EasyExcel的源码流程(导入Excel)
2. EasyExcel类继承了EasyExcelFactory类,EasyExcel自动拥有EasyExcelFactory父类的所有方法,如read(),readSheet(),write(),writerSheet()等等。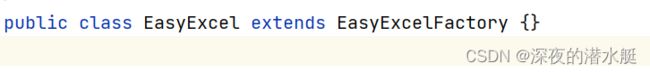
3. 进入.read()方法,需要传入三个参数(文件路径,表头映射类,read监听器)
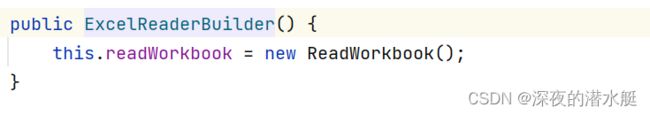
首先调用new ExcelReaderBuilder()方法,初始化ReadWorkbook对象
设置完readWorkbook属性后调,返回excelReaderBuilder对象 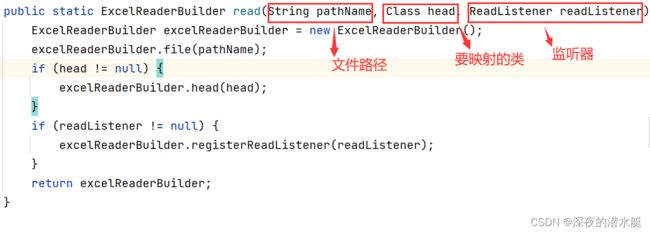
4. 这里又个传入的参数是read监听器,进入其内部看一下,我们自定义了PersonListener实现了ReadListener。ReadListener接口源码 :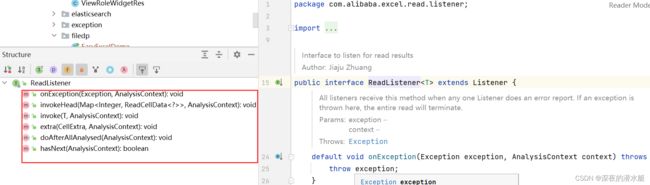
自定义的PersonListener类:
import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext;
import com.alibaba.excel.event.AnalysisEventListener;
import com.aliyun.odps.jdbc.utils.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
@Component
public class PersonListener extends AnalysisEventListener {
//一行一行读出excel内容 不读表头 EasyExcel之所以效率高,也是因它一行一行读取,解析。
@Override
public void invoke(PersonTest personTest, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("***"+personTest);
}
//读取表头
@Override
public void invokeHeadMap(Map headMap, AnalysisContext context) {
System.out.println("表头"+headMap);
}
//读取完执行的方法
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("读取全部后执行");
}
} 5. 接下来调用的是.sheet()方法,这里我们会传入sheetNo、sheetName参数,调用build()方法创建ExcelReader对象,传入ExcelReaderSheetBuilder构造方法中,最终创ExcelReaderSheetBuilder对象 
6. 进入build()方法,build()方法生成了ExcelReader对象,初始化ExcelAnalyser,并实例化ExcelAnalyser。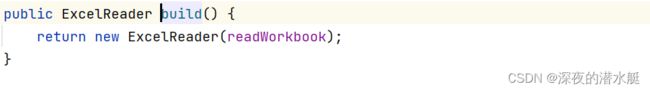
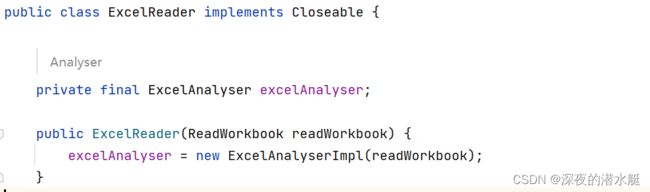
在实例化ExcelAnalyser时,choiceExcelExecutor()方法通过excel格式使用不同的执行器。
我们看XLSX中,初始化了XlsxReadContext上下文对象,给到analysisContext,又初始化了XlsxSaxAnalyser解析器对象
public class ExcelAnalyserImpl implements ExcelAnalyser {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExcelAnalyserImpl.class);
private AnalysisContext analysisContext;
private ExcelReadExecutor excelReadExecutor;
/**
* Prevent multiple shutdowns
*/
private boolean finished = false;
public ExcelAnalyserImpl(ReadWorkbook readWorkbook) {
try {
choiceExcelExecutor(readWorkbook);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
finish();
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
finish();
throw new ExcelAnalysisException(e);
}
}
private void choiceExcelExecutor(ReadWorkbook readWorkbook) throws Exception {
ExcelTypeEnum excelType = ExcelTypeEnum.valueOf(readWorkbook);
switch (excelType) {
case XLS:
POIFSFileSystem poifsFileSystem;
if (readWorkbook.getFile() != null) {
poifsFileSystem = new POIFSFileSystem(readWorkbook.getFile());
} else {
poifsFileSystem = new POIFSFileSystem(readWorkbook.getInputStream());
}
// So in encrypted excel, it looks like XLS but it's actually XLSX
if (poifsFileSystem.getRoot().hasEntry(Decryptor.DEFAULT_POIFS_ENTRY)) {
InputStream decryptedStream = null;
try {
decryptedStream = DocumentFactoryHelper
.getDecryptedStream(poifsFileSystem.getRoot().getFileSystem(), readWorkbook.getPassword());
XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext = new DefaultXlsxReadContext(readWorkbook, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
analysisContext = xlsxReadContext;
excelReadExecutor = new XlsxSaxAnalyser(xlsxReadContext, decryptedStream);
return;
} finally {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(decryptedStream);
// as we processed the full stream already, we can close the filesystem here
// otherwise file handles are leaked
poifsFileSystem.close();
}
}
if (readWorkbook.getPassword() != null) {
Biff8EncryptionKey.setCurrentUserPassword(readWorkbook.getPassword());
}
XlsReadContext xlsReadContext = new DefaultXlsReadContext(readWorkbook, ExcelTypeEnum.XLS);
xlsReadContext.xlsReadWorkbookHolder().setPoifsFileSystem(poifsFileSystem);
analysisContext = xlsReadContext;
excelReadExecutor = new XlsSaxAnalyser(xlsReadContext);
break;
case XLSX:
XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext = new DefaultXlsxReadContext(readWorkbook, ExcelTypeEnum.XLSX);
analysisContext = xlsxReadContext;
excelReadExecutor = new XlsxSaxAnalyser(xlsxReadContext, null);
break;
case CSV:
CsvReadContext csvReadContext = new DefaultCsvReadContext(readWorkbook, ExcelTypeEnum.CSV);
analysisContext = csvReadContext;
excelReadExecutor = new CsvExcelReadExecutor(csvReadContext);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
/*
----------------------------------------略---------------------------------------------
*/
}7. XlsxSaxAnalyser详解
7.1 进入new XlsxSaxAnalyser(xlsxReadContext, null)方法看一下,这里使用到SAX模式模式解析excel
public XlsxSaxAnalyser(XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext, InputStream decryptedStream) throws Exception {
this.xlsxReadContext = xlsxReadContext;
// 初始化缓存(cache)
XlsxReadWorkbookHolder xlsxReadWorkbookHolder = xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadWorkbookHolder();
OPCPackage pkg = readOpcPackage(xlsxReadWorkbookHolder, decryptedStream);
xlsxReadWorkbookHolder.setOpcPackage(pkg);
// Read the Shared information Strings
PackagePart sharedStringsTablePackagePart = pkg.getPart(SHARED_STRINGS_PART_NAME);
if (sharedStringsTablePackagePart != null) {
// 指定默认缓存
defaultReadCache(xlsxReadWorkbookHolder, sharedStringsTablePackagePart);
// 分析sharedStringsTable.xml,解析excel所有数据到readCache
analysisSharedStringsTable(sharedStringsTablePackagePart.getInputStream(), xlsxReadWorkbookHolder);
}
XSSFReader xssfReader = new XSSFReader(pkg);
analysisUse1904WindowDate(xssfReader, xlsxReadWorkbookHolder);
// 设置样式表
setStylesTable(xlsxReadWorkbookHolder, xssfReader);
sheetList = new ArrayList<>();
sheetMap = new HashMap<>();
commentsTableMap = new HashMap<>();
Map packageRelationshipCollectionMap = MapUtils.newHashMap();
xlsxReadWorkbookHolder.setPackageRelationshipCollectionMap(packageRelationshipCollectionMap);
// 获取所有sheet页
XSSFReader.SheetIterator ite = (XSSFReader.SheetIterator)xssfReader.getSheetsData();
int index = 0;
if (!ite.hasNext()) {
throw new ExcelAnalysisException("Can not find any sheet!");
