Netty(四)NIO-优化与源码
Netty优化与源码
1. 优化
1.1 扩展序列化算法
序列化,反序列化主要用于消息正文的转换。
序列化:将java对象转为要传输对象(byte[]或json,最终都是byte[])
反序列化:将正文还原成java对象。
//java自带的序列化
// 反序列化
byte[] body = new byte[bodyLength];
byteByf.readBytes(body);
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(body));
Message message = (Message) in.readObject();
message.setSequenceId(sequenceId);
// 序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
new ObjectOutputStream(out).writeObject(message);
byte[] bytes = out.toByteArray();
为了支持更多序列化算法,抽象一个 Serializer 接口,提供两个实现,将实现加入了枚举类 Serializer.Algorithm 中:
enum SerializerAlgorithm implements Serializer {
// Java 实现
Java {
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
try {
ObjectInputStream in =
new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Object object = in.readObject();
return (T) object;
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("SerializerAlgorithm.Java 反序列化错误", e);
}
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
new ObjectOutputStream(out).writeObject(object);
return out.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("SerializerAlgorithm.Java 序列化错误", e);
}
}
},
// Json 实现(引入了 Gson 依赖)
Json {
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
return new Gson().fromJson(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8), clazz);
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
return new Gson().toJson(object).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
};
// 需要从协议的字节中得到是哪种序列化算法
public static SerializerAlgorithm getByInt(int type) {
SerializerAlgorithm[] array = SerializerAlgorithm.values();
if (type < 0 || type > array.length - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("超过 SerializerAlgorithm 范围");
}
return array[type];
}
}
增加配置类和配置文件:
public abstract class Config {
static Properties properties;
static {
try (InputStream in = Config.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties")) {
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static int getServerPort() {
String value = properties.getProperty("server.port");
if(value == null) {
return 8080;
} else {
return Integer.parseInt(value);
}
}
public static Serializer.Algorithm getSerializerAlgorithm() {
String value = properties.getProperty("serializer.algorithm");
if(value == null) {
return Serializer.Algorithm.Java;
} else {
return Serializer.Algorithm.valueOf(value);
}
}
}
配置文件
serializer.algorithm=Json
修改编解码器
/**
* 必须和 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 一起使用,确保接到的 ByteBuf 消息是完整的
*/
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf, Message> {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> outList) throws Exception {
// 3. 1 字节的序列化方式 jdk 0 , json 1
out.writeByte(Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().ordinal());
byte[] bytes = Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().serialize(msg);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
byte serializerAlgorithm = in.readByte(); // 0 或 1
// 找到反序列化算法
Serializer.Algorithm algorithm = Serializer.Algorithm.values()[serializerAlgorithm];
// 确定具体消息类型
Class<? extends Message> messageClass = Message.getMessageClass(messageType);
Message message = algorithm.deserialize(messageClass, bytes);
out.add(message);
}
}
1.2 参数调优
CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS
- 属于SocketChannel参数,用在客户端建立连接时,如超时则抛出timeout异常
- SO_TIMEOUT主要用在阻塞IO,阻塞IO中accept,read等都是无限等待的
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap().group(group)
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).handler(new LoggingHandler());
附源码部分 io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioChannel.AbstractNioUnsafe#connect
@Override
public final void connect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// ...
// Schedule connect timeout.
int connectTimeoutMillis = config().getConnectTimeoutMillis();
if (connectTimeoutMillis > 0) {
connectTimeoutFuture = eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;
ConnectTimeoutException cause =
new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress); // 断点2
if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}, connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// ...
}
SO_BACKLOG
- 属于ServerSocketChannel参数
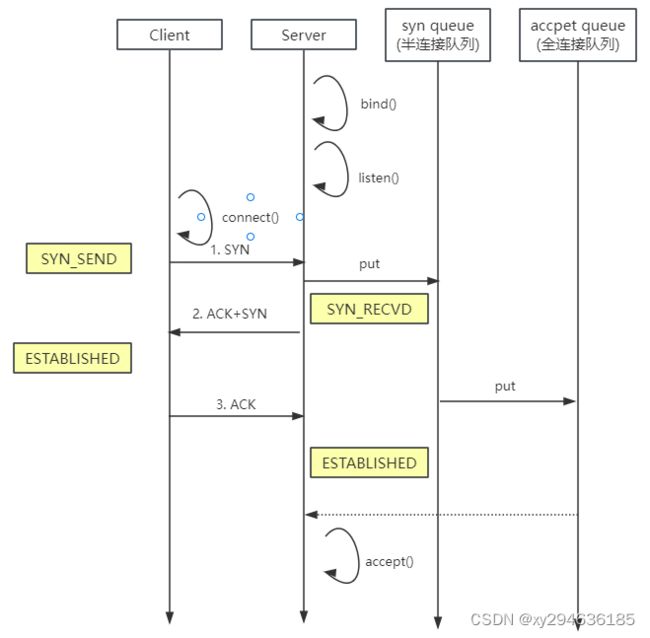
sync queue - 半连接队列- 大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在
syncookies启用的情况下,逻辑上没有最大值限制,这个设置便被忽略
accept queue - 全连接队列 - 其大小通过 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn 指定,在使用 listen 函数时,内核会根据传入的 backlog 参数与系统参数,取二者的较小值
- 如果 accpet queue 队列满了,server 将发送一个拒绝连接的错误信息到 client
netty中可通过option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,值)来设置大小
- 大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在
public class DefaultServerSocketChannelConfig extends DefaultChannelConfig
