tensor数学运算
| 运算 | 函数 |
|---|---|
| 加 | add |
| 减 | sub |
| 乘 | mul |
| 除 | div |
| 矩阵相乘 | matmul |
| 次方 | pow |
| 平方根及其倒数 | sqrt 和 rsqrt |
| 向下/向上取整 | floor / ceil |
| 分离出整数/小数 | trunc / frac |
| 近似解四舍五入 | round |
| 裁剪 | clamp |
1、矩阵元素的加减乘除
注意是矩阵间对应位置元素进行加减乘除
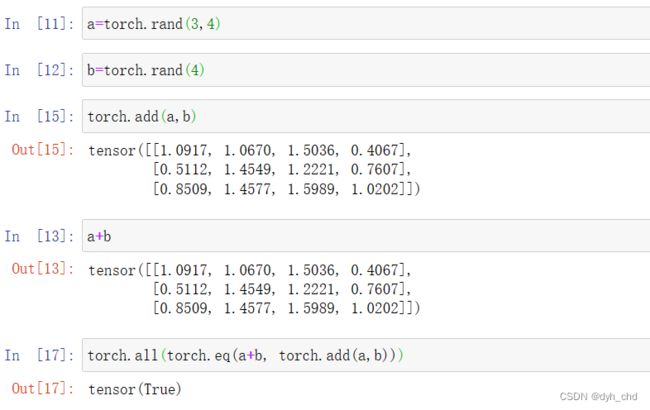
add 和 +
a = torch.rand(3,4)
b = torch.rand(4)
a+b
torch.add(a,b)
# 直接用符号或add函数效果一样,且tensor有broadcast自动扩展b的shape为(3,4)
torch.all(torch.eq(a+b,torch.add(a,b))
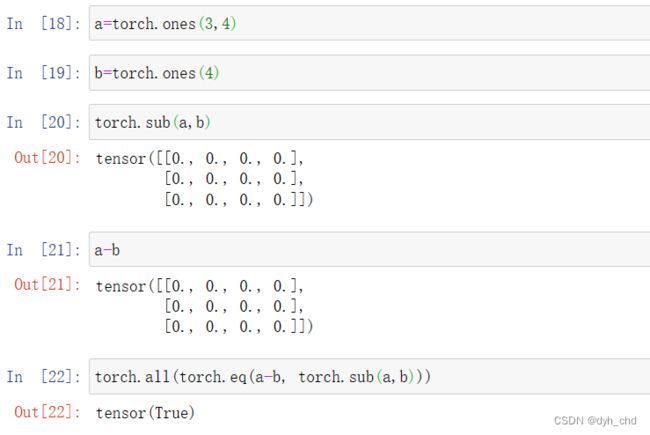
sub 和 -
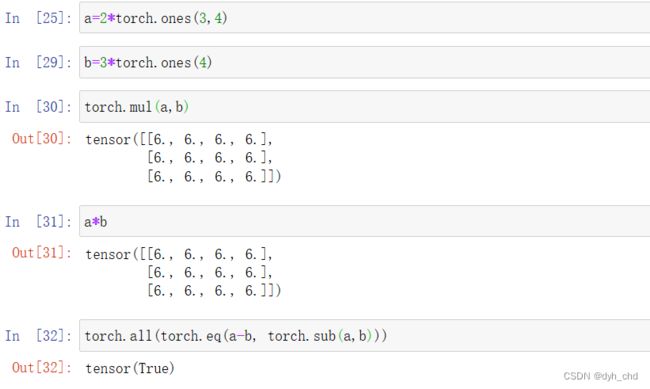
mul 和 *
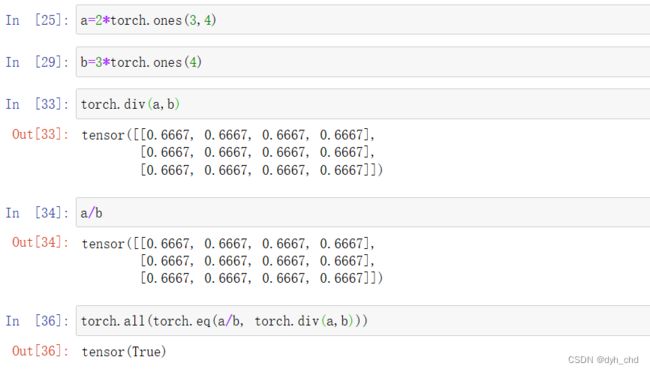
div 和 /
