#数据结构基础知识与刷题笔记----数组;链表;哈希表;队列;栈;堆;树;
一、数组
数组是一系列具有连续内存空间的相同类型的元素。
①内存就是我们所说的RAM,也称主存,是与处理器接近的用于存储信息的实物(如内存条)。数组在内存中开辟已知长度的有限空间,这在很大程度上就限制了数组的特性和适用范围。
②且数组往往在定义时就定义了数据类型,可以是string int这种内置的原始数据类型,也可以是自定义的数据类型(结构体),但前提是数组内必须只有一个类型。
2021.8.6
在JavaScript中,数组中的每个元素的类型是可以不同的;
这是因为JavaScript的弱数据类型决定数组中元素类型可以不同的;
因为在JavaScript中,定义变量的时候不指定其数据类型,仅仅用一个var来表示当前对象是一个变量,至于其是什么类型的不指定,在后面使用的时候可以赋值不同的数值类型。
对于数组的基本操作,
由于数组是连续的内存空间,在增删改时平均需要对一半的元素进行操作,这样时间复杂度就达到了O(n)。
以数组为基础自定义一个顺序表的类,
我们往往用两个类来实现这样一个顺序表,在父类中列写所有的基本操作,但前面加“virtual”即定义为虚函数,不需要实现。接着在派生类中继承父类,自定义基本操作的实现。这样的好处是使得父类能适应于更多的派生类,如用链表实现的时候父类就不需要修改只重新定义新的子类实现即可。
//父类
template class List{
private:
void operator = (const List&){}
List(const List&){}
public:
List(){}
virtual ~List(){}
virtual int length() const = 0;
virtual void moveToPos(int pos) = 0;
virtual const E& getValue() const = 0;
virtual int getValueLetter() const = 0;
virtual int getValueNum() const = 0;
virtual int getValueElse() const = 0;
virtual void append(const E& item) = 0;
virtual void moveToEnd() = 0;
virtual void deleteNum() = 0;
virtual void clear() = 0;
virtual void insert(const E& item) = 0;
virtual void moveToStart() = 0;
virtual void prev() = 0;
virtual void next() = 0;
virtual int currPos() const = 0;
virtual E remove() = 0;
};
//子类
template class AList:public List{
private:
int maxSize;
int listSize;
int curr;
E* listArray;
int numOfLetter;
int numOfNum;
int numOfElse;
public:
AList(int size = 1000){
maxSize = size;
listSize = curr = 0;
listArray = new E[maxSize];
numOfLetter = numOfNum = numOfElse = 0;
}
~AList(){delete []listArray;}
int length() const{return listSize;}
void moveToPos(int pos){
if(pos >= 0 && pos <= listSize) curr = pos;
}
const E& getValue() const{
if(curr >= 0 && curr < listSize) return listArray[curr];
return listArray[0];
}
int getValueLetter() const{
return numOfLetter;
}
int getValueNum() const{
return numOfNum;
}
int getValueElse() const{
return numOfElse;
}
void append(const E& item){
if(listSize < maxSize) listArray[listSize++] = item;
}
void moveToEnd(){curr = listSize-1;}
void deleteNum(){
moveToEnd();
E x = getValue();
if((x >= 'a' && x <= 'z')||(x >= 'A' && x <= 'Z')){
numOfLetter++;
}
else if(x >= '0' && x <= '9'){
numOfNum++;
listSize--;
}
else{
numOfElse++;
}
}
void clear(){
delete []listArray;
listSize = curr = 0;
listArray = new E[maxSize];
}
void insert(const E& item){
if(listSize < maxSize){
for(int i = listSize; i>curr; i--) listArray[i] = listArray[i-1];
listArray[curr] = item;
listSize++;
}
}
void moveToStart(){curr = 0;}
void prev(){if(curr)curr--;}
void next(){if(curr < listSize)curr++;}
int currPos() const{return curr;}
E remove(){
if(curr >= 0 && curr < listSize){
E it = listArray[curr];
for(int i = curr; i < listSize-1; i++) listArray[i] = listArray[i+1];
listSize--;
return it;
}
return listArray[0];
}
};
该顺序表可计算字母数字的数目。
关于数组的LeetCode一般都比较简单,但是既然是总结就从简单的开始。
二、LeetCode1
我用了比较容易想到的办法,相当于暴力查找了:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = {0,0};
int target2;
int temp;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
target2 = nums[i];
temp = getIndex(nums, i, target-target2);
if(temp > 0){
result[0] = i;
result[1] = temp;
}
}
return result;
}
public static int getIndex(int[] arr, int i, int value){
for(int x = i+1; x < arr.length; x++){
if(arr[x] == value){
return x;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
过程中由于太久没用java有点陌生,一直在找java自带的搜索方法,没有找到,于是最后还是自己定义了一个方法找元素下标,其实吧自定义只是比分开写简洁一点没啥用,运行能成功但是效果不佳,因为很明显相当于两层数组的遍历查找,时间复杂度到了O(n^2)。

于是在提交记录里看到自己一年前用C++做的时候优化用了哈希表,这里应该也能用哈希表优化一下。
嗐,java的哈希表和C++稍微有点不一样,我感觉java在调用上对新手不太友好,不百度我怎么知道叫什么函数啊!!而且C++可以直接.[]调用的地方在java这好多都得用函数www
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = {0,0};
int target2;
Map hash = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
target2 = target - nums[i];
if(hash.containsKey(target2)){
result = new int[]{hash.get(target2), i};
break;
}
hash.put(nums[i], i);
}
return result;
}
}
不过凭借哈希表优秀的时间复杂度O(1),这样效率高了不少,针不戳啊~

三、LeetCode268
[0,n]无序数组,找到少的那一个。
如果不考虑性能直接排序一层循环查找就是了:
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int i = 0;
for(; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] != i) return i;
}
return i;
}
}
而如果要线性时间复杂度、仅使用额外常数空间的算法,我最先想到的是优化排序算法比如什么快排希尔排序,但是后来验证这些算法的性能也没那么高。桶排序好像符合要求,但是得到的桶排序实现代码还是用到了插入排序意味着本身代价又高了。
