JavaSE-自定义队列+两栈实现队列+两队列实现栈
1.顺序队列实现
与栈一样,队列也是一种操作受限制的线性表,但与栈不同的是,栈是后进先出,队列的特点是先进先出。
实现与栈类似,队列有一个队头指针和一个队尾指针,入队的时候利用队尾指针进行尾插,出队的时候利用队头指针,把队头指针对应数组中的元素赋值为null,防止内存溢出。
class OrderQueue{
private int header; //队头位置
private int tail; //队尾位置
private int size; //有效元素
private T[] queueArrays;
private static final int defaultcapacity = 5;
public OrderQueue(){
this(defaultcapacity);
}
public OrderQueue(int capacity){
this.queueArrays = (T[])new Object[capacity];
}
//入队
public boolean enqueue(T value){
//判满
if(isFull()){
//扩容
if(size == queueArrays.length){
queueArrays = Arrays.copyOf(queueArrays, queueArrays.length*2);
}else{
System.arraycopy(queueArrays, header, queueArrays, 0, size);
}
}
queueArrays[tail++] = value;
size++;
return true;
}
public boolean isFull(){
return tail == queueArrays.length;
}
//出队
public T dequeue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("the queue has been empty");
}
T result = queueArrays[header];
queueArrays[header++] = null;
size--;
return result;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public void show(){
for(int i=header; i 2. 循环队列实现
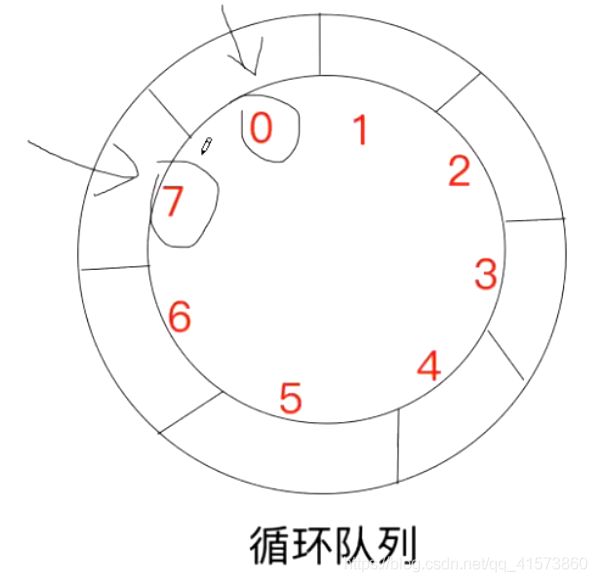
循环队列是把顺序队列首尾相连,把存储队列元素的表从逻辑上看成一个环,成为循环队列。图中有两个名义上的队头head队尾tail指向0和7。
对于循环队列存在一种特殊现象:假溢出。设队头指针为head,队尾指针是tail,约定head指向队头元素的前一位置,tail指向队尾元素。当head等于-1时队空,tail等于m-1时为队满。由于队列的性质(“删除”在队头而“插入”在队尾),所以当队尾指针tail等于m-1时,若head不等于-1,则队列中仍有空闲单元,所以队列并不是真满。这时若再有入队操作,会造成假“溢出”。
解决假溢出:
当添加一个元素时,(tail+1)%MAXSIZE;
当删除一个元素时,(head+1)%MAXSIZE;
当head=front的时候,队列可能是满,也可能是空。
因为存在满和空两种情况,需要分别判断:
满:当队列添加元素到tail的下一个元素是head的时候,也就是转圈子要碰头了,就认为队列满了。(Q.tail+1)%MAXSIZE=Q.head
空:当队列删除元素到head=rear的时候,认为队列空了。Q.tail==Q.head,不一定为0
实现过程:
class LoopQueue{
private int header; //队头位置
private int tail; //队尾位置
private T[] queueArrays;
private static final int defaultcapacity = 5;
public LoopQueue(){
this(defaultcapacity);
}
public LoopQueue(int capacity){
this.queueArrays = (T[])new Object[capacity];
}
//入队
public boolean enqueue(T value){
//判满
if(isFull()){
//扩容
queueArrays = Arrays.copyOf(queueArrays, queueArrays.length*2);
}
queueArrays[tail] = value;
tail = (tail+1) % queueArrays.length;
return true;
}
public boolean isFull(){
return (tail+1)%queueArrays.length == header;
}
//出队
public T dequeue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("the queue has been empty");
}
T result = queueArrays[header];
queueArrays[header] = null;
header = (header+1) % queueArrays.length;
return result;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return header == tail;
}
public void show(){
for(int i=header; i 3. 两个栈实现队列的入队出队
思路:首先定义两个栈,称为栈1和栈2,在进行入队操作的时候直接将元素入栈1,出栈的时候出栈2的栈顶,如果栈2为空的话就将栈1的元素入到栈2中,再进行出栈,两次入栈操作就能完成队列的先进先出操作,如果两个栈都为空的话就抛出异常。
public static Stack stack1 = new Stack<>();
public static Stack stack2 = new Stack<>();
public static void pushQueue(int value){
stack1.push(value);
}
public static int popQueue(){
if(stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty()){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("the stack has been empty");
}
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
} 4.两个队列实现栈的入栈出栈
思路:先定义两个队列,称为队1和队2,LinkedList类型是可以对两端进行操作的。入栈时,起初两个队列都为空,可以先将元素入队1,出队的时候将队1的元素用一个临时队列存储起来,将队中length-1个元素入到另一个临时队列,此时队列中还剩一个元素,对它进行出栈即可。
public static Queue queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
public static Queue queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
public static void pushStack(int value){
if(queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty()){
queue1.add(value);
}else if(queue1.isEmpty()){
queue2.add(value);
}else{
queue1.add(value);
}
}
public static int popStack(){
//popQueue是当前的数据队列
Queue popQueue = queue1.isEmpty() ? queue2 : queue1;
//pushQueue是当前的辅助队列
Queue pushQueue = queue1.isEmpty() ? queue1 : queue2;
while(popQueue.size() > 1){
pushQueue.add(popQueue.remove());
}
return popQueue.remove();
}