Java实现HTTP请求的几种方式-CloseableHttpClient(三)
文章目录
- 通过`Apache`封装好的`CloseableHttpClient`
-
- 引入jar包
- Post方式请求
-
- 关于设置连接超时时间connectTimeout不能设置超过20秒的问题
- Get方式请求
- 问题1:Connection Pool Shut down
- 问题2:返回出现中文问号或乱码的原因
- 其他阅读
通过Apache封装好的CloseableHttpClient
CloseableHttpClient是在HttpClient的基础上修改更新而来的,这里还涉及到请求头token的设置(请求验证),利用fastjson转换请求或返回结果字符串为json格式,当然上面两种方式也是可以设置请求头token、json的,这里只在下面说明。
引入jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponentsgroupId>
<artifactId>httpclientartifactId>
<version>4.5.13version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
dependency>
Post方式请求
基于第一章的测试接口,建立以下程序
- 创建客户端
- 设置HttpPost对象,包括URL,请求头
- 执行方法
- 响应体转化
请求代码:
@Service
@Slf4j
public class CloseableHttpClientService{
private static String tokenString = "";
private static String AUTH_TOKEN_EXPIRED = "AUTH_TOKEN_EXPIRED";
private final CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
//构造客户端对象
public CloseableHttpClientService(ObjectMapper objectMapper){
//1.生成HttpClient对象并设置参数
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
//设置客户端,如果无参数设置可以不用调setDefaultRequestConfig方法
RequestConfig build = RequestConfig.custom()
.setSocketTimeout(6000)
.setConnectTimeout(6000).build();
this.httpClient=HttpClientBuilder.create().setDefaultRequestConfig(build).build();
}
/**
* 以post方式调用第三方接口
* @param url
* @param param
* @return
*/
public <R> R doPost(String url, Object param,Class<R> returnType) throws IOException {
String json = "";
if(Objects.nonNull(param)){
json = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(param);
}
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
if (null != tokenString && tokenString.equals("")) {
tokenString = getToken();
}
//Authorization的header头,用于token验证使用
httpPost.addHeader("Authorization", tokenString);
httpPost.addHeader("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.81 Safari/537.36");
StringBuilder res= new StringBuilder();
//设置编码UTF-8,不然会出现问号
StringEntity se = new StringEntity(json,"UTF-8");
//经过验证,无用
//se.setContentEncoding("UTF-8");
//发送json数据需要设置contentType,否则提供者端提示请求类型not support
se.setContentType("application/json");
//设置请求参数
httpPost.setEntity(se);
//客户端设置了默认值,局部就无需再设置,除非有额外要求
/*RequestConfig build = RequestConfig.custom().setSocketTimeout(40000).setConnectTimeout(40000).build();
httpPost.setConfig(build);*/
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
if (Objects.nonNull(response) && response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
//返回json格式
res.append(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"));
}
//这里不需要手动调用httpClient.close(),因为EntityUtils.toString方法中会自动调用输入流的close方法
//直接调用httpClient.close()反而会再第二次调用时出现Collection Pool shut down的错误
R r = objectMapper.readValue(res.toString(), returnType);
return r;
}
/**
* 获取第三方接口的token
*/
public String getToken() {
String token = "";
Map<String,String> object = new HashMap<>();
object.put("userName", "xxx");
object.put("password", "xxx");
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8082/nacos-service-provider/auth/login");
httpPost.addHeader("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.81 Safari/537.36");
try {
StringEntity se = new StringEntity(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(object));
se.setContentEncoding("UTF-8");
//发送json数据需要设置contentType
se.setContentType("application/json");
//设置请求参数
httpPost.setEntity(se);
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
log.info(String.valueOf(response));
StringBuilder res= new StringBuilder();
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
//返回json格式
res.append(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"));
}
JsonResult jsonResult = objectMapper.readValue(res.toString(), JsonResult.class);
if (Objects.isNull(jsonResult) || !ReturnCode.SUCCESS.getCode().equals(jsonResult.getCode())) {
if (Objects.isNull(jsonResult)) {
throw new BizException(ReturnCode.ERROR);
} else {
throw new BizException(jsonResult.getCode(), jsonResult.getMessage());
}
}
LoginResponse loginResponse = objectMapper.convertValue(jsonResult.getData(), LoginResponse.class);
//这里可以把返回的结果按照自定义的返回数据结果,把string转换成自定义类
//ResultTokenBO result = JSONObject.parseObject(response, ResultTokenBO.class);
//把response转为jsonObject
/*JSONObject result = (JSONObject) JSONObject.parseObject(String.valueOf(response));
if (result.containsKey("token")) {
token = result.getString("token");
}*/
token = loginResponse.getToken();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return token;
}
}
测试程序:
/**
* 使用HttpURLConnection发送Post请求
*/
@SneakyThrows
public TestHttpAccessResponse sendHttpRequestByCloseableHttpClient() {
TestHttpAccessRequest request = new TestHttpAccessRequest();
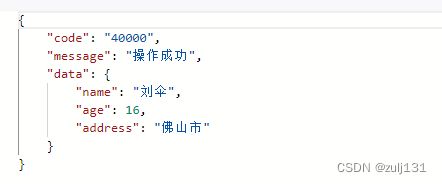
request.setAge(16);
request.setName("刘伞");
request.setAddress("佛山市");
String httpUrl = "http://localhost:8082/nacos-service-provider/testHttpAccess";
// String httpUrl = "http://198.168.22.11:8085/nacos-service-provider/testHttpAccess";
/**
* 如果是List这种带泛型的对象,则需要使用TypeReference<类型> typeRef = new TypeReference...