这样说明不是在考排序,换个思路可以直接用数学方法累加,也可以用官方给出的异或的方法,这个方法非常巧妙,注意异或的时候可以改变先后顺序,满足交换律还是结合律啥的,只要人为加上一个初始值n(即数组长度,否则少一位),最后的结果就是缺失的数字。
四、LeetCode78
恕我直言这一题花了我三个小时时间,其实方法挺好想的,位数以及每一位是什么都能很容易看出来,但是对于java中的List
class Solution {
public List> subsets(int[] nums) {
List> include = new ArrayList<>();
List list = Collections.EMPTY_LIST;
include.add(list);
int size = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i){
include = addsingle(include, nums[i], size);
size *= 2;
}
return include;
}
public List> addsingle(List> include, int num, int size){
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(num);
include.add(list);
for(int i = 1; i < size; ++i){
List list2 = new ArrayList();
list2 = new ArrayList(include.get(i));
list2.add(num);
include.add(list2);
}
return include;
}
}
列写要注意的几点:
- add函数的返回值是Boolean不能直接作为赋值语句,改变的是他本身
- 初始值要实例化,不然会报空指针的错误
- 注意这里第一个位置是空的,有直接赋值的语句,但是此时如果用isEmpty()可以得到此时的List是空的,意味着不能直接调用这个值,要拐个弯,否则后果同上一条
- 以及最重要的一点是在get函数里传的是include的地址,随着循环往后include get的值发生改变,相应的list2也会改变,从而偶数位的数字完全相同,为避免可以重新new一个ArrayList赋值,如上
五、LeetCode90
这一题是LeetCode78更一般的情况,其要考虑有重复元素的情况,那如果继续使用上一题的方法,将重复的旧解排除在外即可。重复元素在单独形成子集时作用相同,故前一个元素出现前的所有子集都会形成旧解,故需要一个新的变量记录前一步的开始位置和一个新的变量记录前一个元素判断是否重复。
class Solution {
public List> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
List> include = new ArrayList<>();
List list = Collections.EMPTY_LIST;
include.add(list);
Arrays.sort(nums);
int size = 1;
int usedsize = 0;
int numused = nums[0] - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i){
include = addsingle(include, nums[i], size, numused, usedsize);
usedsize = size;
size = include.size();
numused = nums[i];
}
return include;
}
public List> addsingle(List> include, int num, int size, int numused, int usedsize){
for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i){
if (num == numused && i < usedsize) {
continue;
}
else if(i == 0){
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(num);
include.add(list);
}
else{
List list2 = new ArrayList();
list2 = new ArrayList(include.get(i));//send include[2]'s address, change will change it also
list2.add(num);
include.add(list2);
}
}
return include;
}
}
看解析里还是用到了回溯和更高级的方法,在后面搞算法的时候再优化吧。
一、链表
与数组的主要差别就是内存空间可以不连续了,对应着增加删除操作更方便,访问搜索则更麻烦。
同样可以用链表来实现顺序表,只用改变子类的具体方法实现:
//子类
template class LList:public List{
private:
Link* head;
Link* tail;
Link* curr;
int cnt; //listSize
int numOfLetter;
int numOfNum;
int numOfElse;
void init() {
curr = tail = head = new Link;
cnt = 0;
}
void removeall() {
while(head != NULL) {
curr = head;
head = head->next;
delete curr;
}
}
public:
LList(int size = 1000){
init();
numOfLetter = numOfNum = numOfElse = 0;
}
~LList(){removeall();}
int length() const{return cnt;}
void moveToPos(int pos){
if(pos >= 0 && pos < cnt){
curr = head;
for(int i=0; inext;
}
}
const E& getValue() const{
if(curr->next != NULL) return curr->next->element;;
return head->next->element;
}
int getValueLetter() const{
return numOfLetter;
}
int getValueNum() const{
return numOfNum;
}
int getValueElse() const{
return numOfElse;
}
void append(const E& item){
tail = tail->next = new Link(item, NULL);
cnt++;
}
E remove(){
if(curr->next != NULL){
E it = curr->next->element;
Link* temp = curr->next;
if(tail == curr->next) tail = curr;
curr->next = curr->next->next;
delete temp;
cnt--;
return it;
}
return head->next->element;
}
void deleteNum(){
moveToPos(cnt-1);
E x = getValue();
if((x >= 'a' && x <= 'z')||(x >= 'A' && x <= 'Z')){
numOfLetter++;
}
else if(x >= '0' && x <= '9'){
numOfNum++;
remove();
}
else{
numOfElse++;
}
}
void clear(){removeall(); init();}
void insert(const E& item){
curr->next = new Link(item, curr->next);
if (tail == curr) tail = curr->next;
cnt++;
}
void moveToStart(){curr = head;}
void moveToEnd(){curr = tail;}
void prev(){
if (curr == head) return;
Link* temp = head;
while (temp->next != curr) temp = temp->next;
curr = temp;
}
void next(){
if (curr != tail) curr = curr->next;
}
int currPos() const{
Link* temp = head;
int i;
for(i = 0; curr != temp; i++) temp = temp->next;
return i;
}
};
二、LeetCode206
链表与数组不同,根据这里的结点类,想到可以借助栈实现链表的反转,栈直接定义为结点类,将整个结点信息(含指针)存进去再逆序依次连起来。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
Stack value = new Stack();
while(head != null){
value.push(head);
