', 'flags', 'float_info', 'float_repr_style', 'get_asyncgen_hooks', 'get_coroutine_origin_tracking_depth', 'getallocatedblocks', 'getdefaultencoding', 'getfilesystemencodeerrors', 'getfilesystemencoding', 'getprofile', 'getrecursionlimit', 'getrefcount', 'getsizeof', 'getswitchinterval', 'gettrace', 'getwindowsversion', 'hash_info', 'hexversion', 'implementation', 'int_info', 'intern', 'is_finalizing', 'maxsize', 'maxunicode', 'meta_path', 'modules', 'path', 'path_hooks', 'path_importer_cache', 'platform', 'platlibdir', 'prefix', 'pycache_prefix', 'set_asyncgen_hooks', 'set_coroutine_origin_tracking_depth', 'setprofile', 'setrecursionlimit', 'setswitchinterval', 'settrace', 'stderr', 'stdin', 'stdout', 'thread_info', 'unraisablehook', 'version', 'version_info', 'warnoptions', 'winver']
>>>
>>> print(help(sys))#查看模块的帮助文档
Help on built-in module sys:
NAME
sys
MODULE REFERENCE
https://docs.python.org/3.9/library/sys
The following documentation is automatically generated from the Python
source files. It may be incomplete, incorrect or include features that
are considered implementation detail and may vary between Python
implementations. When in doubt, consult the module reference at the
location listed above.
DESCRIPTION
This module provides access to some objects used or maintained by the
interpreter and to functions that interact strongly with the interpreter.
Dynamic objects:
argv -- command line arguments; argv[0] is the script pathname if known
path -- module search path; path[0] is the script directory, else ''
modules -- dictionary of loaded modules
displayhook -- called to show results in an interactive session
excepthook -- called to handle any uncaught exception other than SystemExit
To customize printing in an interactive session or to install a custom
top-level exception handler, assign other functions to replace these.
stdin -- standard input file object; used by input()
stdout -- standard output file object; used by print()
stderr -- standard error object; used for error messages
By assigning other file objects (or objects that behave like files)
to these, it is possible to redirect all of the interpreter's I/O.
last_type -- type of last uncaught exception
last_value -- value of last uncaught exception
last_traceback -- traceback of last uncaught exception
These three are only available in an interactive session after a
traceback has been printed.
Static objects:
builtin_module_names -- tuple of module names built into this interpreter
copyright -- copyright notice pertaining to this interpreter
exec_prefix -- prefix used to find the machine-specific Python library
executable -- absolute path of the executable binary of the Python interpreter
float_info -- a named tuple with information about the float implementation.
float_repr_style -- string indicating the style of repr() output for floats
hash_info -- a named tuple with information about the hash algorithm.
hexversion -- version information encoded as a single integer
implementation -- Python implementation information.
int_info -- a named tuple with information about the int implementation.
maxsize -- the largest supported length of containers.
maxunicode -- the value of the largest Unicode code point
platform -- platform identifier
prefix -- prefix used to find the Python library
thread_info -- a named tuple with information about the thread implementation.
version -- the version of this interpreter as a string
version_info -- version information as a named tuple
dllhandle -- [Windows only] integer handle of the Python DLL
winver -- [Windows only] version number of the Python DLL
_enablelegacywindowsfsencoding -- [Windows only]
__stdin__ -- the original stdin; don't touch!
__stdout__ -- the original stdout; don't touch!
__stderr__ -- the original stderr; don't touch!
__displayhook__ -- the original displayhook; don't touch!
__excepthook__ -- the original excepthook; don't touch!
Functions:
displayhook() -- print an object to the screen, and save it in builtins._
excepthook() -- print an exception and its traceback to sys.stderr
exc_info() -- return thread-safe information about the current exception
exit() -- exit the interpreter by raising SystemExit
getdlopenflags() -- returns flags to be used for dlopen() calls
getprofile() -- get the global profiling function
getrefcount() -- return the reference count for an object (plus one :-)
getrecursionlimit() -- return the max recursion depth for the interpreter
getsizeof() -- return the size of an object in bytes
gettrace() -- get the global debug tracing function
setdlopenflags() -- set the flags to be used for dlopen() calls
setprofile() -- set the global profiling function
setrecursionlimit() -- set the max recursion depth for the interpreter
settrace() -- set the global debug tracing function
FUNCTIONS
__breakpointhook__ = breakpointhook(...)
breakpointhook(*args, **kws)
This hook function is called by built-in breakpoint().
