图解LeetCode——1184. 公交站间的距离(难度:简单)
一、题目
环形公交路线上有 n 个站,按次序从 0 到 n - 1 进行编号。我们已知每一对相邻公交站之间的距离,distance[i] 表示编号为 i 的车站和编号为 (i + 1) % n 的车站之间的距离。
环线上的公交车都可以按顺时针和逆时针的方向行驶。
返回乘客从出发点 start 到目的地 destination 之间的最短距离。
二、示例
2.1> 示例1
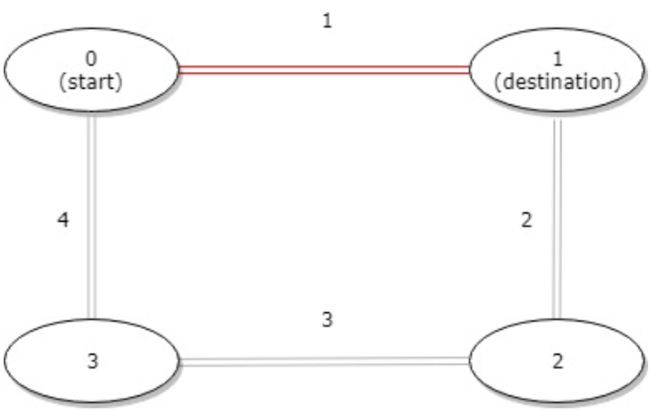
【输入】distance = [1,2,3,4], start = 0, destination = 1
【输出】1
【解释】公交站 0 和 1 之间的距离是 1 或 9,最小值是 1。
2.2> 示例2
【输入】distance = [1,2,3,4], start = 0, destination = 2
【输出】3
【解释】公交站 0 和 2 之间的距离是 3 或 7,最小值是 3。
2.3> 示例3
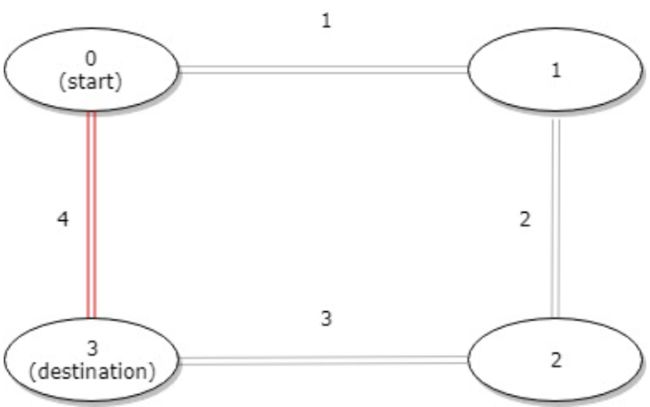
【输入】distance = [1,2,3,4], start = 0, destination = 3
【输出】4
【解释】公交站 0 和 3 之间的距离是 6 或 4,最小值是 4。
提示:
- 1 <= n <= 10^4
- distance.length == n
- 0 <= start, destination < n
- 0 <= distance[i] <= 10^4
三、解题思路
3.1> 思路1:正逆向双指针
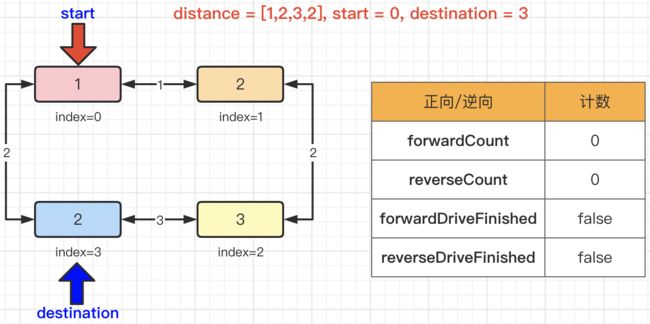
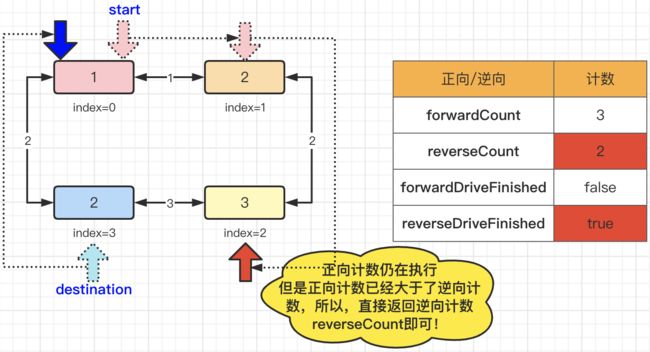
既然环线上的公交车都可以按顺时针和逆时针的方向行驶。那么我们分别通过两个指针,从起点开始和从终点开始,进行行驶,虽然从终点到起点的计算路线也是正向的,但是根据题意实际上都是从起点到终点,且经历的距离一样,所以,我们将从终点向起点计数称之为“逆向”。那么,起始情况下,正向计数:forwardCount=0,逆向计数:reverseCount=0,正向行驶是否结束:forwardDriveFinished=false,逆向行驶是否结束:reverseDriveFinished=false。如下图所示:
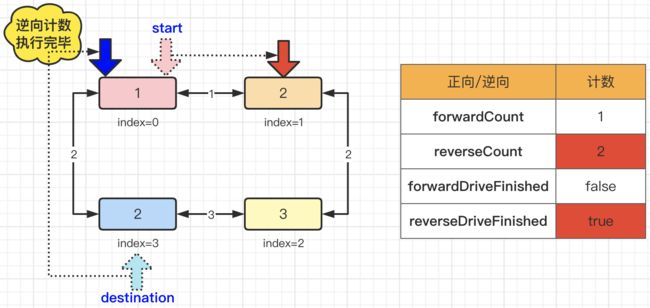
那么当第一次运行结束后,我们发现,逆向形式已经结束了(即:从index(3)到index(0)),逆向计数:reverseCount=2。而正向形式还在进行中,其中正向计数:forwardCount=1。由于reverseCount > forwardCount,所以正向行驶继续。
那么由于逆向形式在上一轮循环中已经结束了,所以本轮只有正向行驶,行驶到index(2)的节点时,正向计数:forwardCount=3,由于reverseCount < forwardCount,所以,可以得出结论,逆向形式距离更短(虽然正向行驶还在继续进行中。。。),既然结果已经确定了,那么我们此时就可以结束正向行驶。返回reverseCount值作为结果。
3.2> 思路2:完整遍历后对比结果
思路一的好处是,对于正向或者逆向有一方步数较少时,我们可以不必等待步数较长一方执行完毕,只要以完成的一端可以确认路程最短,就可以结束遍历了。但是实现起来代码较多。而如果我们想要简便的代码实现的话,我们其实可以通过一次完整的循环遍历,再通过最终结果,来进行判断。
为什么可以通过一次完整遍历就能够确定呢? 假设总的数组是[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],如果我们start=2,destination=7,那么在[2, 7)的范围内计数,就是正向行驶的距离。而由于整个路程是环路,即:是一个圆圈,所以范围之外的,就是逆向行驶的范围。而如果destination=2,start=7怎么办呢?其实和start=2,destination=7的计算方式是一样的,为了方便起见,我们只需要将destination=2,start=7变换为start=2,destination=7,就可以计数了。这种方式,实现代码会比较方便整洁。如下图所示:
四、代码实现
4.1> 实现1:正逆向双指针
public int distanceBetweenBusStops1(int[] distance, int start, int destination) {
int forwardCount = 0, reverseCount = 0, startNum = start, destinationNum = destination;