head = head.next;
}
if(value.isEmpty()) return null;
ListNode node = value.pop();
ListNode result = node;
while(!value.isEmpty()){
result.next = value.pop();
result = result.next;
}
result.next = null;
return node;
}
}
这里稍微要注意的就是要提前判断栈是否为空,否则对空集合的运行会爆编译错误,以及最后一个结点是头结点,重新连接后变成尾结点,要给他清空指针,否则会形成闭环。
也可以将栈定义为integer,不用开辟新的内存空间,但需始终有结点指向最初的头结点:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
Stack value = new Stack();
ListNode new_head = head;
while(head != null){
value.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
if(value.isEmpty()) return head;
ListNode result = new_head;
while(!value.isEmpty()){
new_head.val = value.pop();
new_head = new_head.next;
}
return result;
}
}
好吧我说看着眼熟之前学数据结构的时候用C++写过,有点记不清了:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
//递归
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL){//第二部分不能省略,因为后面有next->next!注意!
return head;
}
ListNode *next = head->next;
ListNode *new_head = reverseList(next);//分解成倒序head-1位的子问题
next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return new_head;
// //头插法(迭代)
// ListNode *new_head = NULL;//指向新链表头节点的指针
// while(head){
// ListNode *next = head->next;
// head->next = new_head;
// new_head = head;
// head = next;//遍历链表
// }
// return new_head;//返回新链表头结点
}
};
头插法还比较好理解,挨个反过来,
递归稍微绕一点,其本质也是挨个倒过来,逆序而已。
三、LeetCode21
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
//我自己写了一大半天冗杂的代码,多是对特殊情况的考虑,效率极低
// if(!l1) return l2;
// ListNode *result = l1;
// while(l1 && l2){
// if(l2->val <= l1->val){
// ListNode *temp = l2->next;
// l2->next = l1;
// result = l2;
// l2 = temp;
// }
// else if(l1->next && l2->val <= l1->next->val){
// ListNode *temp = l2->next;
// l2->next = l1->next;
// l1->next = l2;
// l2 = temp;
// }
// if(!(l1->next)) break;
// l1 = l1->next;
// }
// if(l2 && l1) l1->next = l2;
// return result;
//好像结果还不对
//参考下面这个代码
if(!l1) return l2;
if(!l2) return l1;
if(l1->val < l2->val){
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
};
所以直接用递归写很快就搞出来了,代码还好看:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
//直接用递归
if(l1 == null) return l2;
if(l2 == null) return l1;
if(l1.val < l2.val){
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
四、LeetCode2
将两个链表加起来,逆序其实本身为解题提供了方便,两个思路一个转换为整数直接加,一个按位记录进位相加,前一个思路由于链表长度可以达到100,会超出int范围舍弃,故选择第二个思路。
为了答题而写的代码比较冗杂:
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode num = new ListNode((l1.val + l2.val)%10);
ListNode result = num;
int temp = ((l1.val + l2.val) >= 10)?1:0;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
ListNode next = new ListNode((l1.val + l2.val + temp)%10);
temp = ((l1.val + l2.val + temp) >= 10)?1:0;
num = num.next = next;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
while(l1 != null){
ListNode next = new ListNode((l1.val + temp)%10);
temp = ((l1.val + temp) >= 10)?1:0;
num = num.next = next;
l1 = l1.next;
}
while(l2 != null){
ListNode next = new ListNode((l2.val + temp)%10);
temp = ((l2.val + temp) >= 10)?1:0;
num = num.next = next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
if(temp == 1) num.next = new ListNode(1);
return result;
}
}
这一看很多地方可以稍微化简一下,
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode p1 = l1, p2 = l2;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = dummy;
int carry = 0, newVal = 0;
while (p1 != null || p2 != null || carry > 0) {
newVal = (p1 == null ? 0: p1.val) + (p2 == null ? 0: p2.val) + carry;
carry = newVal / 10;
newVal %= 10;
p.next = new ListNode(newVal);
p1 = p1 == null? null: p1.next;
p2 = p2 == null? null: p2.next;
p = p.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
果然别人的代码就是要好看一些。。。虽然资源消耗差不多。。。
我的三个while语句其实可以加两个判断合到一起,对最后有进位的情况也可以包含在里面了。
(p1 == null ? 0: p1.val)
(p2 == null ? 0: p2.val)
还有一点是循环前面我为了对齐也就是直接输出结果,在循环外提前操作了一次,其实也没必要,按照下面这个直接从result.next返回即可。
五、LeetCode24
将每两个结点交换一下,
先考虑特殊情况只有0或1个时直接返回,
其余没两个交换一次,
最后如果有单个的即奇数情况不用动。
好题目建议是不改变结点值,那我们就不改变,直接交换结点:
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode result = new ListNode();
result = head.next;
ListNode before = new ListNode();
while(head != null && head.next != null){
ListNode temp = new ListNode();
temp = head;
head = head.next;
temp.next = head.next;
head.next = temp;
before.next = head;
before = head.next;
head = head.next.next;
}
return result;
}
}