__displayhook__ = displayhook(object, /)
Print an object to sys.stdout and also save it in builtins._
__excepthook__ = excepthook(exctype, value, traceback, /)
Handle an exception by displaying it with a traceback on sys.stderr.
__unraisablehook__ = unraisablehook(unraisable, /)
Handle an unraisable exception.
The unraisable argument has the following attributes:
* exc_type: Exception type.
* exc_value: Exception value, can be None.
* exc_traceback: Exception traceback, can be None.
* err_msg: Error message, can be None.
* object: Object causing the exception, can be None.
addaudithook(hook)
Adds a new audit hook callback.
audit(...)
audit(event, *args)
Passes the event to any audit hooks that are attached.
breakpointhook(...)
breakpointhook(*args, **kws)
This hook function is called by built-in breakpoint().
call_tracing(func, args, /)
Call func(*args), while tracing is enabled.
The tracing state is saved, and restored afterwards. This is intended
to be called from a debugger from a checkpoint, to recursively debug
some other code.
exc_info()
Return current exception information: (type, value, traceback).
Return information about the most recent exception caught by an except
clause in the current stack frame or in an older stack frame.
excepthook(exctype, value, traceback, /)
Handle an exception by displaying it with a traceback on sys.stderr.
exit(status=None, /)
Exit the interpreter by raising SystemExit(status).
If the status is omitted or None, it defaults to zero (i.e., success).
If the status is an integer, it will be used as the system exit status.
If it is another kind of object, it will be printed and the system
exit status will be one (i.e., failure).
get_asyncgen_hooks()
Return the installed asynchronous generators hooks.
This returns a namedtuple of the form (firstiter, finalizer).
get_coroutine_origin_tracking_depth()
Check status of origin tracking for coroutine objects in this thread.
getallocatedblocks()
Return the number of memory blocks currently allocated.
getdefaultencoding()
Return the current default encoding used by the Unicode implementation.
getfilesystemencodeerrors()
Return the error mode used Unicode to OS filename conversion.
getfilesystemencoding()
Return the encoding used to convert Unicode filenames to OS filenames.
getprofile()
Return the profiling function set with sys.setprofile.
See the profiler chapter in the library manual.
getrecursionlimit()
Return the current value of the recursion limit.
The recursion limit is the maximum depth of the Python interpreter
stack. This limit prevents infinite recursion from causing an overflow
of the C stack and crashing Python.
This IDLE wrapper subtracts 30 to compensate for the 30 IDLE adds when
setting the limit.
getrefcount(object, /)
Return the reference count of object.
The count returned is generally one higher than you might expect,
because it includes the (temporary) reference as an argument to
getrefcount().
getsizeof(...)
getsizeof(object [, default]) -> int
Return the size of object in bytes.
getswitchinterval()
Return the current thread switch interval; see sys.setswitchinterval().
gettrace()
Return the global debug tracing function set with sys.settrace.
See the debugger chapter in the library manual.
getwindowsversion()
Return info about the running version of Windows as a named tuple.
The members are named: major, minor, build, platform, service_pack,
service_pack_major, service_pack_minor, suite_mask, product_type and
platform_version. For backward compatibility, only the first 5 items
are available by indexing. All elements are numbers, except
service_pack and platform_type which are strings, and platform_version
which is a 3-tuple. Platform is always 2. Product_type may be 1 for a
workstation, 2 for a domain controller, 3 for a server.
Platform_version is a 3-tuple containing a version number that is
intended for identifying the OS rather than feature detection.
intern(string, /)
``Intern'' the given string.
This enters the string in the (global) table of interned strings whose
purpose is to speed up dictionary lookups. Return the string itself or
the previously interned string object with the same value.
is_finalizing()
Return True if Python is exiting.
set_asyncgen_hooks(...)
set_asyncgen_hooks(* [, firstiter] [, finalizer])
Set a finalizer for async generators objects.
set_coroutine_origin_tracking_depth(depth)
Enable or disable origin tracking for coroutine objects in this thread.
