第 364 场 LeetCode 周赛题解
A 最大二进制奇数
降序排序字符串,然后将最后一个
1与最后一位交换
class Solution {
public:
string maximumOddBinaryNumber(string s) {
sort(s.begin(), s.end(), greater<>());
for (int i = s.size() - 1;; i--)
if (s[i] == '1') {
swap(s[i], s.back());
break;
}
return s;
}
};
B 美丽塔 I
枚举: 枚举山状数组的最大值的下标 i i i,然后遍历两端 [ 0 , i ) [0,i) [0,i) 和 ( i , n − 1 ] (i,n-1] (i,n−1] ,求各位置能达到的最大高度
class Solution {
public:
using ll = long long;
long long maximumSumOfHeights(vector<int> &maxHeights) {
int n = maxHeights.size();
ll res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ll cur = maxHeights[i];
for (int j = i - 1, last = maxHeights[i]; j >= 0; j--) {
last = min(last, maxHeights[j]);
cur += last;
}
for (int j = i + 1, last = maxHeights[i]; j < n; j++) {
last = min(last, maxHeights[j]);
cur += last;
}
res = max(res, cur);
}
return res;
}
};
C 美丽塔 II
单调栈+枚举:设 l [ i ] l[i] l[i] 为当 h e i g h t s [ i ] = m a x H e i g h t s [ i ] heights[i]=maxHeights[i] heights[i]=maxHeights[i] 时 ∑ k = 0 i h e i g h t s [ k ] \sum_{k=0}^i heights[k] ∑k=0iheights[k] 的最大值,类似地设 r [ i ] r[i] r[i] 为当 h e i g h t s [ i ] = m a x H e i g h t s [ i ] heights[i]=maxHeights[i] heights[i]=maxHeights[i] 时 ∑ k = i h e i g h t s . s i z e ( ) − 1 h e i g h t s [ k ] \sum_{k=i}^{heights.size()-1} heights[k] ∑k=iheights.size()−1heights[k] 的最大值,用单调栈预先求出 l l l 和 r r r 数组,答案即为: m a x { l [ i ] + r [ i ] − m a x H e i g h t s [ i ] ∣ 0 ≤ i < n } max\{ l[i]+r[i]-maxHeights[i] \; | \; 0\le i< n \} max{l[i]+r[i]−maxHeights[i]∣0≤i<n}
class Solution {
public:
using ll = long long;
long long maximumSumOfHeights(vector<int> &maxHeights) {
int n = maxHeights.size();
vector<ll> l(n), r(n);
stack<int> st;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!st.empty() && maxHeights[st.top()] > maxHeights[i])//栈顶位置最大高度大于当前位置最大高度则需要出栈
st.pop();
l[i] = st.empty() ? 1LL * (i + 1) * maxHeights[i] : l[st.top()] + 1LL * (i - st.top()) * maxHeights[i];
st.push(i);
}
st = stack<int>();
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (!st.empty() && maxHeights[st.top()] > maxHeights[i])//栈顶位置最大高度大于当前位置最大高度则需要出栈
st.pop();
r[i] = st.empty() ? 1LL * (n - i) * maxHeights[i] : r[st.top()] + 1LL * (st.top() - i) * maxHeights[i];
st.push(i);
}
ll res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
res = max(res, l[i] + r[i] - maxHeights[i]);
return res;
}
};
D 统计树中的合法路径数目
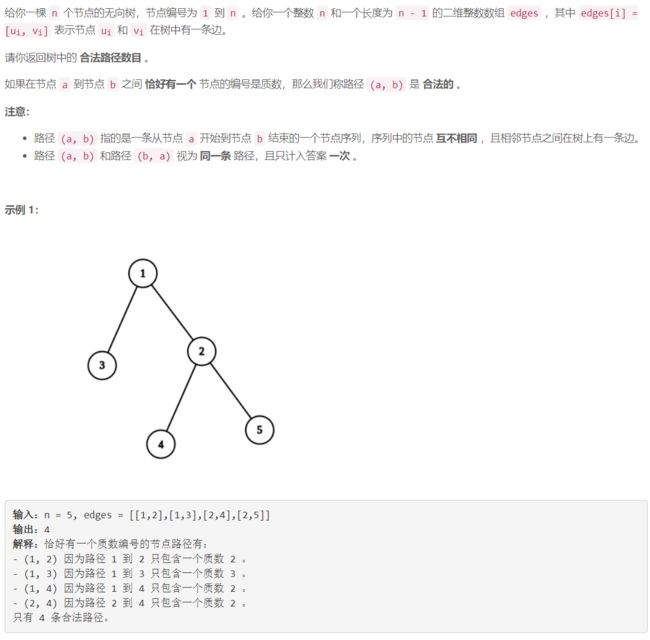
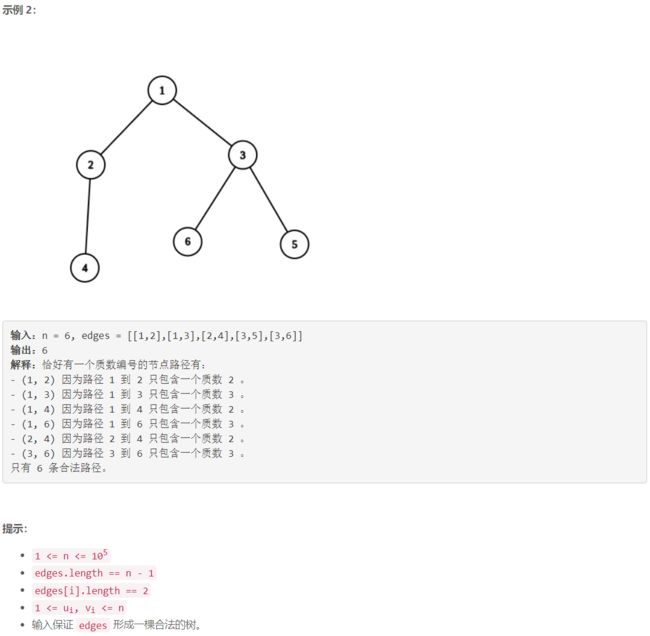
