【每日一题】花期内花的数目+【差分数组】+【二分枚举】
文章目录
- Tag
- 题目来源
- 题目解读
- 解题思路
-
- 方法一:差分数组
- 方法二:二分查找
- 写在最后
Tag
【差分数组】【二分查找】【数组】【2023-09-28】
题目来源
2251. 花期内花的数目

题目解读
每朵花都有自己的花期,有些花的花期会有重叠,也就是说某些时刻会有多朵花同时开放,你需要找出在某些时刻花开的数量。
解题思路
解题的思路其实很明确,即确定某个时刻花开的数目即可。朴素的想法就是枚举的花,根据所有花的花期更新所有的时间点的花开数目。这种方法的最坏时间复杂度为 O(n^2), n n n 为数组 flowers 的长度,由于本题的数据规模达到 1 0 5 10^5 105,因此朴素方法一定超时。
方法一:差分数组
我们维护一个有序哈希表 cnts,表示某个时刻花开的数量(有序哈希表根据时间节点升序排序),我们枚举数组 flowers 中的每朵花 flower:
- 将花期的开始位置时刻(花开的时刻)的花开数量加一,即
++cnts[flower[0]]; - 将花期的开始位置时刻的下一时刻(花谢的下一个时刻)的花开数量减一,即
--cnts[flowers[1] + 1]。
我们对 flowers 中的每朵花都进行以上操作来更新 cnts。
为什么这样更新 cnts?因为这样,我们累加 cnts 的某个时刻的花开数量,即可得到某个时刻的所有花开数量。
我们以上更新的只是两种时刻的花开数量,即花开的时刻和花谢的下一个时刻,其他时刻的花开数量没有更新。因为我们只需要关注 “观赏者” 赏花的时刻,因此将 cnts 中没有覆盖到的观赏者赏花的时刻的花开数量进行更新。通过以下代码进行更新:
for (auto preson : presons) {
cnts[x]; // cnts 中没有键 x,就 cnts[x] = 0;否则不进行任何操作
}
然后,我们更新 cnts:
int t = 0;
for(auto &cnt : cnts){
cnt.second = (t += cnt.second);
}
t 表示当前花开的数目,这里我们利用的是差分数组的性质累加得到某个时刻花开的数目。
最后,输出对应时刻的花开数目到答案数组 res 中,并返回。
图解 cnts 的更新
现在以 示例 1 为例,来对以上的思路进行示例分析。
(1)flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], people = [2,3,7,11];
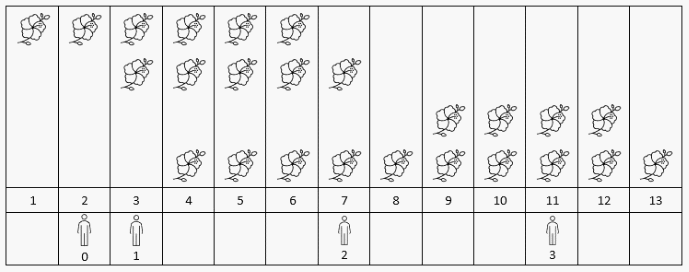
(2)遍历数组 flowers,更新得到的 cnts 如下图所示:

(3)将 cnts 中没有覆盖到的观赏者赏花的时刻的花开数量进行更新:

(4)最后累加更新 cnts。

实现代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> fullBloomFlowers(vector<vector<int>>& flowers, vector<int>& persons) {
map<int, int> cnts; // 统计每个时刻有几朵花开
for(auto &it : flowers){
++cnts[it[0]];
--cnts[it[1]+1];
}
for(auto x : persons){
cnts[x]; // 没有 cnts[x] 就设置 cnts[x] = 0;否则不用管
}
int t = 0;
for(auto &cnt : cnts){
cnt.second = (t += cnt.second);
}
vector<int> ret;
for(auto &x : persons){
ret.push_back(cnts[x]);
}
return ret;
}
};
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O ( n l o g n + m l o g m ) O(nlogn+mlogm) O(nlogn+mlogm), n n n 为数组 flowers 的长度。cnts 是有序哈希表,每次插入的时间为 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn),一共插入 n 个元素,构建有序集合的时间为 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)。 m m m 为数组 presons 的长度,插入 m 个元素到有序哈希表中的时间复杂度为 O ( m l o g m ) O(mlogm) O(mlogm)。
空间复杂度: O ( n + m ) O(n+m) O(n+m)。
方法二:二分查找
设:第 i 个人到达的时间为 presons[i],在 presons[i] 时间点之前的花开数目为 x,在 presons[i] 时间点之前的花谢的数目为 y。则,presons[i] 时间点还处于开花状态的花数目为 x - y。
x 即为 start <= presons[i] 的花朵数目,y 即为 end < presons[i] 的花朵数目。
根据以上的分析,我们可以单独统计起始时间 start 和 结束时间 end,利用二分查找快速查找结果:
- 首先,将所有的
start和end进行升序排序; - 利用二分查找到 s t a r t i < = p e r s o n s [ i ] start_i <= persons[i] starti<=persons[i] 的花朵数目
x,利用二分查找到 e n d i < = p e r s o n s [ i ] end_i <= persons[i] endi<=persons[i] 的花朵数目y,则第i个人可以看到的花朵数目为x - y; - 依次遍历并统计每个人的查询结果。
实现代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> fullBloomFlowers(vector<vector<int>>& flowers, vector<int>& people) {
vector<int> start, end;
for (auto flower : flowers) {
start.push_back(flower[0]);
end.push_back(flower[1]);
}
sort(start.begin(), start.end());
sort(end.begin(), end.end());
int m = people.size();
vector<int> res(m);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x = upper_bound(start.begin(), start.end(), people[i]) - start.begin();
int y = lower_bound(end.begin(), end.end(), people[i]) - end.begin();
res[i] = x - y;
}
return res;
}
};
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: O ( ( n + m ) l o g n ) O((n+m)logn) O((n+m)logn), n n n 为数组 flowers 的长度, m m m 为数组 presons 的长度。对 start,end 排序的时间复杂度为 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn);对每个人进行二分查找的时间为 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn),有 m 个人,因此二分查找总时间复杂度为 O ( m l o g n ) O(mlogn) O(mlogn);所以总的时间复杂度为 O ( ( n + m ) l o g n ) O((n+m)logn) O((n+m)logn)。
空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),使用的额外空间为 start 和 end 数组,这两个数组排序使用的额外空间为 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn),因此总的空间复杂度为 O ( n ) + O ( l o g n ) = O ( n ) O(n) + O(logn) = O(n) O(n)+O(logn)=O(n)。
写在最后
如果文章内容有任何错误或者您对文章有任何疑问,欢迎私信博主或者在评论区指出 。
如果大家有更优的时间、空间复杂度方法,欢迎评论区交流。
最后,感谢您的阅读,如果感到有所收获的话可以给博主点一个 哦。