}
// 遍历sheet页
while (ite.hasNext()) {
InputStream inputStream = ite.next();
// 保存所有sheet页
sheetList.add(new ReadSheet(index, ite.getSheetName()));
// 保存所有sheet页的输入流
sheetMap.put(index, inputStream);
if (xlsxReadContext.readWorkbookHolder().getExtraReadSet().contains(CellExtraTypeEnum.COMMENT)) {
CommentsTable commentsTable = ite.getSheetComments();
if (null != commentsTable) {
commentsTableMap.put(index, commentsTable);
}
}
if (xlsxReadContext.readWorkbookHolder().getExtraReadSet().contains(CellExtraTypeEnum.HYPERLINK)) {
PackageRelationshipCollection packageRelationshipCollection = Optional.ofNullable(ite.getSheetPart())
.map(packagePart -> {
try {
return packagePart.getRelationships();
} catch (InvalidFormatException e) {
log.warn("Reading the Relationship failed", e);
return null;
}
}).orElse(null);
if (packageRelationshipCollection != null) {
packageRelationshipCollectionMap.put(index, packageRelationshipCollection);
}
}
index++;
}
} 7.2 进入analysisSharedStringsTable方法,可以看到创建了一个SharedStringsTableHandler处理器
7.3 再进入parseXmlSource看到xmlReader.setContentHandler(handler)这一行代码,设置了SharedStringsTableHandler处理器
private void parseXmlSource(InputStream inputStream, ContentHandler handler) {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
try {
SAXParserFactory saxFactory;
String xlsxSAXParserFactoryName = xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadWorkbookHolder().getSaxParserFactoryName();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(xlsxSAXParserFactoryName)) {
saxFactory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
} else {
saxFactory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance(xlsxSAXParserFactoryName, null);
}
try {
saxFactory.setFeature("http://apache.org/xml/features/disallow-doctype-decl", true);
} catch (Throwable ignore) {}
try {
saxFactory.setFeature("http://xml.org/sax/features/external-general-entities", false);
} catch (Throwable ignore) {}
try {
saxFactory.setFeature("http://xml.org/sax/features/external-parameter-entities", false);
} catch (Throwable ignore) {}
SAXParser saxParser = saxFactory.newSAXParser();
XMLReader xmlReader = saxParser.getXMLReader();
xmlReader.setContentHandler(handler);
xmlReader.parse(inputSource);
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException | ParserConfigurationException | SAXException e) {
throw new ExcelAnalysisException(e);
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ExcelAnalysisException("Can not close 'inputStream'!");
}
}
}
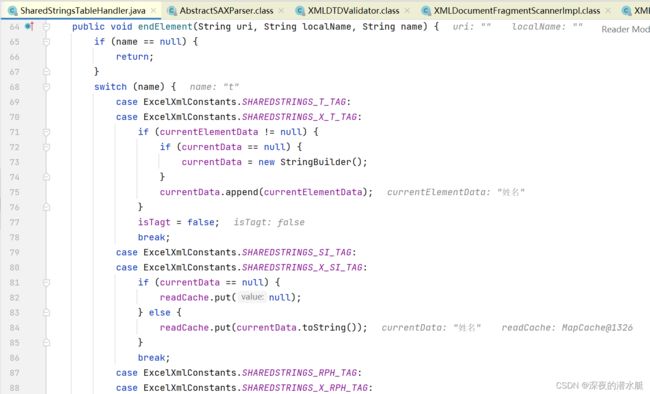
} 7.4 我们将断点打在SharedStringsTableHandler里,发现下一步进入到这里面的startElement()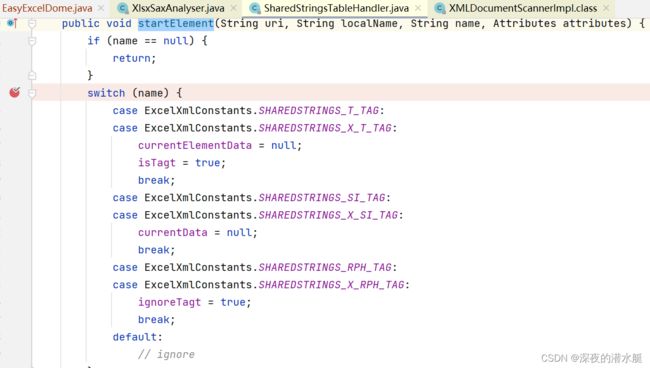
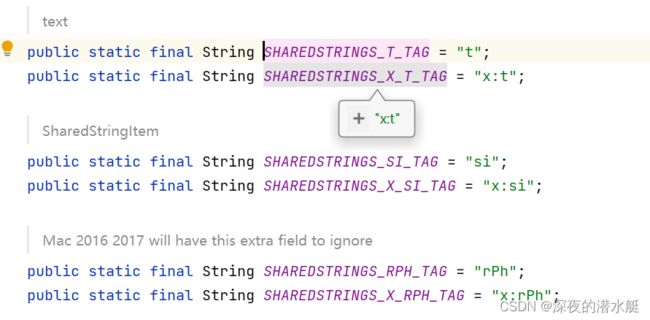 starteElement()后会调用endElement()
starteElement()后会调用endElement()
7.5 反复调用,excel所有数据读取到readcache中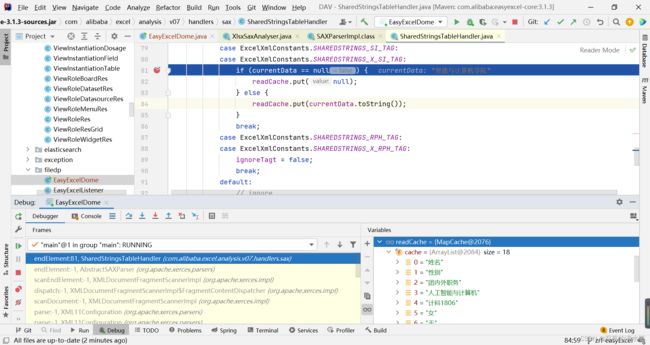
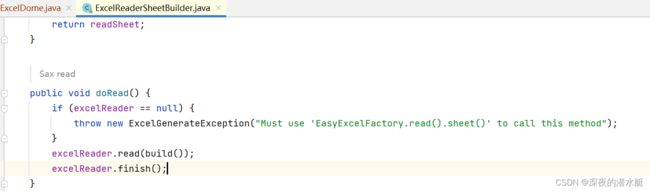
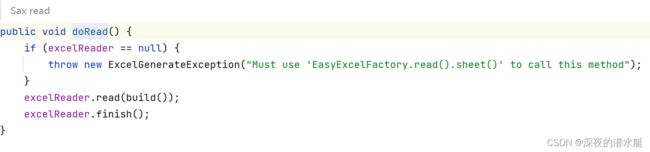
