网络-fetch
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、fetch简介
-
- 优点:
- 缺点:
- 二、使用
-
- get
- post
- 进度实现
- 取消请求
- 超时实现
- 总结
前言
本文主要记录浏览器与服务端网络通讯 fetch 的介绍与使用,将完成get、post、进度、取消请求、和超时请求的功能实现。
一、fetch简介
fetch作为继XMLHttpRequest的网络通讯手段,在使用方面极大的简化了使用方法,通过直观的语义化调用方式让代码更具有可读性,但是它对于一些复杂问题确实有待提高,也有一些实验性的更新还在尝试,如获取请求进度、设置超时时间、中断请求等,他自身都不能完成,需要借助外界的力量。
优点:
- 简洁易用:Fetch API提供了一种简洁的方式来发送网络请求,使用起来非常直观和易于理解。它使用了Promise和链式调用的方式,使得代码更加清晰和可读。
- 强大灵活:Fetch API支持发送不同类型的请求,如GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等,可以满足各种不同的需求。它还支持设置请求头、发送FormData、上传文件等功能,提供了更多的灵活性和功能性。
- 支持异步编程:Fetch API基于Promise,可以使用异步编程的方式处理请求和响应。这使得我们可以更好地处理异步操作,避免回调地狱和复杂的嵌套结构。
- 内置的错误处理:Fetch API内置了错误处理机制,可以通过.catch()方法捕获和处理请求过程中的错误。这使得我们可以更好地处理网络请求中可能出现的问题,提高了代码的健壮性和可靠性。
- 跨域请求支持:Fetch API支持跨域请求,可以发送跨域请求并处理响应。这对于开发跨域应用或与不同域的API进行通信非常有用。
缺点:
- 兼容性问题:Fetch API在一些旧版本的浏览器中可能不被完全支持。特别是在IE浏览器中,需要使用Polyfill或者其他库来提供兼容性支持。
- 不支持取消请求:Fetch API目前不支持取消请求的功能。一旦请求被发送出去,就无法中止或取消。这可能会导致一些问题,特别是在需要处理大量请求或需要及时取消请求的情况下。
- 不支持超时设置:Fetch API也不支持设置请求的超时时间。如果需要在一定时间内没有响应时取消请求,需要使用其他方式来实现,如使用AbortController和AbortSignal。
- 无法直接获取请求进度:Fetch API没有提供直接获取请求进度的功能。如果需要获取请求的进度信息,如上传或下载的进度,需要使用其他方式来实现,如使用XMLHttpRequest或其他库。
- 缺乏一些高级功能:相比于一些第三方库,Fetch API在一些高级功能方面可能有所欠缺。例如,它没有提供自动的请求重试、请求拦截、请求缓存等功能,需要自行实现或使用其他库来满足需求。
二、使用
不用像XMLHttpreques,需要先构造一个XMLHttpreques对象。fetch直接可以使用,就直接 fetch() 使用就行,可以传递;两个参数,参数二在get请求时可不传,fetch默认发送get请求。
- 参数1:url 请求地址
- 参数2:对象,对象包括请求方式、头部、请求体
{
method:'post',
headers:{
'Content-Type':'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
name:'smz'
})
}
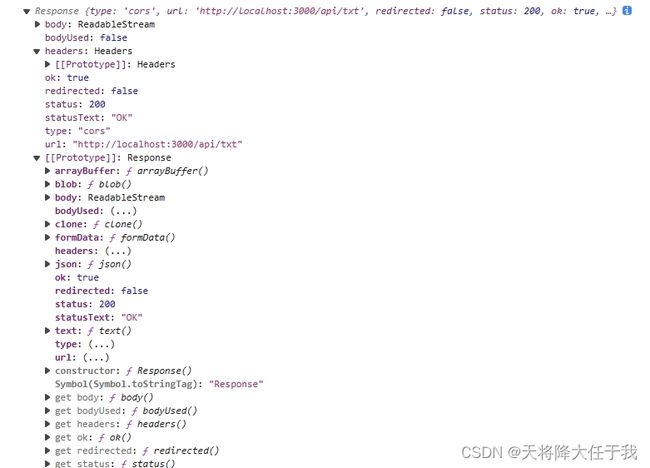
fetch在第一个then返回的是一个promise ===> fetch的response对象,并不是结果,在这个对象里面包括了请求状态、信息、方法等。在这里需要设置一下返回数据的格式,这个一般和后端沟通好。对请求做处理大都是在这里进行的。
response对象
返回格式:
text():将响应体解析为纯文本字符串并返回json():将响应体解析为JSON格式并返回一个JS对象blob():将响应体解析为二进制数据并返回一个Blob对象arrayBuffer():将响应体解析为二进制数据并返回一个ArrayBuffer对象formData():将响应体解析为FormData对象
在第二个then中,才是返回的数据,当然,可以通过链式调用catch来处理请求中发生的错误。
下面就进入使用吧。
get
get请求时,第二个参数可不传,默认就是get请求,当然你需要添加请求头之类的可以传第二个参数,这里需要注意的是第一个then里面需要指定返回数据的格式,上面已经给出了几种格式。遇到跨域问题可以看我这个文章 跨域解决 给出了几个跨域的解决方案。
fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/txt').then(response=>{
console.log(response)
//指定返回的格式
return response.text()
}).then(data=>{
console.log(data)
}).catch(error => {
// 处理错误
console.error(error);
});
post
post请求只要将第二个参数中method属性改为post,headers属性是设置请求头的,body是请求体也就是带的数据。
fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/txt',
{
method:'post',
headers:{
'Content-Type':'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
name:'smz'
}),
}
).then(response=>{
console.log(response)
//指定返回的格式
return res.json()
}).then(data=>{
console.log(data)