* 注意日期的类型,需要事前设置类型转换器
*/
JsonResult jsonResult = closeableHttpClientService.doPost(httpUrl, request, JsonResult.class);
if (Objects.isNull(jsonResult) || !ReturnCode.SUCCESS.getCode().equals(jsonResult.getCode())) {
if (Objects.isNull(jsonResult)) {
throw new BizException(ReturnCode.ERROR);
} else {
throw new BizException(jsonResult.getCode(), jsonResult.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 由于我做了统一的返回体JsonResult,所以还需要再转一遍
* 这里不封装进去是因为,除了JsonResult可能还会有其他的返回体
*/
TestHttpAccessResponse response = objectMapper.convertValue(jsonResult.getData(), TestHttpAccessResponse.class);
return response;
}
关于设置连接超时时间connectTimeout不能设置超过20秒的问题
设置connectTimeout有两种设置方法,一种是设置在客户端级别的,一种是设置在当次请求的。
如果当次请求HttpPost/HttpGet没有设置连接超时时间,那么将会使用客户端级别的值,不需要copy
我在设置连接超时时间时,发现了一个现象,connectTimeout最多只能20秒,超过20秒就会在20秒的时候抛出异常
当我设置了40秒连接超时,结果到20秒之后就抛出了org.apache.http.conn.HttpHostConnectException
如果是设置20秒以内的超时时间,就会抛出org.apache.http.conn.ConnectTimeoutException:
设置的timeout是不变的,追溯到PlainConnectionSocketFactory的代码,猜想应该是Socket内部的优化
@Override
public Socket connectSocket(
final int connectTimeout,
final Socket socket,
final HttpHost host,
final InetSocketAddress remoteAddress,
final InetSocketAddress localAddress,
final HttpContext context) throws IOException {
final Socket sock = socket != null ? socket : createSocket(context);
if (localAddress != null) {
sock.bind(localAddress);
}
try {
sock.connect(remoteAddress, connectTimeout);
} catch (final IOException ex) {
try {
sock.close();
} catch (final IOException ignore) {
}
throw ex;
}
return sock;
}
Get方式请求
基于第一章的测试接口和上面doPost的例子,建立以下程序
- 创建客户端
- 拼接URL参数
- 设置HttpGet对象,包括URL,请求头
- 执行方法
- 响应体转化
请求方法:
/**
* 以get方式调用第三方接口
* @param url
* @return
*/
public <R> R doGet(String url,Object param,Class<R> returnType) throws IOException, IllegalAccessException {
//拼接url参数
if(Objects.nonNull(param)){
List<String> params = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> clazz = param.getClass();
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
Object o = declaredField.get(param);
if (declaredField.getType().equals(String.class)) {
//这里拼接的时候注意要使用URL编码
String s = (String) declaredField.get(param);
s = URLEncoder.encode(s);
o = s;
}
params.add(declaredField.getName() + "=" + o);
}
String paramStr = params.stream().collect(Collectors.joining("&"));
url = url+"?"+paramStr;
}
//创建HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url);
if (null != tokenString && !tokenString.equals("")) {
tokenString = getToken();
}
//api_gateway_auth_token自定义header头,用于token验证使用
httpGet.addHeader("Authorization",tokenString);
//httpGet.addHeader("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.81 Safari/537.36");
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
StringBuilder res= new StringBuilder();
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
//返回json格式
res.append(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()));
}
R r = objectMapper.readValue(res.toString(), returnType);
return r;
}
测试程序:
/**
* 使用HttpURLConnection发送Post请求
*/
@SneakyThrows
public TestHttpAccessResponse sendHttpGetRequestByCloseableHttpClient() {
TestHttpAccessRequest request = new TestHttpAccessRequest();
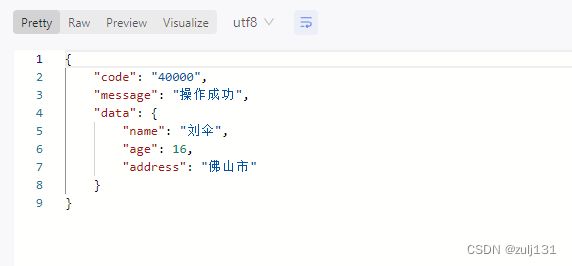
request.setAge(16);
request.setName("刘伞");
request.setAddress("佛山市");
String httpUrl = "http://localhost:8082/nacos-service-provider/testHttpAccessGet";
/**
* 如果是List这种带泛型的对象,则需要使用TypeReference<类型> typeRef = new TypeReference...