8.2 build()执行完后,执行read()方法,read()里还会进入一次read()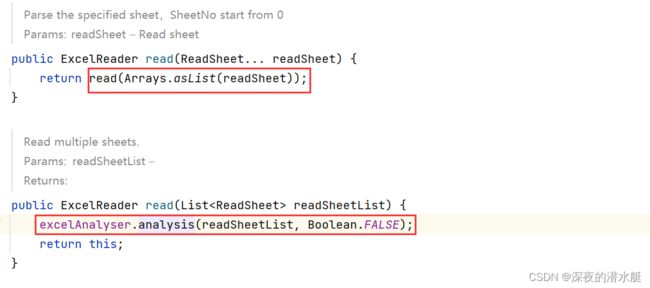
9. 调用ExcelAnalyserImpl里的analysis()方法,设置sheetList,并调用执行器开始执行解析 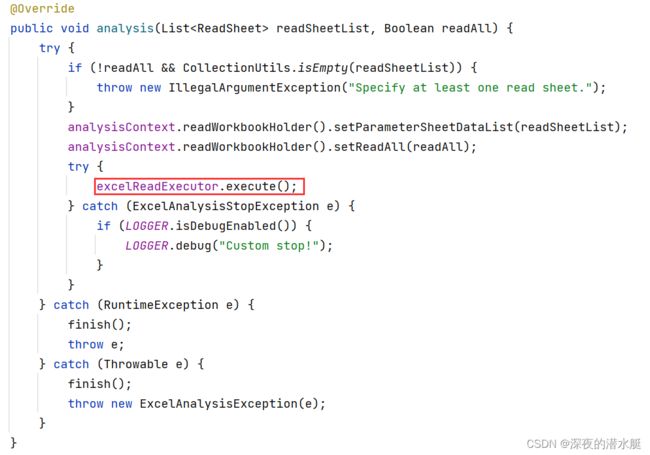
9.1 调用的XlsxSaxAnalyser解析器execute()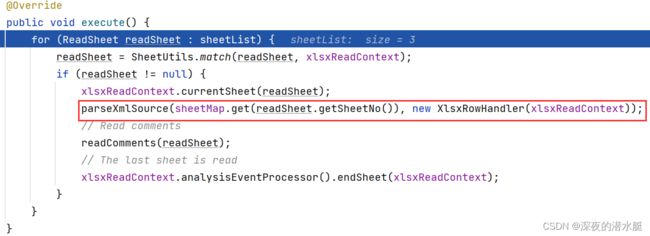
10. 进入parseXmlSource()方法,发现和之前的sax差不多,但只两次传入的handler类型不同,还是看一下传入的ContentHandler参数具体实现,进入XlsxRowHandler 内部
public class XlsxRowHandler extends DefaultHandler {
private final XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext;
private static final Map XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP = new HashMap(32);
static {
CellFormulaTagHandler cellFormulaTagHandler = new CellFormulaTagHandler();
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.CELL_FORMULA_TAG, cellFormulaTagHandler);
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.X_CELL_FORMULA_TAG, cellFormulaTagHandler);
CellInlineStringValueTagHandler cellInlineStringValueTagHandler = new CellInlineStringValueTagHandler();
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.CELL_INLINE_STRING_VALUE_TAG, cellInlineStringValueTagHandler);
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.X_CELL_INLINE_STRING_VALUE_TAG, cellInlineStringValueTagHandler);
CellTagHandler cellTagHandler = new CellTagHandler();
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.CELL_TAG, cellTagHandler);
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.X_CELL_TAG, cellTagHandler);
CellValueTagHandler cellValueTagHandler = new CellValueTagHandler();
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.CELL_VALUE_TAG, cellValueTagHandler);
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.X_CELL_VALUE_TAG, cellValueTagHandler);
CountTagHandler countTagHandler = new CountTagHandler();
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.DIMENSION_TAG, countTagHandler);
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.X_DIMENSION_TAG, countTagHandler);
HyperlinkTagHandler hyperlinkTagHandler = new HyperlinkTagHandler();
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.HYPERLINK_TAG, hyperlinkTagHandler);
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.X_HYPERLINK_TAG, hyperlinkTagHandler);
MergeCellTagHandler mergeCellTagHandler = new MergeCellTagHandler();
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.MERGE_CELL_TAG, mergeCellTagHandler);
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.X_MERGE_CELL_TAG, mergeCellTagHandler);
RowTagHandler rowTagHandler = new RowTagHandler();
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.ROW_TAG, rowTagHandler);
XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.put(ExcelXmlConstants.X_ROW_TAG, rowTagHandler);
}
public XlsxRowHandler(XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext) {
this.xlsxReadContext = xlsxReadContext;
}
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String name, Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
XlsxTagHandler handler = XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.get(name);