implements ServerSocketChannelConfig {
private volatile int backlog = NetUtil.SOMAXCONN;
// ...默认大小
}
ulimit -n
- 限制一个进程打开最大文件描述符的数目,属于操作系统参数
TCP_NODELAY
- nagle算法的延迟,一般设为true不延迟,数据赞属于 SocketChannal 参数
SO_SNDBUF & SO_RECVBUF
滑动接口的参数,现在的操作系统会根据实际情况自动调整。
- SO_SNDBUF 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- SO_RCVBUF 既可用于 SocketChannal 参数,也可以用于 ServerSocketChannal 参数(建议设置到 ServerSocketChannal 上)
ALLOCATOR
ByteBuf分配器,属于 SocketChannal 参数,用来分配 ByteBuf, ctx.alloc()。源码详解P128
RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR
- 属于 SocketChannal 参数,控制 netty 接收缓冲区大小。源码详解:P129
- 负责入站数据的分配,决定入站缓冲区的大小(并可动态调整),统一采用 direct 直接内存,具体池化还是非池化由 allocator 决定
1.3 RPC 框架
通过反射获取配置
public class ServicesFactory {
static Properties properties;
static Map<Class<?>, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static {
try {
InputStream in = Config.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties");
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
Set<String> names = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String name : names) {
if (name.endsWith("Services")) {
Class<?> interfaceClass = Class.forName(name);
Class<?> instanceClass = Class.forName(properties.getProperty(name));
map.put(interfaceClass, instanceClass.newInstance());
}
}
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static <T> T getService(Class<T> interfaceClass) {
return (T) map.get(interfaceClass);
}
}
RPC消息处理器
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcRequestMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequestMessage message) {
RpcResponseMessage response = new RpcResponseMessage();
try {
HelloService service = (HelloService) ServicesFactory.getService(Class.forName(message.getInterfaceName()));
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(message.getMethodName(), message.getParameterTypes());
Object invoke = method.invoke(service, message.getParameterValue());
response.setReturnValue(invoke);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
response.setExceptionValue(e);
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
//本地调试
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
RpcRequestMessage message = new RpcRequestMessage(1,
"com.aric.server.service.HelloService",
"sayHello",
String.class,
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"aric"});
HelloService service = (HelloService) ServicesFactory.getService(Class.forName(message.getInterfaceName()));
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(message.getMethodName(), message.getParameterTypes());
Object invoke = method.invoke(service, message.getParameterValue());
System.out.println(invoke);
}
}
客户端优化,抽取使用代理对象发送消息
/**
* 使用代理对象替换,主线程发送
* NioEventLoop线程接收结果,需要线程间通信,使用promise对象接收结果
* @author
* @created by xuyu on 2023/9/23-23:10
*/
@Slf4j
public class RpcClientManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//后期创建代理类优化发送结构
getChannel().writeAndFlush(new RpcRequestMessage(
1,
"com.aric.server.service.HelloService",
"sayHello",
String.class,
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"test"}
));
//使用代理发送
HelloService service = getProxyService(HelloService.class);
service.sayHello("test");
}
//创建代理类
public static <T> T getProxyService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
ClassLoader loader = serviceClass.getClassLoader(); //当前类加载器
Class[] interfaces = new Class[]{serviceClass};//代理类要实现的接口
//jdk自带的代理
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, (proxy, method, arg) -> {
//proxy代理对象,method:代理方法,arg:代理参数
//1.将方法调用转换为消息对象
RpcRequestMessage message = new RpcRequestMessage(
SequenceIdGenerator.nextId(),
serviceClass.getName(),
method.getName(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
arg
);
//2.将消息对象发送出去
getChannel().writeAndFlush(message);
//3.TODO:待优化异步等待返回结果
return null;
});
return (T)o;
}
private static Channel channel = null;
private static final Object LOCK = new Object();
//单例构造获取唯一channel对象
public static Channel getChannel() {
if (channel != null) {
return channel;
}
synchronized (LOCK) {
if (channel != null) {
return channel;
}
initChannel();
return channel;
}
}
//初始化channel方法
private static void initChannel() {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
try {
channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
//改为异步
channel.closeFuture().addListener(future -> {
group.shutdownGracefully();
});
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.debug("client error", e);
}
}
}
//创建代理类
public static <T> T getProxyService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
ClassLoader loader = serviceClass.getClassLoader(); //当前类加载器
Class[] interfaces = new Class[]{serviceClass};//代理类要实现的接口
//jdk自带的代理