每两个交换一次,每一次操作里先存下head结点为temp,然后将后一个作为新的head结点,同时将temp的下一个结点连到操作结束后的第一个结点(也有可能为空),再将新的head结点下一个结点连到temp,(不能反,否则前一个操作的结点找不到)。
显然还要有一个结点存上一次操作后的最后一个结点即这里的temp,否则以第二次操作为例,操作完后temp还是连着操作前的头指针,达不到目的。
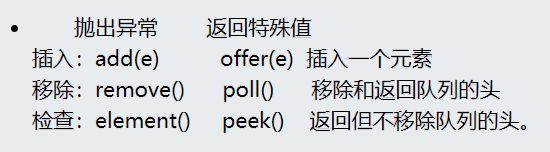
一、哈希表
哈希表里最重要的两个参数就是
二、LeetCode217
用哈希表的方法可以很快做出来,给每个数字一个key值,这样每次添加前先查找一下有没有,有直接终止程序。
class Solution {
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
//从哈希表来
Map hash = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i){
if(hash.get(nums[i]) != null) return true;
hash.put(nums[i], nums[i]);
}
return false;
}
}
效率比我想象的低很多倒是。
还可以直接排序查找,但是排序的效率就更低了。
三、LeetCode389
这题是上一题更深一点的题目,考虑到哈希表的知识点,对应的是char型。
| 原始类型 | 封装类 |
|---|---|
| boolean | Boolean |
| char | Character |
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
最初写出来的是这样,忽略了如上一题会有重复数字(字符)的情况,所以会报错。
class Solution {
public char findTheDifference(String s, String t) {
Map hash = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
hash.put(s.charAt(i), s.charAt(i));
}
for(int i = 0; i < s.length() + 1; i++){
if(hash.get(t.charAt(i)) == null) return t.charAt(i);
}
return s.charAt(0);
}
}
于是将统计方法记录在哈希表中,用两个哈希表分别记录两个字符串中各字符出现的次数(0为null),从而在循环时一边找没有出现的一边找出现了但数字不对的,找出来立刻返回,否则就是剩下来的t字符串中的最后一个。
class Solution {
public char findTheDifference(String s, String t) {
Map hashs = new HashMap();
Map hasht = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(hashs.get(s.charAt(i)) == null) hashs.put(s.charAt(i), 1);
else hashs.put(s.charAt(i), hashs.get(s.charAt(i))+1);
if(hasht.get(t.charAt(i)) == null) hasht.put(t.charAt(i), 1);
else hasht.put(t.charAt(i), hasht.get(t.charAt(i))+1);
}
if(hasht.get(t.charAt(s.length())) == null) hasht.put(t.charAt(s.length()), 1);
else hasht.put(t.charAt(s.length()), hasht.get(t.charAt(s.length()))+1);
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(hashs.get(t.charAt(i)) == null) return t.charAt(i);
if(hashs.get(s.charAt(i)) != hasht.get(s.charAt(i))) return s.charAt(i);
}
return t.charAt(s.length());
}
}
这题好像和前面哪天的找缺失的数字有点像,也可以用数学方法,毕竟字符也可以用数字来表示,也可以用异或位运算来算。
四、LeetCode49
这题输出的是ArrayList,放在哈希表的例题里,一开始还是想单纯用哈希表记录出现的字母,然后整不出来,看了一下题解发现可以直接用哈希表存ArrayList,稍微用到了一下排序,每次将string转换为char数组排序完又转换回去,这样方便比较就不用挨个数了。
class Solution {
public List> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map> hash = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; ++i){
char[] chars = strs[i].toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(chars);
String key = String.valueOf(chars);
if(hash.get(key) == null) hash.put(key, new ArrayList<>());
hash.get(key).add(strs[i]);
}
return new ArrayList<>(hash.values());
}
}
五、LeetCode560
统计满足条件的子集,这题可以直接用暴力算法写,但是耗费比较大,而且我一开始没有用暴力法,企图用哈希表对每一个数进行分析,耗费没那么大但是需要额外考虑很多特殊情况,尤其是有很多零的情况,然后反复报错还是参考了官方的建议。
class Solution {
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
Map hash = new HashMap();
int sum = 0, result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(hash.containsKey(sum)) hash.put(sum, hash.get(sum)+1);
else hash.put(sum, 1);
sum += nums[i];
if(hash.containsKey(sum - k)) result += hash.get(sum - k);
// System.out.println(result);
}
return result;
}
}
这像是一道数学题,有点像什么等差数列虽然这里不是等差,就是考虑前n项和把问题从求子集转换为求前缀和一个值的问题,这样实现简便很多但是比较绕,可以中间把统计值先列出来方便观察。
哈希表可以充分用到其优越的存与查的特性,键与值的合理设置可以很大程度简化问题,不过呢,哈希表可以直接载入列表(答案),最好不要看成简单的数组的优化而单独用来统计。
一、队列
二、LeetCode993
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
Queue cousin = new LinkedList();
TreeNode xfather = null;
TreeNode yfather = null;
cousin.offer(root);
while(!cousin.isEmpty()){
int size = cousin.size();
while(size > 0){
root = cousin.poll();
if(root.left != null){
if(root.left.val == x) xfather = root;
if(root.left.val == y) yfather = root;
cousin.offer(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null){
System.out.print("right"+root.right.val);
if(root.right.val == x) xfather = root;
if(root.right.val == y) yfather = root;
cousin.offer(root.right);
}
System.out.print("root"+root.val);
size--;
}
if((xfather != null && yfather == null)||(xfather == null && yfather != null)) return false;
}
if(xfather != yfather) return true;
return false;
}
}
原来输出不会影响结果。
这题其实在考广度优先搜索,可以用队列实现,两个点,同一层+不同父亲,记录各自的父亲,以队列的长度作为一层循环可表示树的同一层。
三、LeetCode225
经典的用队列实现栈,之前用C++实现过一次,现在用Java反而不会了,主要还是对java这个初始化什么的不熟悉,要用到的两个队列在方法外面定义,在方法里实例化。
class MyStack {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
q1.offer(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
while(q1.size() > 1) q2.offer(q1.poll());
while(q2.size() > 0) q1.offer(q2.poll());
return q1.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
while(q1.size() > 1) q2.offer(q1.poll());
int a = q1.peek();
q2.offer(q1.poll());
while(q2.size() > 0) q1.offer(q2.poll());
return a;
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
q1为主,q2为辅。
四、LeetCode622
循环队列
class MyCircularQueue {
int size;
int length;
int tail;
Queue q;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
q = new LinkedList<>();
size = length = k;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(length == 0) return false;
q.offer(value);
length--;
tail = value;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(q.isEmpty()) return false;
q.poll();
length++;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(q.isEmpty()) return -1;
return q.peek();
}
public int Rear() {
if(q.isEmpty()) return -1;
return tail;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return length == size;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return length == 0;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/
哈哈我这记录的越来越简洁了,这个可以提交没有问题,但是我后来发现这样好像没有实现内存的不浪费,好像还是一个队列只实现了循环,看解析的话是用了链表或者数组,好吧那我再用数组实现一遍,也不过把队列换成数组,用head和tail指向头尾,记得求余,其他没什么变化。
class MyCircularQueue {
int size;
int length;
int head;
int tail;
int[] q;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
q = new int[k];
size = length = k;
head = tail = 0;
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(length == 0) return false;
q[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % size;
length--;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(length == size) return false;
head = (head + 1) % size;
length++;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(length == size) return -1;
return q[head];
}
public int Rear() {
if(length == size) return -1;
if(tail == 0) return q[size-1];
return q[tail-1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return length == size;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return length == 0;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/
想起上课的时候老师好像也提过循环队列,有三个方法判断循环队列的空和满(但是用布尔变量的方法也得统计容量吧??),以及还有链表的方法,看我以后有心情再试试。
五、LeetCode641
这题跟上一题差不多,上一题用了数组,这一题继续,那这里因为两边都能移动,在判断空和满时就需要浪费两个内存,或者像上一题用统计容量的方法判断空满,其他的按要求实现就行了。
class MyCircularDeque {
int[] q;
int head;
int tail;
int size;
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the deque to be k. */
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
q = new int[k+2];
size = k+2;
head = tail = 0;
}
/** Adds an item at the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if(head == (tail+2)%size) return false;
head = (head-1+size)%size;
q[head] = value;
return true;
}
/** Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if(head == (tail+2)%size) return false;
q[tail] = value;
tail = (tail+1)%size;
return true;
}
/** Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deleteFront() {
if(head == tail) return false;
head = (head+1)%size;
return true;
}
/** Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deleteLast() {
if(head == tail) return false;
tail = (tail-1+size)%size;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the deque. */
public int getFront() {
if(head == tail) return -1;
return q[head];
}
/** Get the last item from the deque. */
public int getRear() {
if(head == tail) return -1;
return q[(tail-1+size)%size];
}
/** Checks whether the circular deque is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
/** Checks whether the circular deque is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
return head == (tail+2)%size;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularDeque object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularDeque obj = new MyCircularDeque(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.insertFront(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.insertLast(value);
* boolean param_3 = obj.deleteFront();
* boolean param_4 = obj.deleteLast();
* int param_5 = obj.getFront();
* int param_6 = obj.getRear();
* boolean param_7 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_8 = obj.isFull();
*/
有上一题的经验,虽然隔了一天这一题也做得很顺利耶!