Coroutine objects will track 'depth' frames of traceback information
about where they came from, available in their cr_origin attribute.
Set a depth of 0 to disable.
setprofile(...)
setprofile(function)
Set the profiling function. It will be called on each function call
and return. See the profiler chapter in the library manual.
setrecursionlimit(limit, /)
Set the maximum depth of the Python interpreter stack to n.
This limit prevents infinite recursion from causing an overflow of the C
stack and crashing Python. The highest possible limit is platform-
dependent.
This IDLE wrapper adds 30 to prevent possible uninterruptible loops.
setswitchinterval(interval, /)
Set the ideal thread switching delay inside the Python interpreter.
The actual frequency of switching threads can be lower if the
interpreter executes long sequences of uninterruptible code
(this is implementation-specific and workload-dependent).
The parameter must represent the desired switching delay in seconds
A typical value is 0.005 (5 milliseconds).
settrace(...)
settrace(function)
Set the global debug tracing function. It will be called on each
function call. See the debugger chapter in the library manual.
unraisablehook(unraisable, /)
Handle an unraisable exception.
The unraisable argument has the following attributes:
* exc_type: Exception type.
* exc_value: Exception value, can be None.
* exc_traceback: Exception traceback, can be None.
* err_msg: Error message, can be None.
* object: Object causing the exception, can be None.
DATA
__stderr__ = None
__stdin__ = None
__stdout__ = None
api_version = 1013
argv = ['']
base_exec_prefix = r'D:\python'
base_prefix = r'D:\python'
builtin_module_names = ('_abc', '_ast', '_bisect', '_blake2', '_codecs...
byteorder = 'little'
copyright = 'Copyright (c) 2001-2020 Python Software Foundati...ematis...
dllhandle = 140729869860864
dont_write_bytecode = False
exec_prefix = r'D:\python'
executable = r'D:\python\pythonw.exe'
flags = sys.flags(debug=0, inspect=0, interactive=0, opt...ation=1, is...
float_info = sys.float_info(max=1.7976931348623157e+308, max_...epsilo...
float_repr_style = 'short'
hash_info = sys.hash_info(width=64, modulus=2305843009213693...iphash2...
hexversion = 50921712
implementation = namespace(name='cpython', cache_tag='cpython-39'...as...
int_info = sys.int_info(bits_per_digit=30, sizeof_digit=4)
maxsize = 9223372036854775807
maxunicode = 1114111
meta_path = [<class '_frozen_importlib.BuiltinImporter'>, <class '_fro...
modules = {'__main__': <module '__main__' (built-in)>, '_abc': <module...
path = ['', r'D:\python', r'D:\python\python39.zip', r'D:\python\DLLs'...
path_hooks = [<class 'zipimport.zipimporter'>, <function FileFinder.pa...
path_importer_cache = {r'D:\python': FileFinder('D:\\python'), r'D:\py...
platform = 'win32'
platlibdir = 'lib'
prefix = r'D:\python'
pycache_prefix = None
stderr = <idlelib.run.StdOutputFile object>
stdin = <idlelib.run.StdInputFile object>
stdout = <idlelib.run.StdOutputFile object>
thread_info = sys.thread_info(name='nt', lock=None, version=None)
version = '3.9.0 (tags/v3.9.0:9cf6752, Oct 5 2020, 15:34:40) [MSC v.1...
version_info = sys.version_info(major=3, minor=9, micro=0, releaseleve...
warnoptions = []
winver = '3.9'
FILE
(built-in)
None
>>>
★
abs() 函数:函数返回数字的绝对值。
- 语法:abs( 表达式 )
例:
>>> print(abs(-6))
6
>>> print (abs(16.8))
16.8
>>>
★
加载词库:
def load_word(file):
print("开始加载数据…")
f = open(file,encoding="utf-8")
data = f. readlines()
f. close()
print("加载成功!")
return data
def find_word():
data = load_word("1.txt")
while True:
o = input("请输入您要查询的内容,输入Q退出:")
if o =="Q":
break
n = 0
for line in data:
if o in line:
n += 1
print(n,line,end="")
find_word()
input()
#运行结果
;
开始加载数据…
加载成功!
请输入您要查询的内容,输入Q退出: