Redis相关-03
Redis相关-03
- Redis配置文件详解
- 持久化——RDB操作
- 持久化——AOF操作
- Redis订阅发布
- Redis集群环境搭建
- 主从复制
- 宕机手动配置主机
- 哨兵模式
- 缓存穿透以及雪崩
一、Redis配置文件详解
1、单位说明:
# Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specify
# it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth:
#
# 1k => 1000 bytes
# 1kb => 1024 bytes
# 1m => 1000000 bytes
# 1mb => 1024*1024 bytes
# 1g => 1000000000 bytes
# 1gb => 1024*1024*1024 bytes
#
# units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same.
2、可以引用其他配置文件:
# Note that option "include" won't be rewritten by command "CONFIG REWRITE"
# from admin or Redis Sentinel. Since Redis always uses the last processed
# line as value of a configuration directive, you'd better put includes
# at the beginning of this file to avoid overwriting config change at runtime.
#
# If instead you are interested in using includes to override configuration
# options, it is better to use include as the last line.
#
include /path/to/local.conf
include /path/to/other.conf
3、绑定host说明:
默认绑定host为127.0.0.1,即仅限本机访问redis服务,将其注释掉为远程访问Redis的充分条件之一,同时,可以绑定多个host。
# By default, if no "bind" configuration directive is specified, Redis listens
# for connections from all available network interfaces on the host machine.
# It is possible to listen to just one or multiple selected interfaces using
# the "bind" configuration directive, followed by one or more IP addresses.
#
# Examples:
#
bind 192.168.1.100 10.0.0.1
bind 127.0.0.1 ::1
#
# ~~~ WARNING ~~~ If the computer running Redis is directly exposed to the
# internet, binding to all the interfaces is dangerous and will expose the
# instance to everybody on the internet. So by default we uncomment the
# following bind directive, that will force Redis to listen only on the
# IPv4 loopback interface address (this means Redis will only be able to
# accept client connections from the same host that it is running on).
#
# IF YOU ARE SURE YOU WANT YOUR INSTANCE TO LISTEN TO ALL THE INTERFACES
# JUST COMMENT OUT THE FOLLOWING LINE.
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
bind 127.0.0.1
4、保护模式(protected-mode):
一般将其关闭允许远程访问
# Protected mode is a layer of security protection, in order to avoid that
# Redis instances left open on the internet are accessed and exploited.
#
# When protected mode is on and if:
#
# 1) The server is not binding explicitly to a set of addresses using the
# "bind" directive.
# 2) No password is configured.
#
# The server only accepts connections from clients connecting from the
# IPv4 and IPv6 loopback addresses 127.0.0.1 and ::1, and from Unix domain
# sockets.
#
# By default protected mode is enabled. You should disable it only if
# you are sure you want clients from other hosts to connect to Redis
# even if no authentication is configured, nor a specific set of interfaces
# are explicitly listed using the "bind" directive.
protected-mode no
5、端口号:
即Redis远程访问或本地访问的端口号
# Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379 (IANA #815344).
# If port 0 is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket.
port 6379
6、守护进程:
开启表示允许后台运行,除非服务器关闭
################################# GENERAL #####################################
# By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it.
# Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemonized.
daemonize yes
7、pid进程文件:
即Redis运行时产生的进程文件,在做单机模拟集群的时候需要做出响应更改便于区分不同的Redis服务器
# If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup
# and removes it at exit.
#
# When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is
# specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid file
# is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid".
#
# Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it
# nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally.
pidfile /var/run/redis/redis.pid
8、日志输出等级与输出位置:
在做单机模拟集群的时候需要做出响应更改便于区分不同的Redis服务器
# Specify the server verbosity level.
# This can be one of:
# debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing)
# verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level)
# notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably)
# warning (only very important / critical messages are logged)
loglevel notice
# Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force
# Redis to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard
# output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null
logfile /usr/local/redis/var/redis.log
9、快照写入保存:
# save
即经过多少秒,判断至少有多少键被更改则将数据库中的数据写入快照进行保存
################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################