一、栈
先进先出
方法如下:
1 boolean empty() 测试堆栈是否为空。
2 Object peek( ) 查看堆栈顶部的对象,但不从堆栈中移除它。
3 Object pop( ) 移除堆栈顶部的对象,并作为此函数的值返回该对象。
4 Object push(Object element) 把项压入堆栈顶部。
5 int search(Object element) 返回对象在堆栈中的位置,以 1 为基数。
二、LeetCode20
经典括号题,用栈实现
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if(s.charAt(0) == ')' || s.charAt(0) == ']' || s.charAt(0) == '}') return false;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
switch(s.charAt(i)){
case '(':
case '[':
case '{':
stack.push(s.charAt(i)); break;
case ')':
if(stack.isEmpty()) return false;
if(stack.peek() == '('){
stack.pop();break;
}
else return false;
case ']':
if(stack.isEmpty()) return false;
while(stack.peek() != '['){
if(stack.peek() == '{') return false;
stack.pop();
if(stack.isEmpty()) return false;
}
stack.pop();break;
case '}':
if(stack.isEmpty()) return false;
while(stack.peek() != '{'){
stack.pop();
if(stack.isEmpty()) return false;
}
stack.pop();break;
default:break;
}
}
if(stack.isEmpty()) return true;
return false;
}
}
switch case语句用的很漂亮。
用一个hashmap更好看了。
这里我好像把问题看复杂了还是,其实每次删除只会发生在加进来符号的那一步,能删就能删,不能删就有问题了。就是配对只会在栈顶发生,就不用再判断碰到其他的情况,反而这样输入{([}还会出现错误的答案,只是没这个测试样例。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
switch(s.charAt(i)){
case '(':
case '[':
case '{':
stack.push(s.charAt(i)); break;
case ')':
if(stack.isEmpty()) return false;
if(stack.peek() == '('){
stack.pop();break;
}
else return false;
case ']':
if(stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != '[') return false;
stack.pop();break;
case '}':
if(stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != '{') return false;
stack.pop();break;
default:break;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
三、LeetCode232
与用队列实现栈刚好相反,也用到两个栈。
class MyQueue {
Stack stack1;
Stack stack2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
return stack2.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
return stack2.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
改进一下的地方是,这里不需要把重心放在一个栈上了,进到1出看2没有再从1里调,如此能减少一定的时间。
四、LeetCode71
这道题处理的是字符串,有点像ccf的第三题,也用到栈来处理。
class Solution {
public String simplifyPath(String path) {
String[] s = path.split("/");
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
if (!stack.isEmpty() && s[i].equals(".."))
stack.pop();
else if (!s[i].equals("") && !s[i].equals(".") && !s[i].equals(".."))
stack.push(s[i]);
}
if (stack.isEmpty())
return "/";
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < stack.size(); i++) {
res.append("/");
res.append(stack.get(i));
}
return res.toString();
}
}
我开始栈定义的是Character类型,最后输出的时候稍微麻烦一点,处理的时候要对每一位分情况讨论也比较麻烦,而且对样例给的’/…‘的情况还判断错误,这就很尴尬了,不如利用一下string的split函数,以’/'为分隔符将字符串分割成不同的子串进行处理。这样只用考虑极个别情况就很好处理。
2021.8.6
其实对字符串的处理JavaScript有天然的优势,也能很快做出来
/**
@param {string} path
@return {string}
*/
var simplifyPath = function(path) {
let part = path.split('/');
let listSize = 0;
let answer = [];
part.forEach(item=>{
if(item == '..') listSize>0?listSize--:0;
else if(item.length > 0 && item != '.') answer[listSize++] = item;
})
let array = '';
for(let i = 0; i < listSize; i++){
array += '/' + answer[i];
}
return array.length>0?array:'/';
};
五、LeetCode394
我发现栈经常用于处理字符串的问题,而队列可以帮助处理树的层次遍历问题。
这题联系到的知识点可以是(逆)波兰式,用两个栈分别存数字和字符,从内向外从左向右处理,只是这个栈的字符串输出只是照葫芦画瓢地用了stringbuffer,还没有深入理解。
class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
Stack numstack = new Stack<>();
Stack stringstack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(s.charAt(i)-'0' < 10 && s.charAt(i)-'0' >= 0) numstack.push(s.charAt(i)-'0');
else if(s.charAt(i) != ']'){
stringstack.push(s.charAt(i));
if(s.charAt(i) == '[') numstack.push(-1);
}
else{
StringBuffer a = new StringBuffer();
while(stringstack.peek() != '[') a.append(stringstack.pop());
stringstack.pop();
int temp = 0;
int dd = 1;
numstack.pop();
while(!numstack.isEmpty() && numstack.peek() != -1){
temp += dd*numstack.pop();
dd *= 10;
}
StringBuffer aa = new StringBuffer();
for(int j = 0; j < temp; j++) aa.append(a);
aa.toString();
for(int j = aa.length()-1; j >= 0; j--) stringstack.push(aa.charAt(j));
}
}
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < stringstack.size(); i++) res.append(stringstack.get(i));
return res.toString();
}
}
我看了看解析,还是将存字符的栈定义为string类比较方便,不用这么多分隔符,存数字的栈也可以将一个数字存到一个内存里,都是先在外面用一个变量记录,再一次性存,值得参考。
一、堆
两种:最大最小堆;
是一种完全二叉树;
搜索通常是对堆顶的操作O(1);
添加删除操作O(n);
二、LeetCode703
找数据流里第k大的元素
从堆过来自然想着用堆实现,找到的堆在这里不能运行,好吧那就熟悉一下自己实现,写了一上午实现了这个堆好家伙测试样例规模达到了20000,直接给我超出时间限度,可惜了我写的堆。
class KthLargest {
protected int[] data;
