elasticsearch(ES)分布式搜索引擎03——(RestClient查询文档,ES旅游案例实战)
目录
- 3.RestClient查询文档
-
- 3.1.快速入门
-
- 3.1.1.发起查询请求
- 3.1.2.解析响应
- 3.1.3.完整代码
- 3.1.4.小结
- 3.2.match查询
- 3.3.精确查询
- 3.4.布尔查询
- 3.5.排序、分页
- 3.6.高亮
-
- 3.6.1.高亮请求构建
- 3.6.2.高亮结果解析
- 4.旅游案例
-
- 4.1.酒店搜索和分页
-
- 4.1.1.需求分析
- 4.1.2.定义实体类
- 4.1.3.定义controller
- 4.1.4.实现搜索业务
- 4.2.酒店结果过滤
-
- 4.2.1.需求分析
- 4.2.2.修改实体类
- 4.2.3.修改搜索业务
- 4.3.我周边的酒店
-
- 4.3.1.需求分析
- 4.3.2.修改实体类
- 4.3.3.距离排序API
- 4.3.4.添加距离排序
- 4.3.5.排序距离显示
- 4.4.酒店竞价排名
-
- 4.4.1.需求分析
- 4.4.2.修改HotelDoc实体
- 4.4.3.添加广告标记
- 4.4.4.添加算分函数查询
3.RestClient查询文档
文档的查询同样适用昨天学习的 RestHighLevelClient对象,基本步骤包括:
- 1)准备Request对象
- 2)准备请求参数
- 3)发起请求
- 4)解析响应
3.1.快速入门
我们以match_all查询为例
3.1.1.发起查询请求
-
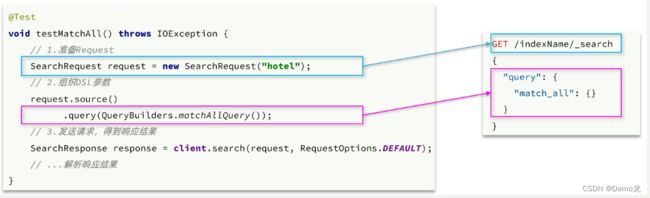
第一步,创建
SearchRequest对象,指定索引库名 -
第二步,利用
request.source()构建DSL,DSL中可以包含查询、分页、排序、高亮等query():代表查询条件,利用QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery()构建一个match_all查询的DSL
-
第三步,利用client.search()发送请求,得到响应
这里关键的API有两个,一个是request.source(),其中包含了查询、排序、分页、高亮等所有功能: 另一个是
另一个是QueryBuilders,其中包含match、term、function_score、bool等各种查询:
3.1.2.解析响应
响应结果的解析:
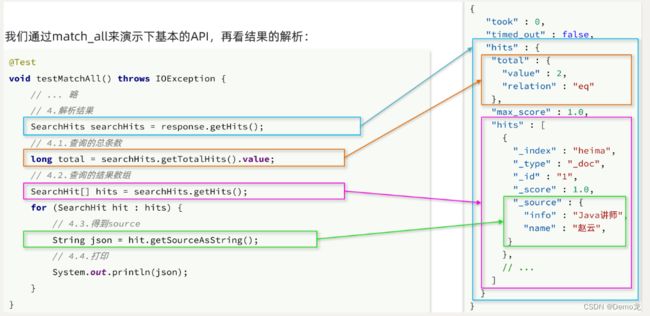
elasticsearch返回的结果是一个JSON字符串,结构包含:
hits:命中的结果total:总条数,其中的value是具体的总条数值max_score:所有结果中得分最高的文档的相关性算分hits:搜索结果的文档数组,其中的每个文档都是一个json对象_source:文档中的原始数据,也是json对象
因此,我们解析响应结果,就是逐层解析JSON字符串,流程如下:
SearchHits:通过response.getHits()获取,就是JSON中的最外层的hits,代表命中的结果SearchHits#getTotalHits().value:获取总条数信息SearchHits#getHits():获取SearchHit数组,也就是文档数组SearchHit#getSourceAsString():获取文档结果中的_source,也就是原始的json文档数据
3.1.3.完整代码
完整代码如下:
@Test
void testMatchAll() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
request.source()
.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
private void handleResponse(SearchResponse response) {
// 4.解析响应
SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits();
// 4.1.获取总条数
long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value;
System.out.println("共搜索到" + total + "条数据");
// 4.2.文档数组
SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits();
// 4.3.遍历
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