boolean forwardDriveFinished = false, reverseDriveFinished = false;
while (!forwardDriveFinished || !reverseDriveFinished) {
// 正向走一步
if (!forwardDriveFinished) {
forwardCount += distance[startNum];
startNum = (startNum + 1) % distance.length;
if (startNum == destination) {
forwardDriveFinished = true;
}
} else if (forwardCount <= reverseCount) {
return forwardCount;
}
// 逆向走一步
if (!reverseDriveFinished) {
reverseCount += distance[destinationNum];
destinationNum = (destinationNum + 1) % distance.length;
if (start == destinationNum) {
reverseDriveFinished = true;
}
} else if (reverseCount <= forwardCount) {
return reverseCount;
}
}
return Math.min(forwardCount, reverseCount);
}4.2> 实现2:完整遍历后对比结果
public int distanceBetweenBusStops2(int[] distance, int start, int destination) {
int forwardCount = 0, reverseCount = 0;
if (start > destination) {
int temp = destination;
destination = start;
start = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < distance.length; i++) {
if (i >= start && i < destination) {
forwardCount += distance[i];
} else {
reverseCount += distance[i];
}
}
return Math.min(forwardCount, reverseCount);
}今天的文章内容就这些了:
写作不易,笔者几个小时甚至数天完成的一篇文章,只愿换来您几秒钟的点赞&分享。
更多技术干货,欢迎大家关注公众号@爪哇缪斯「干货分享,每天更新」
往期推荐
图解LeetCode——731. 我的日程安排表 II(难度:中等)![]() https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/125884328图解LeetCode——3. 无重复字符的最长子串(难度:中等)
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/125884328图解LeetCode——3. 无重复字符的最长子串(难度:中等)![]() https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/125857066LeetCode精讲——21. 合并两个有序链表(难度:简单)
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/125857066LeetCode精讲——21. 合并两个有序链表(难度:简单)![]() https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/125840103LeetCode精讲——565. 数组嵌套(难度:中等)
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/125840103LeetCode精讲——565. 数组嵌套(难度:中等)![]() https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/125831251
https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/125831251
题目来源:力扣(LeetCode)