C# 多线程三:临界区 Monitor的理解与运用
目录
一.Monitor特点
二.Monitor和Lock的关系
1.关系
2.示例
例1.使用Lock
例2.使用Monitor.Entor(obj,ref lockTaken)
三.方法
常用方法
其他方法:
四.使用Monitor实现阻塞队列BlackQueue
一.Monitor特点
它使用独占锁的方式控制线程同步,一个线程只有得到这把锁才可以对该对象进行操作,对象锁机制保证了同一时刻只有一个线程可以访问这个对象
注:一定是锁定引用类型 值类型被锁会有装箱操作 下次再次锁这个值又将装箱成一个新的对象 导致报错
二.Monitor和Lock的关系
1.关系
其实Lock在IL代码中会被翻译成Monitor。也就是Monitor.Enter(obj)和Monitor.Exit(obj).
Lock(obj)
{
....
}
等同于
try
{
Monitor.Entor(obj,ref lockTaken)
....
}catch()
{}finally
{
if(lockTaken)
Monitor.Exit(obj);
}
2.示例
例1.使用Lock
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
public class LudwigLock {
public List obj;
int maxLength;
public LudwigLock(int _max) {
maxLength = _max;
obj = new List();
}
public void AddCharByObj(T a) {
lock(obj) {
while(obj.Count == maxLength) {
Monitor.Wait(obj);
}
obj.Add(a);
if(obj.Count == 1)
Monitor.PulseAll(obj);
}
}
public void SubCharByObj() {
lock(obj) {
while(obj.Count == 0) {
Monitor.Wait(obj);
}
obj.RemoveAt(0);
if(obj.Count == maxLength - 1)
Monitor.PulseAll(obj);
}
}
public int Count() {
lock(obj) {
return obj.Count;
}
}
public string GetStr() {
lock(obj) {
string str = "";
for(int i = 0; i < obj.Count; i++) {
str += obj[i] + " - ";
}
return str;
}
}
} static void Main(string[] args) {
LudwigLock ludwigLock = new LudwigLock(5);
Thread thread = new Thread(() => {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
ludwigLock.AddCharByObj(i.ToString());
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() => {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ludwigLock.SubCharByObj();
Console.WriteLine(ludwigLock.GetStr());
}
});
thread.Start();
thread2.Start();
Console.Read();
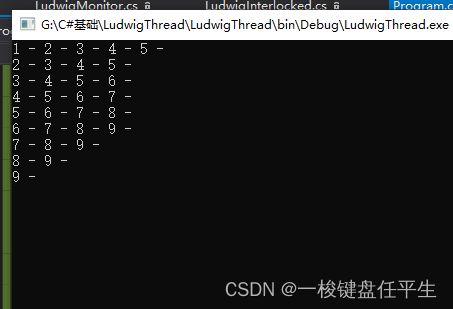
} 打印:
例2.使用Monitor.Entor(obj,ref lockTaken)
public class LudwigMonitor {
public List ts = new List();
private int max;
public LudwigMonitor(int _max) {
max = _max;
}
public void Add(T item) {
try {
Monitor.Enter(ts, ref flag);
while(ts.Count == max) {
Monitor.Wait(ts);
}
ts.Add(item);
if(ts.Count == 1)
Monitor.PulseAll(ts);
} catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
} finally {
if(flag)
Monitor.Exit(ts);
}
}
public void Sub() {
try {
Monitor.Enter(ts);
while(ts.Count == 0) {
Monitor.Wait(ts);
}
ts.RemoveAt(0);
if(ts.Count == max - 1)
Monitor.PulseAll(ts);
} catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex);
} finally {
Monitor.Exit(ts);
}
}
public string GetString() {
string str = "";
try {
Monitor.Enter(ts);
for(int i = 0; i < ts.Count; i++) {
str += ts[i] + " - ";
}
} finally {
Monitor.Exit(ts);
}
return str;
}
} static void Main(string[] args) {
LudwigMonitor ludwigMonitor = new LudwigMonitor(5);
Thread thread = new Thread(() => {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