#
# Save the DB on disk:
#
# save
#
# Will save the DB if both the given number of seconds and the given
# number of write operations against the DB occurred.
#
# In the example below the behavior will be to save:
# after 900 sec (15 min) if at least 1 key changed
# after 300 sec (5 min) if at least 10 keys changed
# after 60 sec if at least 10000 keys changed
#
# Note: you can disable saving completely by commenting out all "save" lines.
#
# It is also possible to remove all the previously configured save
# points by adding a save directive with a single empty string argument
# like in the following example:
#
# save ""
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
10、最后一次保存失败是否继续支持向Redis数据库写入:
# By default Redis will stop accepting writes if RDB snapshots are enabled
# (at least one save point) and the latest background save failed.
# This will make the user aware (in a hard way) that data is not persisting
# on disk properly, otherwise chances are that no one will notice and some
# disaster will happen.
#
# If the background saving process will start working again Redis will
# automatically allow writes again.
#
# However if you have setup your proper monitoring of the Redis server
# and persistence, you may want to disable this feature so that Redis will
# continue to work as usual even if there are problems with disk,
# permissions, and so forth.
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes
11、数据持久化配置:
- 是否应用RDB压缩?
- 是否检查RDB文件数量
- 快照文件名
- 快照文件保存位置
# Compress string objects using LZF when dump .rdb databases?
# By default compression is enabled as it's almost always a win.
# If you want to save some CPU in the saving child set it to 'no' but
# the dataset will likely be bigger if you have compressible values or keys.
rdbcompression yes
# Since version 5 of RDB a CRC64 checksum is placed at the end of the file.
# This makes the format more resistant to corruption but there is a performance
# hit to pay (around 10%) when saving and loading RDB files, so you can disable it
# for maximum performances.
#
# RDB files created with checksum disabled have a checksum of zero that will
# tell the loading code to skip the check.
rdbchecksum yes
# The filename where to dump the DB
dbfilename dump.rdb
# The working directory.
#
# The DB will be written inside this directory, with the filename specified
# above using the 'dbfilename' configuration directive.
#
# The Append Only File will also be created inside this directory.
#
# Note that you must specify a directory here, not a file name.
dir /usr/local/redis/var
12、主从复制:
单机模拟集群时用到
-
replicaof <masterip> <masterport>- 绑定主机IP与端口号(认谁做老大)
-
masterauth <master-password>- 若主机有密码,则应当做出配置
-
masteruser <username>- 主机用户名
################################# REPLICATION #################################
# Master-Replica replication. Use replicaof to make a Redis instance a copy of
# another Redis server. A few things to understand ASAP about Redis replication.
#
# +------------------+ +---------------+
# | Master | ---> | Replica |
# | (receive writes) | | (exact copy) |
# +------------------+ +---------------+
#
# 1) Redis replication is asynchronous, but you can configure a master to
# stop accepting writes if it appears to be not connected with at least
# a given number of replicas.
# 2) Redis replicas are able to perform a partial resynchronization with the
# master if the replication link is lost for a relatively small amount of
# time. You may want to configure the replication backlog size (see the next
# sections of this file) with a sensible value depending on your needs.
# 3) Replication is automatic and does not need user intervention. After a
# network partition replicas automatically try to reconnect to masters
# and resynchronize with them.
#
replicaof <masterip> <masterport>
# If the master is password protected (using the "requirepass" configuration
# directive below) it is possible to tell the replica to authenticate before
# starting the replication synchronization process, otherwise the master will
# refuse the replica request.
#
masterauth <master-password>
#
# However this is not enough if you are using Redis ACLs (for Redis version
# 6 or greater), and the default user is not capable of running the PSYNC
# command and/or other commands needed for replication. In this case it's
# better to configure a special user to use with replication, and specify the
# masteruser configuration as such:
#
masteruser <username>
13、AOF持久化
将所有的命令都记录下来,恢复数据时全部都执行一遍。
############################## APPEND ONLY MODE ###############################
# By default Redis asynchronously dumps the dataset on disk. This mode is
# good enough in many applications, but an issue with the Redis process or
# a power outage may result into a few minutes of writes lost (depending on
# the configured save points).
#
# The Append Only File is an alternative persistence mode that provides
# much better durability. For instance using the default data fsync policy
# (see later in the config file) Redis can lose just one second of writes in a
# dramatic event like a server power outage, or a single write if something
# wrong with the Redis process itself happens, but the operating system is
# still running correctly.
#
# AOF and RDB persistence can be enabled at the same time without problems.
# If the AOF is enabled on startup Redis will load the AOF, that is the file
# with the better durability guarantees.
#
# Please check http://redis.io/topics/persistence for more information.
appendonly no
# The name of the append only file (default: "appendonly.aof")
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
AOF and RDB persistence can be enabled at the same time without problems.