}).catch(error => {
// 处理错误
console.error(error);
});
进度实现
在fetch中没有像 XMLHttpReques 中 progress事件的loaded和total属性用来监听请求的进度,所以这个功能只能自己实现。实现思路大致如下:
- 在第一个
then中利用response.body.getReader()返回一个流
// 返回一个流
const reader = response.body.getReader()
- 利用
response.headers.get('Content-Length')获取资源总长度
// 响应头上有总长度信息
const total = response.headers.get('Content-Length')
- 循环流分片,利用
reader.read()得到请求信息,计算当前进度,并传递给元素
每个分片利用reader.read()会得到done和value,done表示是否完成,value表示当前长度。
let loaded = 0
while (true){
const {done,value} = await reader.read()
if (done){
break
}
loaded += value.length// 当前进度
console.log(loaded)
const progress = document.getElementById('progress')
progress.innerHTML = `${(loaded/total*100).toFixed(2)+ '%'}`
}
这里需要注意因为response被getReader()占用了,所以需要提前拷贝一份response,返回用拷贝的response
const res = response.clone()// 拷贝一份,因为被getReader()占用
return res.text()
完整代码:
fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/txt').then(async response=>{
console.log(response)
const res = response.clone()// 拷贝一份,因为被getReader()占用
// 返回一个流
const reader = response.body.getReader()
// 响应头上有总长度信息
const total = response.headers.get('Content-Length')
let loaded = 0
while (true){
const {done,value} = await reader.read()
if (done){
break
}
loaded += value.length// 当前进度
console.log(loaded)
const progress = document.getElementById('progress')
progress.innerHTML = `${(loaded/total*100).toFixed(2)+ '%'}`
}
//指定返回的格式
return res.text()
}).then(data=>{
console.log(data)
}).catch(error => {
// 处理错误
console.error(error);
});
取消请求
同样在fetch中是无法通过它内部API实现请求的中断的,需要借助AbortController和AbortSignal对象来实现请求中断。
- 创建了一个
AbortController对象
在请求外部创建AbortController对象
const controller = new AbortController();
- 通过
controller.signal获取对应的AbortSignal对象。
const signal = controller.signal
- 将
AbortSignal对象作为Fetch请求的signal选项传递给fetch函数
fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/txt',
{
signal // AbortSignal对象
}
)
- 调用
controller.abort()方法,触发AbortSignal对象的abort事件,终止Fetch请求
stop.addEventListener('click',()=>{
// 终止请求
controller.abort();
})
- 在请求被终止后,进入
catch块,进行错误处理。
需要注意的是,终止请求后,Fetch请求的Promise会被拒绝,并且会抛出一个AbortError错误。因此,在处理错误时,可以通过判断错误类型为AbortError来区分是否是请求被终止的情况。
catch(error => {
// 处理错误
if (error.name === 'AbortError'){// 中断请求
alert('请求被终止')
}else {
console.error(error);
}
});
使用AbortController和AbortSignal可以灵活地控制和终止Fetch请求,特别适用于需要及时取消请求的场景,如用户取消操作或超时处理。
超时实现
fetch也是不能设置超时时间的。
先定义一个自定义错误,用来标识超时错误
class TimeoutError extends Error {
constructor(message = '请求超时') {
super(message)
this.name = 'TimeoutError'
}
}
超时有两种办法:
- 使用setTimeout和AbortController实现
在指定的时间内调用请求终止 controller.abort();
function fetchWithTimeout(url, timeout) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 创建一个AbortController对象