计数+ d f s dfs dfs:设一个质数点 r o o t root root 的 v v v 集合为: { 从 u 出发只通过非质数点能到达的非质数点的数目 ∣ u 是 r o o t 的邻接点 } \{ 从u出发只通过非质数点能到达的非质数点的数目 | u是root的邻接点 \} {从u出发只通过非质数点能到达的非质数点的数目∣u是root的邻接点},例如下图中 r o o t root root 的 v v v 集合为 { 1 , 2 , 3 } \{1,2,3 \} {1,2,3}。
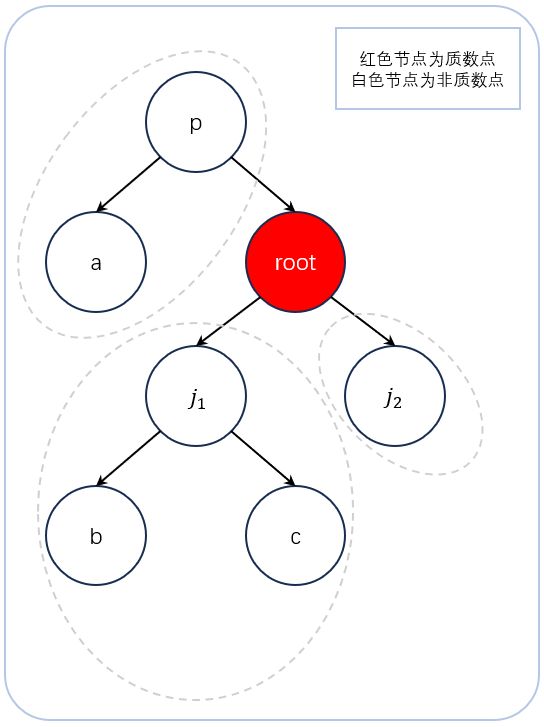
知道 r o o t root root 的 v v v 集合后,则树中含 r o o t root root 的合法路径可分为两类:
- 一个端点为 r o o t root root 的路径,这类路径数为: ∑ v i ∈ v v i \sum_{v_i\in v} v_i ∑vi∈vvi
- 两个端点都不为 r o o t root root 的路径,这类路径数为: 1 2 ∑ v i ∈ v ∑ j ≠ i v i v j = 1 2 ( ( ∑ v i ∈ v v i ) 2 − ∑ v i ∈ v v i 2 ) \frac 1 2 \sum_{v_i\in v} \sum_{j\ne i} v_iv_j=\frac 1 2 \left ( ( \sum_{v_i\in v} v_i )^2 -\sum_{v_i\in v} v_i^2 \right ) 21∑vi∈v∑j=ivivj=21((∑vi∈vvi)2−∑vi∈vvi2)
不妨以 1 1 1 为树根,首先通过 d f s dfs dfs 计算 c n t _ n p cnt\_np cnt_np 数组: c n t _ n p [ i ] cnt\_np[i] cnt_np[i] 为以 i i i 为根的子树中从 i i i 出发只通过非质数点能到达的非质数点的数目。然后再次 d f s dfs dfs ,并在遍历过程中记录“从当前节点的父节点出发(且不经过当前节点)只通过非质数点能到达的非质数点的数目”,这样每到达一个质数点,就能求出它的 v v v 集合,从而计算含该点的合法路径数。
class Solution {
public:
using ll = long long;
long long countPaths(int n, vector<vector<int>> &edges) {
vector<int> isp(n + 1, 1);//isp[i]:i是否是质数
isp[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {//预处理判断数是否是质数
for (int j = 2; j * j <= i; j++)
if (i % j == 0) {
isp[i] = 0;
break;
}
}
vector<vector<int>> e(n + 1);
for (auto &ei: edges) {//建图
e[ei[0]].push_back(ei[1]);
e[ei[1]].push_back(ei[0]);
}
vector<ll> cnt_np(n + 1);//以i为根的子树中从i出发只通过非质数点到达的非质数点的数目
function<int(int, int)> comp_path = [&](int root, int p) {//当前点为root,父节点为p
if (isp[root]) {//当前点为质数点
cnt_np[root] = 0;
for (auto j: e[root])
if (j != p)
comp_path(j, root);
} else {//当前点非质数点
cnt_np[root] = 1;
for (auto j: e[root])
if (j != p)
cnt_np[root] += comp_path(j, root);
}
return cnt_np[root];
};
comp_path(1, 0);
ll res = 0;
function<void(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int root, int p, int up) {//当前点为root,父节点为p,up:从p出发(且不经过当前节点)只通过非质数点能到达的非质数点的数目
if (isp[root]) {//当前点为质数点
vector<ll> v;// v集合
if (up != 0)
v.push_back(up);
for (auto j: e[root])
if (j != p) {
dfs(j, root, 0);
if (cnt_np[j])
v.push_back(cnt_np[j]);
}
ll s = 0, s2 = 0;
for (auto it: v) {
s += it;
s2 += it * it;
}
res += s + (s * s - s2) / 2;//+=含当前质数点的合法路径数目
} else {//当前点非质数点
ll s = up + 1;
for (auto j: e[root])
if (j != p && cnt_np[j])
s += cnt_np[j];
for (auto j: e[root])
if (j != p)
dfs(j, root, s - cnt_np[j]);
}
};
dfs(1, 0, 0);
return res;
}
};