二、持久化——RDB操作
-
在指定时间间隔内,将内存中的数据集快照写入数据库 ;在恢复时候,直接读取快照文件,进行数据的恢复 ;
-
在进行 RDB 的时候,redis 的主线程是不会做 io 操作的,主线程会 fork 一个子线程来完成该操作;
-
Redis 调用forks。同时拥有父进程和子进程。子进程将数据集写入到一个临时 RDB 文件中。
-
当子进程完成对新 RDB 文件的写入时,Redis 用新 RDB 文件替换原来的 RDB 文件,并删除旧的 RDB 文件。
-
缺点是最后一次持久化后的数据可能丢失。
-
默认是使用RDB方式来进行持久化。
-
RDB文件默认名dump.rdb
三、持久化——AOF操作
-
将所有的命令都记录下来,恢复数据时全部都执行一遍。
-
每一次修改都会同步,文件的完整性会更加好
-
每秒同步一次,可能会丢失一秒的数据
-
从不同步,效率最高
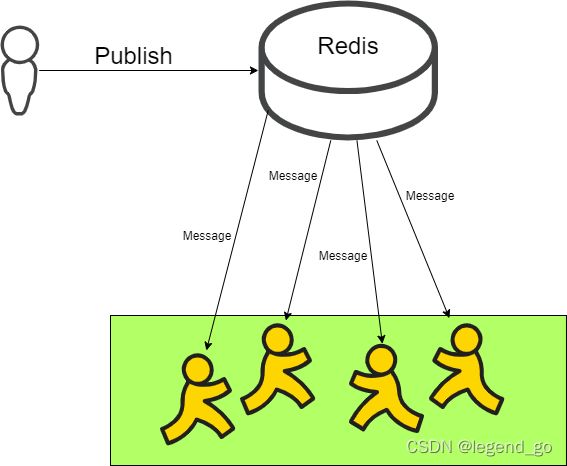
四、Redis订阅发布
Redis 发布订阅(pub/sub)是一种消息通信模式:发送者(pub)发送消息,订阅者(sub)接收消息
实践演示:
订阅端命令:
#订阅一个或多个频道
SUBSCRIBE channel [channels...]
#退订一个或多个频道
UNSUBSCRIBE channel [channels...]
#订阅一个或多个符合给定模式的频道
PSUBSCRIBE pattern [pattern…]
#退订一个或多个符合给定模式的频道
PUNSUBSCRIBE pattern [pattern…]
127.0.0.1:6379> SUBSCRIBE jackshuo
Reading messages... (press Ctrl-C to quit)
1) "subscribe"
2) "jackshuo"
3) (integer) 1
1) "message"
2) "jackshuo"
3) "Hello,Jack,This is a message."
发布端命令:
#向指定频道发布消息
PUBLISH channel message
#查看订阅与发布系统状态
PUBSUB subcommand [argument[argument]]
127.0.0.1:6379> PUBLISH jackshuo "Hello,Jack,This is a message."
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> PUBLISH jackshuo "Hello,My name is Mary,Nice to meet you"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379>
#订阅端显示如下:
127.0.0.1:6379> SUBSCRIBE jackshuo
Reading messages... (press Ctrl-C to quit)
1) "subscribe"
2) "jackshuo"
3) (integer) 1
1) "message"
2) "jackshuo"
3) "Hello,Jack,This is a message."