const controller = new AbortController();
const signal = controller.signal;
// 设置超时定时器
const timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
// 终止请求
controller.abort();
reject(new TimeoutError();
}, timeout);
fetch(url, { signal })
.then(response => {
clearTimeout(timeoutId); // 清除超时定时器
resolve(response);
})
.catch(error => {
clearTimeout(timeoutId); // 清除超时定时器
reject(error);
});
});
}
- 使用setTimeout和Promise.race方法实现
定义好一个超时promise对象,利用Promise.race()方法返回 超时promise和请求promise对象第一个完成的状态。
function fetchWithTimeout2(url, timeout) {
const fetchPromise = fetch(url);
const timeoutPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// 终止请求
controller.abort();
reject(new TimeoutError());
}, timeout);
});
// 使用Promise.race方法,同时等待fetchPromise和timeoutPromise
return Promise.race([fetchPromise, timeoutPromise]);
}
两种方式使用就和fetch使用方式一样。
// fetchWithTimeout('http://localhost:3000/api/txt', 3000)
fetchWithTimeout2('http://localhost:3000/api/txt', 3000)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
})
.catch(error => {
if (error.name === 'TimeoutError'){
alert('请求超时,请重试')
}else {
console.error(error);
}
});
方式二这里只能将超时实现,并不能将请求杀死,请求还会继续进行,直到后端处理了该请求
完整代码:
// 超时设置
// 自定义错误
class TimeoutError extends Error {
constructor(message = '请求超时') {
super(message)
this.name = 'TimeoutError'
}
}
// 方案一
function fetchWithTimeout(url, timeout) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 创建一个AbortController对象
const controller = new AbortController();
const signal = controller.signal;
// 设置超时定时器
const timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
// 请求中断
controller.abort();
reject(new TimeoutError());
}, timeout);
fetch(url, { signal })
.then(response => {
clearTimeout(timeoutId); // 清除超时定时器
resolve(response);
})
.catch(error => {
clearTimeout(timeoutId); // 清除超时定时器
reject(error);
});
});
}
// 方案二
function fetchWithTimeout2(url, timeout) {
const fetchPromise = fetch(url);
const timeoutPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// 超时
reject(new TimeoutError());
}, timeout);
});
// 使用Promise.race方法,同时等待fetchPromise和timeoutPromise
return Promise.race([fetchPromise, timeoutPromise]);
}
const overtime = ()=>{
// fetchWithTimeout('http://localhost:3000/api/txt', 300)
fetchWithTimeout2('http://localhost:3000/api/txt', 300)
.then(response => response.text())
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
})
.catch(error => {
if (error.name === 'TimeoutError'){
alert('请求超时,请重试')
}else {
console.error(error);
}
});
}
总结
fetch请求目前来说处理简单请求,日后等fetch API完善吧。其他复杂的请求还是使用ajax来完成,而且还有axios对ajax做了封装。这里值得一提的是XMLHttpReques已经不再更新了。