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, (proxy, method, arg) -> {
//proxy代理对象,method:代理方法,arg:代理参数
//1.将方法调用转换为消息对象
int sequenceId = SequenceIdGenerator.nextId();
RpcRequestMessage message = new RpcRequestMessage(
sequenceId,
serviceClass.getName(),
method.getName(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
arg
);
//2.将消息对象发送出去
getChannel().writeAndFlush(message);
//3.返回
//准备好空的promise对象来接收结果,参数为指定promise对象异步接收结果的线程
DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(getChannel().eventLoop());
RpcResponseMessageHandler.PROMISE.put(sequenceId, promise);
// promise.addListener(future -> {
// //创建线程处理任务
// });
//原线程等待promise的结果
promise.await();
if (promise.isSuccess()) {
return promise.getNow();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(promise.cause());
}
});
return (T) o;
}
/**
* rpc响应消息处理器
*/
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
//序号-promise<结果类型>,多个线程访问,用于异步接收rpc调用的返回结果
public static final Map<Integer, Promise<Object>> PROMISE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponseMessage msg) throws Exception {
//拿到空的promise
Promise<Object> promise = PROMISE.remove(msg.getSequenceId()); //返回并移除
if (promise != null) {
Object returnValue = msg.getReturnValue();
Exception exceptionValue = msg.getExceptionValue();
if (exceptionValue != null) {
promise.setFailure(exceptionValue);
} else {
promise.setSuccess(returnValue);
}
}
System.out.println(msg);
}
代码:https://gitee.com/xuyu294636185/netty-demo.git
2. 源码
2.1 netty启动剖析
//1. netty中使用EventLoopGroup(Nio boss线程),来封装线程和selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//创建NioServerSocketChannel,同时初始化它关联的handler,以及为原生ssc存储config
NioServerSocketChannel attachment = new NioServerSocketChannel();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//2.启动nio boss线程执行
//建立selector和channel的注册,sscKey是事件的句柄,是将来事件发生后,通过它可以知道事件和哪个channel的事件
SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, 0, attachment);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
//表示sscKey只关注accept事件
sscKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
启动流程
EventLoop
EventLoop重要组成:selector,线程,任务队列
EventLoop既会处理io事件,也会处理普通任务和定时任务
- selector何时创建?
在构造方法创建时通过SelectorProvider.openSelector(); - eventloop为什么会有两个selector成员?
为了在遍历selectedKey时提高性能。
一个是原始的unwrappedselector(底层是hashset实现),一个是包装后的selector(底层是数组实现) - eventLoop的nio线程在何时启动?
在首次调用exectue方法时executor中将当前线程赋给nio线程,并通过state状态控制位只会启动一次 - 提交普通任务会不会结束select阻塞?
会
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
protected void wakeup(boolean inEventLoop) {
if(!inEventLoop && wakeUp.compareAndSet(false,true)) {
selector.wakeup();
}
} - wakeup方法理解
inEventLoop:用于判断当前wakeup线程是否和nio线程是否相同,不同才能进入。
wakeUp:原子Boolean变量,如果有多个线程来提交任务,为了避免wakeup被频繁调用。只有一个成功。 - 每次循环时,什么时候会进入SelectStrategy.SELECT分支?
public void run(){
for(; {
switch(selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTask())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
select(wakeUp.getAndSet(false));
if(wakeUp.get()) {…}
default:
}
}
}
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier supplier,boolean hasTasks) {
return hasTasks ? suppplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}
没有任务时,才会进入SELECT。
当有任务时,会调用SelectNow方法,顺便拿到io事件。 - 何时会select阻塞,阻塞多久?
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(cuurrentTimeNanos);
for(;{
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
}
没有定时任务的情况
selectDeadLineNanos:截至时间 = 当前时间 + 1s
timeoutMillis:超时时间 = 1s + 0.5ms - nio空轮询bug在哪体现,如何解决?
for(;{
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
}
在select中没有阻塞,一直在死循环
解决:引入selectCnt,每循环一次++,当超过设置的阈值(默认512),selectRebuildSelector(selectCnt)重新创建一个selector,替换旧的。 - ioRatio控制什么,设置为100有何作用?
if(ioRatio == 100) {
processSelectedKeys(); //处理所有ioio事件
runAllTasks();
} else {
long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
processSelectedKeys();
long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio); //避免普通事件执行时间太长
}
ioRatio控制处理io事件所占用的事件比例50%,ioTime代表执行io事件处理耗时。 - selectedKeys优化,在哪区分不同事件类型。
selectedKeys由hashset集合替换为数组实现。
private void processSelectedKeys() [
if(selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized(); //优化后的
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys()); //原始的
}
}
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
for(int i = 0;i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];
selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
Objected a = k.attachment();
if(a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a); //处理具体的事件类型
}
}
}
accept流程
- selector.select()阻塞直到事件发生
- 遍历处理selectedKeys
- 拿到一个key,判断事件类型是否为accpet
- 创建socketChannel,设置非阻塞
- 将socketChannel注册到selector
- 关注selectionKey的read事件。
read流程
- selector.select()阻塞直到事件发生
- 遍历处理selectedKeys
- 拿到一个key,判断事件类型是否为read
- 读取操作