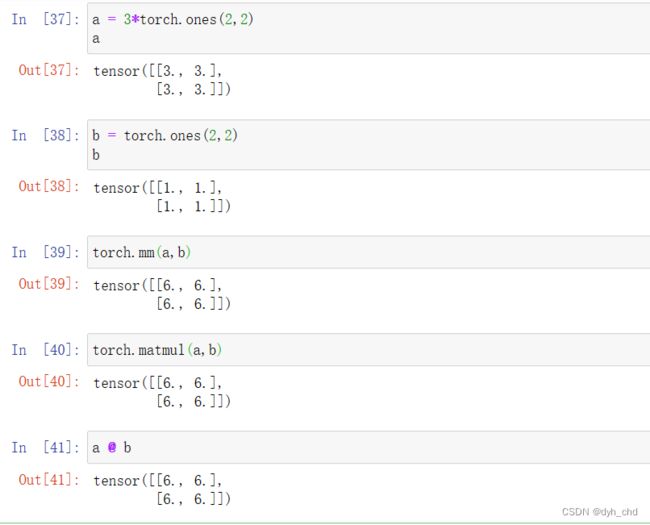
2、矩阵相乘 matmul和@
三种方式:
1、torch.mm
2、torch.matmul
3、运算符@
#其中,mm只支持2d的tensor,不建议使用。直接用matmul或者运算符@
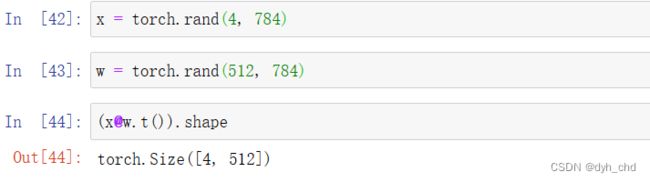
以神经网络中的线性层为例:
将shape为(4,784)的x降维度到(4,512)
x = torch.rand(4,784)
w = torch.rand(512,784)
#pytorch的习惯写法是out维度在前,要@运算的时候将w转置即可
(x@w.t()).shape
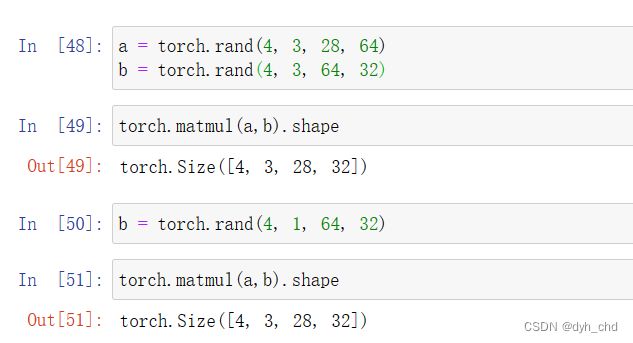
多维情况下的matmul
依旧只对后两维矩阵进行相乘,并且还是有broadcast自动扩展机制
a = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 64)
b = torch.rand(4, 3, 64, 32)
torch.matmul(a,b).shape
b = torch.rand(4, 1, 64, 32)
torch.matmul(a,b).shape
3、次方运算