1) "message"
2) "jackshuo"
3) "Hello,My name is Mary,Nice to meet you"
五、Redis集群环境搭建
原则:只配置从机,不配置主机
1、进入redis.conf的目录
cd /usr/local/redis/etc/
2、复制至少3个conf文件模拟多台Redis服务器
#6380端口Redis服务器
cp redis.conf redis80.conf
#6381端口Redis服务器
cp redis.conf redis81.conf
#6382端口Redis服务器
cp redis.conf redis82.conf
3、编辑这三个conf文件,保证不与其他服务冲突
更改如下配置(建议与端口号对应起来便于区分):
- 端口号 port 91行左右
- 守护进程 daemonize 224行左右
- 进程文件保存位置 pidfile 247行左右
- 日志文件输出位置 logfile 260行左右
- RDB快照文件名 dbfilename 342行左右
4、在XShell中新开两个窗口并运行所有的客户端
redis-server ./redis(80,81,82)
redis-cli -p 端口号(6380,6381,6382)
ps -ef | grep redis
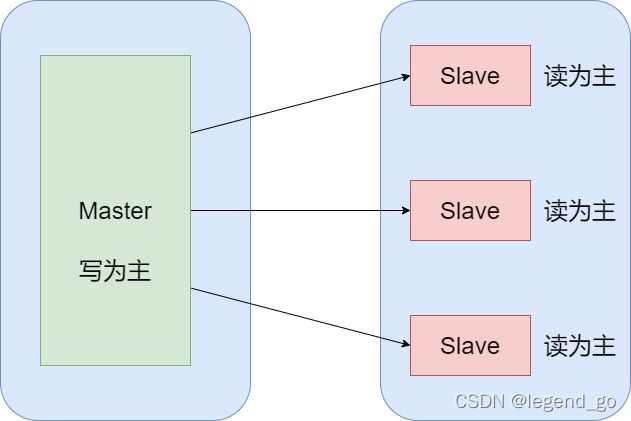
六、主从复制
概念:主从复制,是指将一台Redis服务器的数据,复制到其他的Redis服务器。前者称为主节点(Master/Leader),后者称为从节点(Slave/Follower), 数据的复制是单向的!只能由主节点复制到从节点(主节点以写为主、从节点以读为主)
默认情况下,每台Redis服务器都是主节点,一个主节点可以有0个或者多个从节点,但每个从节点只能由一个主节点
作用:
数据冗余:主从复制实现了数据的热备份,是持久化之外的一种数据冗余的方式。
故障恢复:当主节点故障时,从节点可以暂时替代主节点提供服务,是一种服务冗余的方式
负载均衡:在主从复制的基础上,配合读写分离,由主节点进行写操作,从节点进行读操作,分担服务器的负载;尤其是在多读少写的场景下,通过多个从节点分担负载,提高并发量。
高可用基石:主从复制还是哨兵和集群能够实施的基础。
用到的命令:
#查看当前数据库的信息
INFO REPLICATION
#指定哪一台服务器作为自己的主机(认老大)
SLAVEOF [master-host] [master-port]
127.0.0.1:6380> INFO replication
# Replication
role:master #角色信息
connected_slaves:0 #下属的从机个数
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:fedd7cae2eb8eba4d902e8e8f9d6131d0d4308b8
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:0
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:0
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0
repl_backlog_histlen:0
127.0.0.1:6380>
配置一主二从集群:
只需要在其中任意两个窗口中执行“认老大”的命令即可:
主机:
127.0.0.1:6380> INFO replication
# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:2
slave0:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6381,state=online,offset=98,lag=1
slave1:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6382,state=online,offset=98,lag=1
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:9c781bd89909cde9aaa7c6fa5ef9296b897d9b24
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:98
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1
repl_backlog_histlen:98
127.0.0.1:6380>
从机一:
127.0.0.1:6381> INFO replication
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6380
master_link_status:up
master_last_io_seconds_ago:8
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:84
slave_repl_offset:84
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:9c781bd89909cde9aaa7c6fa5ef9296b897d9b24
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:84
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1
repl_backlog_histlen:84
127.0.0.1:6381>
从机二:
127.0.0.1:6382> INFO replication
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6380
master_link_status:up
master_last_io_seconds_ago:4
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:98
slave_repl_offset:98
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:9c781bd89909cde9aaa7c6fa5ef9296b897d9b24
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:98
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:29
repl_backlog_histlen:70
127.0.0.1:6382>
七、宕机手动配置主机
若将主机直接关闭,我们来手动配置主机:
首先声明自己不属于任何主机:
127.0.0.1:6381> SLAVEOF no one
OK
127.0.0.1:6381> info replication
# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:a5229d078c30be48e0dd20be66dc78019a18e598
master_replid2:9c781bd89909cde9aaa7c6fa5ef9296b897d9b24
master_repl_offset:364
second_repl_offset:365
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1
repl_backlog_histlen:364
127.0.0.1:6381>
将另一台从机设置为自己的从机:
127.0.0.1:6382> slaveof 127.0.0.1 6381
OK