if (handler == null || !handler.support(xlsxReadContext)) {
return;
}
xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadSheetHolder().getTagDeque().push(name);
handler.startElement(xlsxReadContext, name, attributes);
}
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length) throws SAXException {
String currentTag = xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadSheetHolder().getTagDeque().peek();
if (currentTag == null) {
return;
}
XlsxTagHandler handler = XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.get(currentTag);
if (handler == null || !handler.support(xlsxReadContext)) {
return;
}
handler.characters(xlsxReadContext, ch, start, length);
}
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String name) throws SAXException {
XlsxTagHandler handler = XLSX_CELL_HANDLER_MAP.get(name);
if (handler == null || !handler.support(xlsxReadContext)) {
return;
}
handler.endElement(xlsxReadContext, name);
xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadSheetHolder().getTagDeque().pop();
}
} 10.1 startElement()和endElement()都有多种实现
11. 进入用到的重要的几个类CellTagHandler、RowTagHandler
CellTagHandler: 读取cell的值,并放入tempCellData
public void startElement(XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext, String name, Attributes attributes) {
XlsxReadSheetHolder xlsxReadSheetHolder = xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadSheetHolder();
xlsxReadSheetHolder.setColumnIndex(PositionUtils.getCol(attributes.getValue(ExcelXmlConstants.ATTRIBUTE_R),
xlsxReadSheetHolder.getColumnIndex()));
// t="s" ,it means String
// t="str" ,it means String,but does not need to be read in the 'sharedStrings.xml'
// t="inlineStr" ,it means String,but does not need to be read in the 'sharedStrings.xml'
// t="b" ,it means Boolean
// t="e" ,it means Error
// t="n" ,it means Number
// t is null ,it means Empty or Number
CellDataTypeEnum type = CellDataTypeEnum.buildFromCellType(attributes.getValue(ExcelXmlConstants.ATTRIBUTE_T));
xlsxReadSheetHolder.setTempCellData(new ReadCellData<>(type));
xlsxReadSheetHolder.setTempData(new StringBuilder());
// Put in data transformation information
String dateFormatIndex = attributes.getValue(ExcelXmlConstants.ATTRIBUTE_S);
int dateFormatIndexInteger;
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(dateFormatIndex)) {
dateFormatIndexInteger = DEFAULT_FORMAT_INDEX;
} else {
dateFormatIndexInteger = Integer.parseInt(dateFormatIndex);
}
xlsxReadSheetHolder.getTempCellData().setDataFormatData(
xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadWorkbookHolder().dataFormatData(dateFormatIndexInteger));
}
@Override
public void endElement(XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext, String name) {
XlsxReadSheetHolder xlsxReadSheetHolder = xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadSheetHolder();
ReadCellData tempCellData = xlsxReadSheetHolder.getTempCellData();