ludwigMonitor.Add(i.ToString());
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() => {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ludwigMonitor.Sub();
Console.WriteLine(ludwigMonitor.GetString());
}
});
thread.Start();
thread2.Start();
Console.Read();
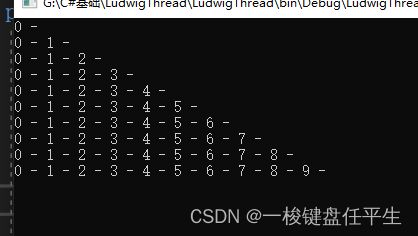
} 打印:
由上面可以看出俩个例子效果一样
三.方法
常用方法
以下几个常用方法大多在例子1和例子2中已有使用,不再赘述
Enter(Object)
在指定对象上获取排他锁。
Exit(Object)
释放指定对象上的排他锁。
Wait(Object)
释放对象上的锁并阻止当前线程,直到它重新获取该锁。
Pulse(Object)
通知等待队列中的线程锁定对象状态的更改。
PulseAll(Object)
通知所有的等待线程对象状态的更改。
Wait(Object, Int32)
释放对象上的锁并阻止当前线程,直到它重新获取该锁。 如果已用指定的超时时间间隔,则线程进入就绪队列。
和Wait(Object)类似 添加了一个超时间隔 超过时间自动加入就绪队列
我们改一下例子2的Add方法
代码:
public void Add(T item) {
try {
Monitor.Enter(ts);
while(ts.Count == max) {
Monitor.Wait(ts, 1000);
if(ts.Count == max)
max ++;
}
ts.Add(item);
if(ts.Count == 1)
Monitor.PulseAll(ts);
} catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
} finally {
Monitor.Exit(ts);
}
}设置超时之后max自增
打印:
Enter(Object, Boolean)
获取指定对象上的排他锁,并自动设置一个值,指示是否获取了该锁。
这个bool值的作用是防止未调用Monitor.Enter就调用Monitor.Exit会引发异常
一般用法:
try {
Monitor.Enter(ts, ref flag);
} catch(Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
} finally {
if(flag) {
Monitor.Exit(ts);
}
}其他方法:
IsEntered(Object)
确定当前线程是否保留指定对象上的锁。
TryEnter(Object)
尝试获取指定对象的排他锁。
TryEnter(Object, Boolean)
尝试获取指定对象上的排他锁,并自动设置一个值,指示是否获取了该锁。
TryEnter(Object, Int32)
在指定的毫秒数内尝试获取指定对象上的排他锁。
TryEnter(Object, Int32, Boolean)
在指定的毫秒数内尝试获取指定对象上的排他锁,并自动设置一个值,指示是否获取了该锁。
TryEnter(Object, TimeSpan)
在指定的时间内尝试获取指定对象上的排他锁。
TryEnter(Object, TimeSpan, Boolean)
在指定的一段时间内尝试获取指定对象上的排他锁,并自动设置一个值,指示是否获得了该锁。
Wait(Object, Int32, Boolean)
释放对象上的锁并阻止当前线程,直到它重新获取该锁。 如果已用指定的超时时间间隔,则线程进入就绪队列。 此方法还指定是否在等待之前退出上下文的同步域(如果在同步上下文中)然后重新获取该同步域。
Wait(Object, TimeSpan)
释放对象上的锁并阻止当前线程,直到它重新获取该锁。 如果已用指定的超时时间间隔,则线程进入就绪队列。
Wait(Object, TimeSpan, Boolean)
释放对象上的锁并阻止当前线程,直到它重新获取该锁。 如果已用指定的超时时间间隔,则线程进入就绪队列。 可以在等待之前退出同步上下文的同步域,随后重新获取该域。
四.使用Monitor实现阻塞队列BlackQueue
代码:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading;
public class BlackQueue {
private Queue queue;
int maxLen;
bool isClose;
public BlackQueue(int max) {
queue = new Queue();
maxLen = max;
}
public void Enqueue(T item) {
lock(queue) {
while(queue.Count >= maxLen) {
Monitor.Wait(queue);
}
queue.Enqueue(item);
if(queue.Count == 1)
Monitor.PulseAll(queue);
}
}
public int Count() {
lock(queue) {
return queue.Count;
}
}
public bool TryDequeue(out T item) {
lock(queue) {
while(queue.Count <= 0) {
if(isClose) {
item = default(T);
return false;
}
Monitor.Wait(queue);
}
item = queue.Dequeue();
if(queue.Count == maxLen - 1)
Monitor.PulseAll(queue);
return true;
}
}
public void Close() {
lock(queue) {
isClose = true;
Monitor.PulseAll(queue);
}
}
}