netty实现简单rpc
RPC是Remote Procedure Call的简称,即远程过程调用,通过rpc,我们可以像调用本地接口一样,调用远程接口。在这个过程中,接口的实现对我们透明。实现rpc的框架很多,比如著名的dubbo框架,这里介绍通过netty来实现一个简单的rpc。
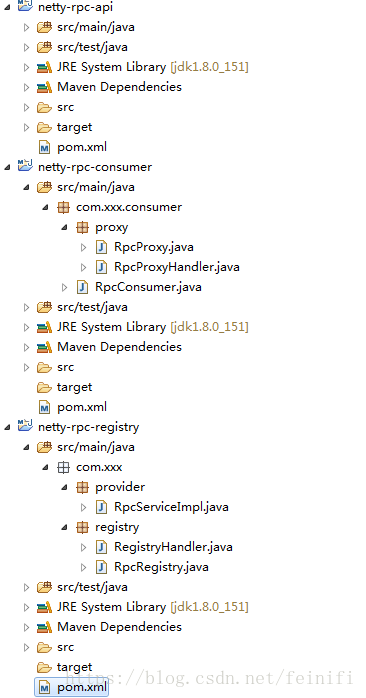
这里分为三个项目,分别是netty-rpc-api(定义接口),netty-rpc-consumer(客户端),netty-rpc-registry(服务端)。他们的职责这里简单说明一下:
netty-rpc-api:定义一个接口和rpc调用过程中传输的消息体InvokeMsg,无需任何依赖,被其他两个项目引用。
netty-rpc-consumer:依赖netty-rpc-api,通过proxy的方式调用接口。
netty-rpc-registry:实现netty-rpc-api项目中定义的接口,并注册服务,等待客户端调用。
三个工程结构如下:
netty-rpc-api项目
RpcService.java
package com.xxx.service;
public interface RpcService {
String hello(String name);
int add(int a,int b);
int sub(int a,int b);
}
InvokeMsg.java
package com.xxx.core.msg;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class InvokeMsg implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String className;
private String methodName;
private Class[] paramTypes;
private Object[] values;
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public String getMethodName() {
return methodName;
}
public void setMethodName(String methodName) {
this.methodName = methodName;
}
public Class[] getParamTypes() {
return paramTypes;
}
public void setParamTypes(Class[] paramTypes) {
this.paramTypes = paramTypes;
}
public Object[] getValues() {
return values;
}
public void setValues(Object[] values) {
this.values = values;
}
}
netty-rpc-registry项目
pom.xml
com.xxx
netty-rpc-api
1.0
io.netty
netty-all
4.1.27.Final
RpcServiceImpl.java
package com.xxx.provider;
import com.xxx.service.RpcService;
public class RpcServiceImpl implements RpcService{
@Override
public String hello(String name) {
return "hello,my name is "+name;
}
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
@Override
public int sub(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
}
RegistryHandler.java
package com.xxx.registry;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import com.xxx.core.msg.InvokeMsg;
public class RegistryHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
public static ConcurrentHashMap classMap = new ConcurrentHashMap();
private List classCache = new ArrayList();
public RegistryHandler() {
scannerClass("com.xxx.provider");
doRegister();
}
private void doRegister() {
if(classCache.size() ==0 ){return;}
for(String name:classCache){
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(name);
Class interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces()[0];
classMap.put(interfaces.getName(), clazz.newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
private void scannerClass(String packageName) {
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File dirFile = new File(url.getFile());
for(File file:dirFile.listFiles()){
if(file.isDirectory()){
scannerClass(packageName+"."+file.getName());
}else{
classCache.add(packageName+"."+file.getName().replace(".class", ""));
}
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
Object result = new Object();
InvokeMsg request = (InvokeMsg)msg;
if(classMap.containsKey(request.getClassName())){
Object clazz = classMap.get(request.getClassName());
Method method = clazz.getClass().getMethod(request.getMethodName(),
request.getParamTypes());
result = method.invoke(clazz, request.getValues());
}
ctx.writeAndFlush(result);
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.flush();
ctx.close();
}
}
RpcRegistry.java
package com.xxx.registry;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldPrepender;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ClassResolvers;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectEncoder;
public class RpcRegistry{
private int port;
public RpcRegistry(int port){
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0,4,0,4));
pipeline.addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(4));
pipeline.addLast("encoder",new ObjectEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("decoder",new
ObjectDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE,
ClassResolvers.cacheDisabled(null)));
pipeline.addLast(new RegistryHandler());
}
}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("server listener at port : "+port);
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main( String[] args ){
new RpcRegistry(8080).start();
}
}
netty-rpc-consumer项目
pom.xml
com.xxx
netty-rpc-api
1.0
io.netty
netty-all
4.1.27.Final
RpcProxyHandler.java
package com.xxx.consumer.proxy;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
public class RpcProxyHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
private Object response;
public Object getResponse(){
return this.response;
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("client receive message: "+msg);
response = msg;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.flush();
ctx.close();
}
}
RpcProxy.java
package com.xxx.consumer.proxy;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldPrepender;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ClassResolvers;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectEncoder;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import com.xxx.core.msg.InvokeMsg;
public class RpcProxy {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static T create(Class clazz){
MethodProxy proxy = new MethodProxy(clazz);
T result = (T)Proxy.newProxyInstance(clazz.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{clazz}, proxy);
return result;
}
}
class MethodProxy implements InvocationHandler{
private Class clazz;
public MethodProxy(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
if(Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())){
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else{
return rpcInvoke(proxy,method,args);
}
return args;
}
private Object rpcInvoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
InvokeMsg msg = new InvokeMsg();
msg.setClassName(this.clazz.getName());
msg.setMethodName(method.getName());
msg.setValues(args);
msg.setParamTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
final RpcProxyHandler handler = new RpcProxyHandler();
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder",new
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 4,0,4));
pipeline.addLast("frameEncoder",
new LengthFieldPrepender(4));
pipeline.addLast("encoder",new ObjectEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("decoder",new
ObjectDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE,
ClassResolvers.cacheDisabled(null)));
pipeline.addLast("handler",handler);
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync();
future.channel().writeAndFlush(msg).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
return handler.getResponse();
} catch (Exception e) {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
return null;
}
}
RpcConsumer.java
package com.xxx.consumer;
import com.xxx.consumer.proxy.RpcProxy;
import com.xxx.service.RpcService;
public class RpcConsumer {
public static void main( String[] args ){
RpcService service = RpcProxy.create(RpcService.class);
String hello = service.hello("rpc");
System.out.println(hello);
System.out.println(service.add(5, 3));
System.out.println(service.sub(5, 3));
}
}
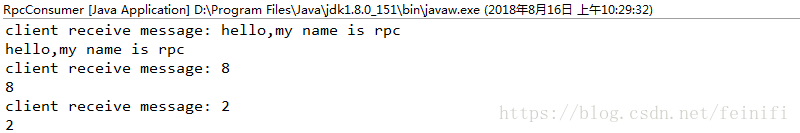
启动netty-rpc-registry项目,然后启动客户端消费者netty-rpc-consumer,有如下打印信息。
这样一个简易的rpc框架就完成了。
整理一下整个流程的示意图:
这中间消息体invokeMsg,起到了关键的纽带作用,客户端调用时,将请求接口,请求方法,请求参数封装到一起,传递给服务端,服务端根据收到的消息,解析请求接口,请求方法,请求参数,采用反射调用本地方法,并将结果返回给客户端。客户端监听到有数据返回,将结果返回给调用者。