StringBuilder tempData = xlsxReadSheetHolder.getTempData();
String tempDataString = tempData.toString();
CellDataTypeEnum oldType = tempCellData.getType();
switch (oldType) {
case STRING:
// In some cases, although cell type is a string, it may be an empty tag
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(tempDataString)) {
break;
}
String stringValue = xlsxReadContext.readWorkbookHolder().getReadCache().get(
Integer.valueOf(tempDataString));
tempCellData.setStringValue(stringValue);
break;
case DIRECT_STRING:
case ERROR:
tempCellData.setStringValue(tempDataString);
tempCellData.setType(CellDataTypeEnum.STRING);
break;
case BOOLEAN:
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(tempDataString)) {
tempCellData.setType(CellDataTypeEnum.EMPTY);
break;
}
tempCellData.setBooleanValue(BooleanUtils.valueOf(tempData.toString()));
break;
case NUMBER:
case EMPTY:
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(tempDataString)) {
tempCellData.setType(CellDataTypeEnum.EMPTY);
break;
}
tempCellData.setType(CellDataTypeEnum.NUMBER);
tempCellData.setNumberValue(BigDecimal.valueOf(Double.parseDouble(tempDataString)));
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot set values now");
}
if (tempCellData.getStringValue() != null
&& xlsxReadContext.currentReadHolder().globalConfiguration().getAutoTrim()) {
tempCellData.setStringValue(tempCellData.getStringValue().trim());
}
tempCellData.checkEmpty();
tempCellData.setRowIndex(xlsxReadSheetHolder.getRowIndex());
tempCellData.setColumnIndex(xlsxReadSheetHolder.getColumnIndex());
xlsxReadSheetHolder.getCellMap().put(xlsxReadSheetHolder.getColumnIndex(), tempCellData);
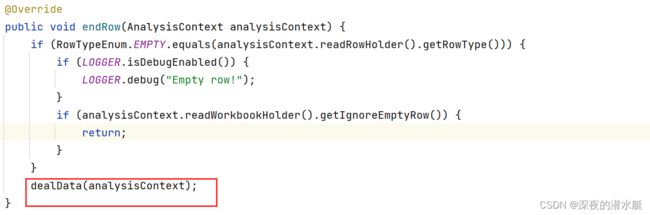
}RowTagHandler: 当一行读取完毕后,调用分析事件处理器,处理一行数据
xlsxReadContext.analysisEventProcessor().endRow(xlsxReadContext);
public void startElement(XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext, String name, Attributes attributes) {
XlsxReadSheetHolder xlsxReadSheetHolder = xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadSheetHolder();
int rowIndex = PositionUtils.getRowByRowTagt(attributes.getValue(ExcelXmlConstants.ATTRIBUTE_R),
xlsxReadSheetHolder.getRowIndex());
Integer lastRowIndex = xlsxReadContext.readSheetHolder().getRowIndex();
while (lastRowIndex + 1 < rowIndex) {
xlsxReadContext.readRowHolder(new ReadRowHolder(lastRowIndex + 1, RowTypeEnum.EMPTY,
xlsxReadSheetHolder.getGlobalConfiguration(), new LinkedHashMap()));
xlsxReadContext.analysisEventProcessor().endRow(xlsxReadContext);
xlsxReadSheetHolder.setColumnIndex(null);
xlsxReadSheetHolder.setCellMap(new LinkedHashMap());
lastRowIndex++;
}
xlsxReadSheetHolder.setRowIndex(rowIndex);
}
@Override
public void endElement(XlsxReadContext xlsxReadContext, String name) {
XlsxReadSheetHolder xlsxReadSheetHolder = xlsxReadContext.xlsxReadSheetHolder();
RowTypeEnum rowType = MapUtils.isEmpty(xlsxReadSheetHolder.getCellMap()) ? RowTypeEnum.EMPTY : RowTypeEnum.DATA;