127.0.0.1:6382> info replication
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6381
master_link_status:up
master_last_io_seconds_ago:6
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:378
slave_repl_offset:378
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:a5229d078c30be48e0dd20be66dc78019a18e598
master_replid2:9c781bd89909cde9aaa7c6fa5ef9296b897d9b24
master_repl_offset:378
second_repl_offset:365
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:29
repl_backlog_histlen:350
127.0.0.1:6382>
这样便手动设置完成
八、哨兵模式
主从切换技术的方法是:当主服务器宕机后,需要手动把一台从服务器切换为主服务器,这就需要人工干预,费事费力,还会造成一段时间内服务不可用。这不是一种推荐的方式,更多时候,我们优先考虑哨兵模式(当主机宕机后自动选举主机)
作用:
- 通过发送命令,监控Redis服务器的运行状态,包括主服务器和从服务器。
- 当哨兵监测到master宕机,会自动将 slave 切换成master,然后通过发布订阅模式通知其他的从服务器,修改配置文件,让它们切换主机。
哨兵模式核心配置文件:
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 1
#监控master
#数字1表示 :当一个哨兵主观认为主机断开,就可以认为主机故障,然后开始选举新的主机。
1、在redis.conf同级目录下创建sentinel.conf配置文件:
vim sentinel.conf
2、添加上面的核心配置文件保存退出
3、运行哨兵:
redis-sentinel ./sentinel.conf
#运行结果:
root@jklove:/usr/local/redis/etc# redis-sentinel ./sentinel.conf
4399:X 19 Feb 2022 21:37:34.817 # oO0OoO0OoO0Oo Redis is starting oO0OoO0OoO0Oo
4399:X 19 Feb 2022 21:37:34.817 # Redis version=6.2.6, bits=64, commit=00000000, modified=0, pid=4399, just started
4399:X 19 Feb 2022 21:37:34.817 # Configuration loaded
4399:X 19 Feb 2022 21:37:34.818 * monotonic clock: POSIX clock_gettime
_._
_.-``__ ''-._
_.-`` `. `_. ''-._ Redis 6.2.6 (00000000/0) 64 bit
.-`` .-```. ```\/ _.,_ ''-._
( ' , .-` | `, ) Running in sentinel mode
|`-._`-...-` __...-.``-._|'` _.-'| Port: 26379
| `-._ `._ / _.-' | PID: 4399
`-._ `-._ `-./ _.-' _.-'
|`-._`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'_.-'|
| `-._`-._ _.-'_.-' | https://redis.io
`-._ `-._`-.__.-'_.-' _.-'
|`-._`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'_.-'|
| `-._`-._ _.-'_.-' |
`-._ `-._`-.__.-'_.-' _.-'
`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'
`-._ _.-'
`-.__.-'
4399:X 19 Feb 2022 21:37:34.822 # Sentinel ID is 5890013d361df5738dead42b8fee8e9501736589
4399:X 19 Feb 2022 21:37:34.822 # +monitor master master 127.0.0.1 6380 quorum 1
4399:X 19 Feb 2022 21:37:34.823 * +slave slave 127.0.0.1:6382 127.0.0.1 6382 @ master 127.0.0.1 6380
4399:X 19 Feb 2022 21:37:34.826 * +slave slave 127.0.0.1:6381 127.0.0.1 6381 @ master 127.0.0.1 6380
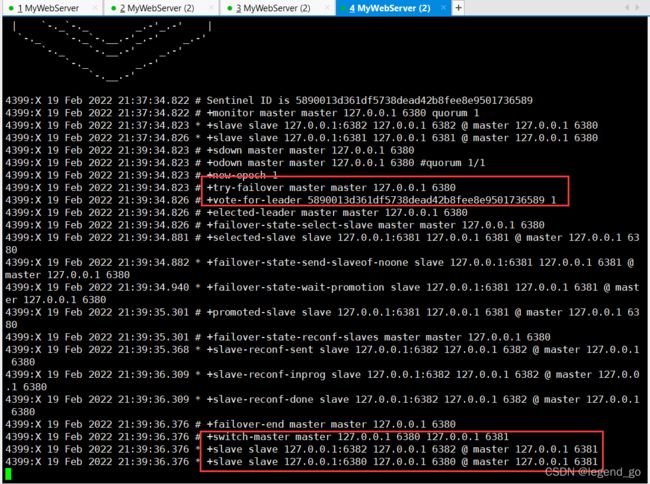
这时我们断开主机看看会发生什么:
我们可以看到6381端口的从机变为了主机,6382从机自动变为6381端口的从机
6381端口:
127.0.0.1:6381> info replication
# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:1
slave0:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6382,state=online,offset=17332,lag=1
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:bccb92b856acd8e71199b955e359cb8877dc61d3
master_replid2:6d2e0a16288ee3122ae68cd7be6afe97ee5f041a
master_repl_offset:17332
second_repl_offset:6068
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:29
repl_backlog_histlen:17304
127.0.0.1:6381>
6382端口:
127.0.0.1:6382> info replication
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6381
master_link_status:up
master_last_io_seconds_ago:0
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:17187
slave_repl_offset:17187
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:bccb92b856acd8e71199b955e359cb8877dc61d3
master_replid2:6d2e0a16288ee3122ae68cd7be6afe97ee5f041a
master_repl_offset:17187
second_repl_offset:6068
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1
repl_backlog_histlen:17187
127.0.0.1:6382>
那么这时我们将6380端口机再次开启会发生什么事呢?