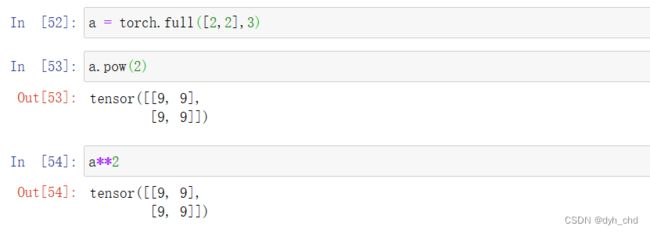
① 次方 pow 或 **
a.pow(x)
#a为张量,x为次方数
a = torch.full([2,2],3)
a.pow(2)
a**2
② 平方根 sqrt
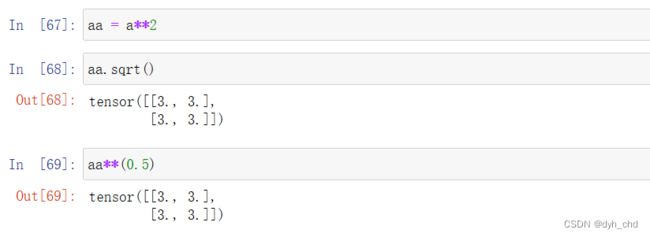
a.sqrt()相当于 a**(0.5)
aa = a**2
aa.sqrt()
aa**(0.5)
③rsqrt
a.rsqrt() 是a.sqrt()结果的倒数
也可以是a.sqrt()**(-1)
aa.rsqrt()
aa.sqrt()**(-1)
4、近似解运算
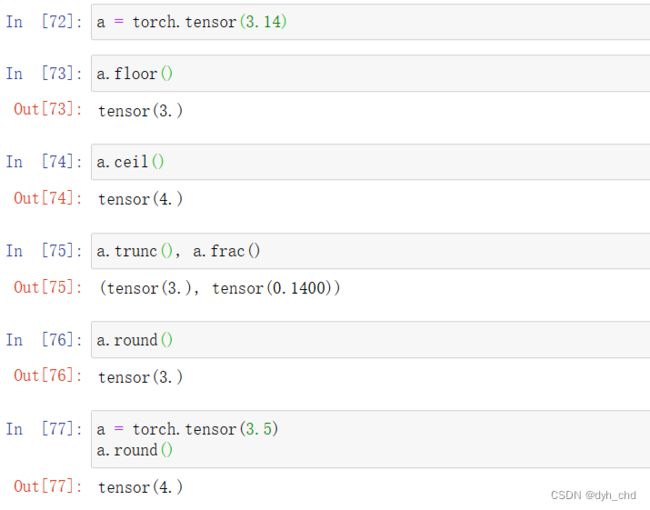
例子:
a=torch.tensor(3.14)
a.floor()向下取整得到3
a.ceil()向上取整得到4
a.trunc()分离出整数部分3
a.frac()分离出小数部分0.14
a.round()四舍五入得到3
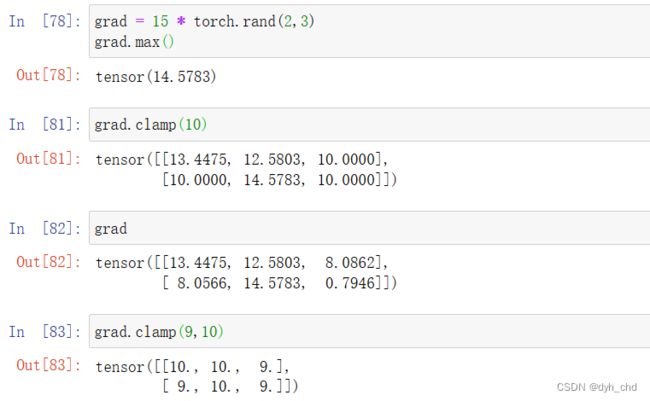
5、裁剪运算
grad = 15 * torch.rand(2,3)
grad.max()
grad
grad.clamp(10)
#只有一个参数10表示限定grad中元素数值最小为10
grad.clamp(9,10)
#限制最小为9,最大为10