protected int count;
protected int num;
protected int maxnum;
//建堆
public KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) {
num = 0;
count = k;
maxnum = 10000;
data = new int[maxnum];
for( int i = 0 ; i < nums.length ; i++ ){
this.insert(nums[i]);
}
}
public int add(int val) {
int[] res =new int[count];
this.insert(val);
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) res[i] = this.extractMax();
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) this.insert(res[i]);
// System.out.print(Arrays.toString(res));
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
return res[count - 1];
}
public void insert(int val){
num++;
if(num > maxnum-1){
data[maxnum-1] = val;
int k = maxnum-1;
shiftUp(k);
}
else{
data[num] = val;
int k = num;
shiftUp(k);
}
}
public int extractMax(){
int ret = data[1];
// if(num == 2 && data[2] > data[1]){
// num--;return data[2];
// }
swap( 1 , Math.min(maxnum-1, num));
num--;
shiftDown(1);
return ret;
}
public void shiftUp(int k){
while( k > 1 && data[k/2] < data[k]){
swap(k, k/2);
k /= 2;
}
}
public void shiftDown(int k){
while( 2*k <= Math.min(num, maxnum-1) ){
int j = 2*k;
if( j+1 <= Math.min(num, maxnum-1) && data[j+1] > data[j]) j ++;
if( data[k] >= data[j]) break;
swap(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
public void swap(int i, int j){
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
}
/**
* Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such:
* KthLargest obj = new KthLargest(k, nums);
* int param_1 = obj.add(val);
*/
我觉得还是这样实现堆的代价太大了,看一眼别人的解法。
class KthLargest {
PriorityQueue queue;
int size;
//建堆
public KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) {
queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
size = k;
for(int num:nums) this.add(num);
}
public int add(int val) {
queue.add(val);
if(queue.size() > size) queue.poll();
return queue.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such:
* KthLargest obj = new KthLargest(k, nums);
* int param_1 = obj.add(val);
*/
我惊了,我几十行的代码就这十几行搞定了???
好吧他用的是一个比较高级的队列PriorityQueue,虽然是队列,但也是用堆实现的,我说一直找不到堆的使用,原来可以跳过原本的堆直接用他的衍生物。
PriorityQueue小顶堆实现,队列内按输入值有序排列。
这一题自定义堆也还是可以,相当于手动实现这个优先队列,本质是小顶堆,因为大顶堆的话就是我上一份代码,会出现在数组满了之后,在数组最后添加把原来较大的值替换掉的问题,那用小顶堆再实现一遍。
class KthLargest {
protected int size;
protected int capcity;
protected int[] data;
public KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) {
capcity = 0;
size = k;
data = new int[size];
for(int num:nums){
if(capcity < size-1) data[capcity++] = num;
else add(num);
}
}
public int add(int val) {
if(capcity < size){
data[capcity++] = val;
for(int i = capcity-1; i >= 0; i--) shiftdown(i);
}
else{
if(val <= data[0]) return data[0];
data[0] = val;
shiftdown(0);
}
return data[0];
}
public void shiftdown(int i){
while(i*2 + 1 < size){
int j = i*2 + 1;
if(j + 1 < size && data[j+1] < data[j]) j++;
if(data[i] < data[j]) break;
swap(i, j);
i = j;
}
}
public void swap(int i, int j){
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
}
/**
* Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such:
* KthLargest obj = new KthLargest(k, nums);
* int param_1 = obj.add(val);
*/
三、LeetCode1046
这题用了上一题的最大堆,
class Solution {
protected int size;
protected int capcity;
protected int[] data;
public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) {
capcity = size = stones.length;
if(capcity == 1) return stones[0];
if(capcity == 2) return Math.abs(stones[1]-stones[0]);
data = new int[capcity];
for(int i = 0; i < capcity; i++){
data[i] = stones[i];
}
for(int i = capcity-1; i >= 0; i--) shiftdown(i);
while(size > 1){
int j = 1;
if(size > 2 && data[2] > data[1]) j++;
data[0] -= data[j];
swap(j, --size);shiftdown(j);
if(data[0] != 0) shiftdown(0);
else{
swap(0, --size);shiftdown(0);
}
}
if(size == 0) return 0;
return data[0];
}
public void shiftdown(int i){
while(i*2 + 1 < size){
int j = i*2 + 1;
if(j + 1 < size && data[j+1] > data[j]) j++;
if(data[i] > data[j]) break;
swap(i, j);
i = j;
}
}
public void swap(int i, int j){
int t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
}
改一下要求,这题明显要最大堆改一下下拉条件就能很快写出来,
上一问的优先队列这么写:
PriorityQueue< Integer > pq = new PriorityQueue< Integer >((a, b) -> b - a);
好像就是最大堆可以直接用了。
四、LeetCode692
这道题我一下子想到了方法,但是用Java来做一下子就不会了,不得不学习一下官方语言的精炼:
class Solution {
public List topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
Map hash = new HashMap<>();
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>(
(w1, w2) -> hash.get(w1).equals(hash.get(w2)) ?