// It's possible that all of the cells in the row are empty
if (rowType == RowTypeEnum.DATA) {
boolean hasData = false;
for (Cell cell : xlsxReadSheetHolder.getCellMap().values()) {
if (!(cell instanceof ReadCellData)) {
hasData = true;
break;
}
ReadCellData readCellData = (ReadCellData)cell;
if (readCellData.getType() != CellDataTypeEnum.EMPTY) {
hasData = true;
break;
}
}
if (!hasData) {
rowType = RowTypeEnum.EMPTY;
}
}
xlsxReadContext.readRowHolder(new ReadRowHolder(xlsxReadSheetHolder.getRowIndex(), rowType,
xlsxReadSheetHolder.getGlobalConfiguration(), xlsxReadSheetHolder.getCellMap()));
xlsxReadContext.analysisEventProcessor().endRow(xlsxReadContext);
xlsxReadSheetHolder.setColumnIndex(null);
xlsxReadSheetHolder.setCellMap(new LinkedHashMap<>());
} 13. 进入dealData()方法
private void dealData(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
ReadRowHolder readRowHolder = analysisContext.readRowHolder();
Map> cellDataMap = (Map)readRowHolder.getCellMap();
readRowHolder.setCurrentRowAnalysisResult(cellDataMap);
int rowIndex = readRowHolder.getRowIndex();
int currentHeadRowNumber = analysisContext.readSheetHolder().getHeadRowNumber();
boolean isData = rowIndex >= currentHeadRowNumber;
// Last head column
if (!isData && currentHeadRowNumber == rowIndex + 1) {
buildHead(analysisContext, cellDataMap);
}
// Now is data
for (ReadListener readListener : analysisContext.currentReadHolder().readListenerList()) {
try {
if (isData) {
readListener.invoke(readRowHolder.getCurrentRowAnalysisResult(), analysisContext);
} else {
readListener.invokeHead(cellDataMap, analysisContext);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
onException(analysisContext, e);
break;
}
if (!readListener.hasNext(analysisContext)) {
throw new ExcelAnalysisStopException();
}
}
} 14. 退回XlsxSaxAnalyser的解析器execute()方法
进入readComments()方法,读取额外信息(批注、超链接、合并单元格信息读取)
private void readComments(ReadSheet readSheet) {
if (!xlsxReadContext.readWorkbookHolder().getExtraReadSet().contains(CellExtraTypeEnum.COMMENT)) {
return;
}
CommentsTable commentsTable = commentsTableMap.get(readSheet.getSheetNo());
if (commentsTable == null) {
return;
}
Iterator cellAddresses = commentsTable.getCellAddresses();
while (cellAddresses.hasNext()) {
CellAddress cellAddress = cellAddresses.next();
XSSFComment cellComment = commentsTable.findCellComment(cellAddress);
CellExtra cellExtra = new CellExtra(CellExtraTypeEnum.COMMENT, cellComment.getString().toString(),
cellAddress.getRow(), cellAddress.getColumn());
xlsxReadContext.readSheetHolder().setCellExtra(cellExtra);
xlsxReadContext.analysisEventProcessor().extra(xlsxReadContext);
}
}
15. 最后进入.endSheet(xlsxReadContext)方法
@Override
public void endSheet(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
// 这里会调用所有监听器中的doAfterAllAnalysed方法,执行最后的操作
for (ReadListener readListener : analysisContext.currentReadHolder().readListenerList()) {
readListener.doAfterAllAnalysed(analysisContext);
}
}
16. 在读取完毕之后,执行finish()方法,关闭所有流