* 注意日期的类型,需要事前设置类型转换器
*/
JsonResult jsonResult = closeableHttpClientService.doGet(httpUrl, request, JsonResult.class);
if (Objects.isNull(jsonResult) || !ReturnCode.SUCCESS.getCode().equals(jsonResult.getCode())) {
if (Objects.isNull(jsonResult)) {
throw new BizException(ReturnCode.ERROR);
} else {
throw new BizException(jsonResult.getCode(), jsonResult.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 由于我做了统一的返回体JsonResult,所以还需要再转一遍
* 这里不封装进去是因为,除了JsonResult可能还会有其他的返回体
*/
TestHttpAccessResponse response = objectMapper.convertValue(jsonResult.getData(), TestHttpAccessResponse.class);
return response;
}
问题1:Connection Pool Shut down
这个问题是出现在,当我使用httpClient.close()方法之后,用相同的httpClient实例进行第二次请求就提示错误了。
CloseableHttpClient 采用的连接池管理,无需在业务代码中进行close资源回收。
问题2:返回出现中文问号或乱码的原因
首先设置StringEntity的编码有两种方式:
//第一种方式:后端无法解码
StringEntity stringEntity = new StringEntity(json);
stringEntity.setContentType("UTF-8");
//第二种方式:请求成功
StringEntity stringEntity = new StringEntity(json,"UTF-8");
这里我先说出我的实践结果:方式一出现问号,方式二可行。
先来看看这两种方式有什么不同。
第一种方式:
//这里设置了contentEncoding 属性
public void setContentEncoding(final String ceString) {
Header h = null;
if (ceString != null) {
h = new BasicHeader(HTTP.CONTENT_ENCODING, ceString);
}
//这里调用了上层的方法
setContentEncoding(h);
}
上层AbstractHttpEntity方法
public void setContentEncoding(final Header contentEncoding) {
this.contentEncoding = contentEncoding;
}
第二种方式:
//这里设置了contentType 属性
public StringEntity(final String string, final String charset)
throws UnsupportedCharsetException {
this(string, ContentType.create(ContentType.TEXT_PLAIN.getMimeType(), charset));
}
public StringEntity(final String string, final ContentType contentType) throws UnsupportedCharsetException {
super();
Args.notNull(string, "Source string");
Charset charset = contentType != null ? contentType.getCharset() : null;
if (charset == null) {
charset = HTTP.DEF_CONTENT_CHARSET;
}
this.content = string.getBytes(charset);
if (contentType != null) {
setContentType(contentType.toString());
}
}
上层AbstractHttpEntity方法
public void setContentType(final String ctString) {
Header h = null;
if (ctString != null) {
h = new BasicHeader(HTTP.CONTENT_TYPE, ctString);
}
setContentType(h);
}
public void setContentType(final Header contentType) {
this.contentType = contentType;
}
方式一设置属性contentEncoding
方式二设置属性contentType
而这两个属性的区别就在于,将HttpResponse的内容解析出Json的时候,我这边使用了EntityUtils.toString这个方法来解析,这个方法里面是从contentType 获取到编码的设置的,如果没有设置,将会使用默认编码"ISO-8859-1"
private static String toString(
final HttpEntity entity,
final ContentType contentType) throws IOException {
final InputStream inStream = entity.getContent();
if (inStream == null) {
return null;
}
try {
//....
//这里使用charset
Charset charset = null;
if (contentType != null) {
charset = contentType.getCharset();
if (charset == null) {
final ContentType defaultContentType = ContentType.getByMimeType(contentType.getMimeType());
charset = defaultContentType != null ? defaultContentType.getCharset() : null;
}
}
if (charset == null) {
charset = HTTP.DEF_CONTENT_CHARSET;
}
//...
} finally {
inStream.close();
}
}
所以如果没有使用方式二设置charset的话,就会设置为默认编码
其他阅读
Java实现HTTP请求的几种方式-HttpURLConnection(一)
Java实现HTTP请求的几种方式-Apache HttpClient(二)
Java实现HTTP请求的几种方式-RestTemplate(四)
Java实现HTTP请求的几种方式-OKHttp(五)