w2.compareTo(w1) : hash.get(w1) - hash.get(w2) );
for(String string:words){
hash.put(string, hash.getOrDefault(string, 0) + 1);
}
for(String string:hash.keySet()){
queue.offer(string);
if(queue.size() > k) queue.poll();
}
List res = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()) res.add(queue.poll());
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
}
看这自定义排序,看这赋值,看这反转,太妙了。
太妙的结果是看不懂时间复杂度。
五、LeetCode451
上一题是字符串,这一题是字符,把字符串类型改成字符就差不多了,而且对输出顺序没啥要求,只是要全输出来。
class Solution {
public String frequencySort(String s) {
Map hash = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
hash.put(s.charAt(i), hash.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>(
(w1, w2) -> hash.get(w1).equals(hash.get(w2)) ?
w1.compareTo(w2) : hash.get(w2) - hash.get(w1) );
for(char c:hash.keySet()){
queue.offer(c);
}
String res = new String();
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
char c = queue.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < hash.get(c); i++) res += c;
}
return res;
}
}
效率有点低倒是。
但是解析差不多也这些方法,或许我手写一个堆不用优先队列会效率高一些,然后还有一个桶排序的方法用于处理这种频率问题。
一、树
我懒得写了。。。
二、LeetCode938
直接二叉搜索树找范围内的值,
class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
int num = 0;
if(root.val <= high && root.val >= low) num += root.val;
if(root.left != null) num += rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high);
if(root.right != null) num += rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
return num;
}
}
单纯遍历一遍每个位置,效率较低,要注意到这是搜索树,可以得到一些捷径减少消耗。
class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
int num = 0;
if(root.val <= high && root.val >= low){
num += root.val;
if(root.left != null) num += rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high);
if(root.right != null) num += rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
}
if(root.val < low && root.right != null) num += rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
if(root.val > high && root.left != null) num += rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high);
return num;
}
}
三、LeetCode700
也是搜索,秒做出来
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
TreeNode node = null;
if(root.val == val) node = root;
if(root.val < val && root.right != null) node = searchBST(root.right, val);
if(root.val > val && root.left != null) node = searchBST(root.left, val);
return node;
}
}
哈哈我觉得我又行了
好吧应该是题目太简单
四、LeetCode144
前序遍历,嗯递归真香
class Solution {
public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null) res.add(root.val);
else return res;
if(root.left != null) res.addAll(preorderTraversal(root.left));
if(root.right != null) res.addAll(preorderTraversal(root.right));
return res;
}
}
五、LeetCode94
中序遍历
不直接递归了,改用迭代试一试
class Solution {
public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
while(root != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
}
看了一眼解析还是,也使用栈,前序栈是按广搜,中序用深搜,都是为了方便遍历。
不过这种遍历好像用那个Morris更简便。
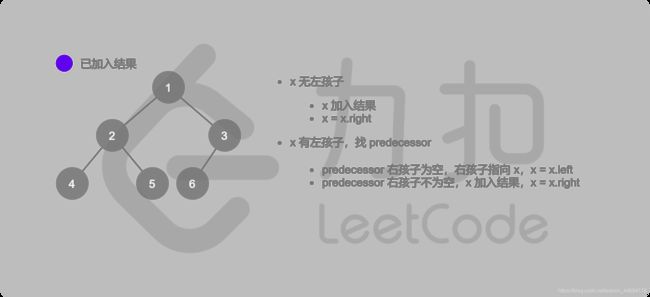
class Solution {
public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList();
TreeNode predecessor = null;
while (root != null) {
if (root.left != null) {
// predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
predecessor = root.left;
while (predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != root) {
predecessor = predecessor.right;
}
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if (predecessor.right == null) {
predecessor.right = root;
root = root.left;
}
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
else {
res.add(root.val);
predecessor.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
// 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
else {
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/solution/er-cha-shu-de-zhong-xu-bian-li-by-leetcode-solutio/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
六、LeetCode145
后序遍历
class Solution {
public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode temp = new TreeNode();
while(root != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(root != null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if(root.right == null || root.right == temp){
res.add(root.val);
temp = root;
root = null;
}
else{
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
这个迭代我还是没能一下子写出来,这样的话这题不止easy难度吧,
这个用Morris方法也挺麻烦的,
嗯递归真香。