哨兵报告:
可以看到直接将加入的6380机变为了6381的从机!6381机成功篡位!
6380机:
127.0.0.1:6380> info replication
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6381
master_link_status:up
master_last_io_seconds_ago:1
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:26183
slave_repl_offset:26183
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:bccb92b856acd8e71199b955e359cb8877dc61d3
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:26183
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:25230
repl_backlog_histlen:954
127.0.0.1:6380>
这种模式非常好用~
九、缓存穿透以及雪崩
一、缓存穿透:
在默认情况下,用户请求数据时,会先在缓存(Redis)中查找,若没找到即缓存未命中,再在数据库中进行查找,数量少可能问题不大,可是一旦大量的请求数据(例如秒杀场景)缓存都没有命中的话,就会全部转移到数据库上,造成数据库极大的压力,就有可能导致数据库崩溃。网络安全中也有人恶意使用这种手段进行攻击被称为洪水攻击。
解决方案:
- 布隆过滤器
- 对所有可能查询的参数以Hash的形式存储,以便快速确定是否存在这个值,在控制层先进行拦截校验,校验不通过直接打回,减轻了存储系统的压力。
- 缓存空对象
一次请求若在缓存和数据库中都没找到,就在缓存中放一个空对象用于处理后续这个请求。
这样做有一个缺陷:存储空对象也需要空间,大量的空对象会耗费一定的空间,存储效率并不高。解决这个缺陷的方式就是设置较短过期时间
即使对空值设置了过期时间,还是会存在缓存层和存储层的数据会有一段时间窗口的不一致,这对于需要保持一致性的业务会有影响。
二、缓存击穿
相较于缓存穿透,缓存击穿的目的性更强,一个存在的key,在缓存过期的一刻,同时有大量的请求,这些请求都会击穿到数据库,造成瞬时数据库请求量大、压力骤增。这就是缓存被击穿,只是针对其中某个key的缓存不可用而导致击穿,但是其他的key依然可以使用缓存响应。比如热搜排行上,一个热点新闻被同时大量访问就可能导致缓存击穿。
解决方案:
- 设置热点数据永不过期
- 这样就不会出现热点数据过期的情况,但是当Redis内存空间满的时候也会清理部分数据,而且此种方案会占用空间,一旦热点数据多了起来,就会占用部分空间。
- 加互斥锁(分布式锁)
- 在访问key之前,采用SETNX(set if not exists)来设置另一个短期key来锁住当前key的访问,访问结束再删除该短期key。保证同时刻只有一个线程访问。这样对锁的要求就十分高。
三、缓存雪崩
大量的key设置了相同的过期时间,导致在缓存在同一时刻全部失效,造成瞬时数据库请求量大、压力骤增,引起雪崩。
解决方案:
- redis高可用
- 这个思想的含义是,既然redis有可能挂掉,那我多增设几台redis,这样一台挂掉之后其他的还可以继续工作,其实就是搭建集群
- 限流降级
- 这个解决方案的思想是,在缓存失效后,通过加锁或者队列来控制读数据库写缓存的线程数量。比如对某个key只允许一个线程查询数据和写缓存,其他线程等待。
- 数据预热
- 数据加热的含义就是在正式部署之前,我先把可能会被大量访问的数据预先访问一遍,这样就会将数据加载到缓存中。在即将发生大并发访问前手动触发加载缓存不同的key,设置不同的过期时间,让缓存失效的时间点尽量均匀。
相关文章:
- Redis-01
- 什么是Redis
- 在Linux下安装Redis
- Redis常用命令以及基本数据类型
- 三大特殊类型
- Redis-02
- Redis实现基本的事务操作
- Redis实现乐观锁
- 通过Jedis操作Redis
- 通过Jedis理解事务
- SpringBoot集成Redis
- 自定义RedisTemplate
- Redis-03
- Redis配置文件详解
- 持久化——RDB操作
- 持久化——AOF操作
- Redis订阅发布
- Redis集群环境搭建
- 主从复制
- 宕机手动配置主机
- 哨兵模式
- 缓存穿透以及雪崩
参考链接:
Redis笔记
【狂神说Java】Redis最新超详细版教程通俗易懂