// 获取文档source
String json = hit.getSourceAsString();
// 反序列化
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
System.out.println("hotelDoc = " + hotelDoc);
}
}
3.1.4.小结
查询的基本步骤是:
-
创建SearchRequest对象
-
准备Request.source(),也就是DSL。
① QueryBuilders来构建查询条件
② 传入Request.source() 的 query() 方法
-
发送请求,得到结果
-
解析结果(参考JSON结果,从外到内,逐层解析)
3.2.match查询
全文检索的match和multi_match查询与match_all的API基本一致。差别是查询条件,也就是query的部分。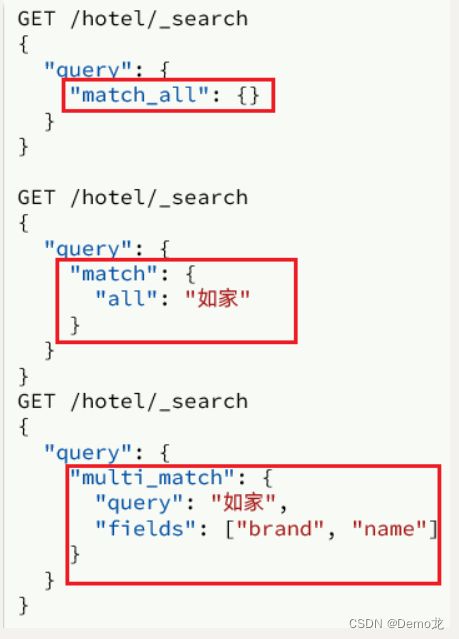
因此,Java代码上的差异主要是request.source().query()中的参数了。同样是利用QueryBuilders提供的方法:
而结果解析代码则完全一致,可以抽取并共享。
完整代码如下:
@Test
void testMatch() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
request.source()
.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", "如家"));
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
3.3.精确查询
精确查询主要是两者:
- term:词条精确匹配
- range:范围查询
与之前的查询相比,差异同样在查询条件,其它都一样。
3.4.布尔查询
布尔查询是用must、must_not、filter等方式组合其它查询,代码示例如下: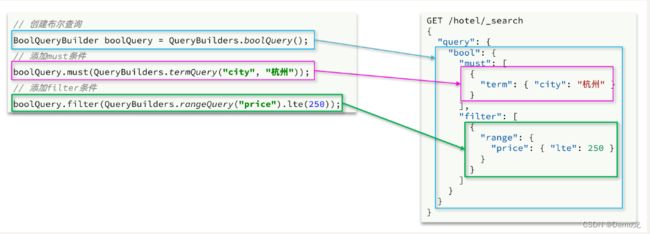
可以看到,API与其它查询的差别同样是在查询条件的构建,QueryBuilders,结果解析等其他代码完全不变。
完整代码如下:
@Test
void testBool() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.准备BooleanQuery
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// 2.2.添加term
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", "杭州"));
// 2.3.添加range
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").lte(250));
request.source().query(boolQuery);
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
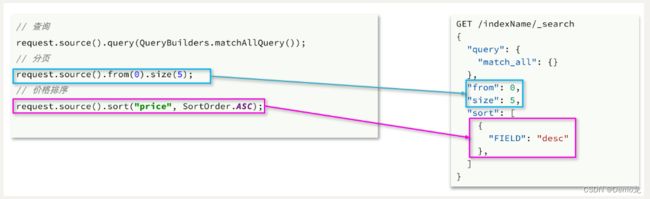
3.5.排序、分页
搜索结果的排序和分页是与query同级的参数,因此同样是使用request.source()来设置。
对应的API如下:
@Test
void testPageAndSort() throws IOException {
// 页码,每页大小
int page = 1, size = 5;
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
// 2.2.排序 sort
request.source().sort("price", SortOrder.ASC);
// 2.3.分页 from、size
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(5);
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
3.6.高亮
高亮的代码与之前代码差异较大,有两点:
- 查询的DSL:其中除了查询条件,还需要添加高亮条件,同样是与query同级。
- 结果解析:结果除了要解析_source文档数据,还要解析高亮结果
3.6.1.高亮请求构建
高亮请求的构建API如下:
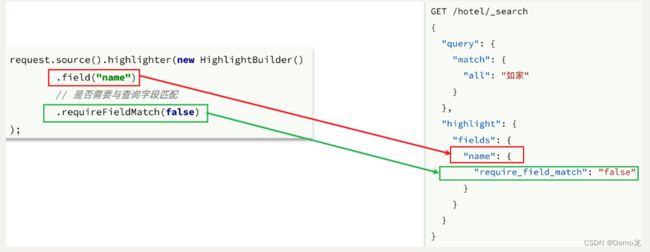
上述代码省略了查询条件部分,但是大家不要忘了:高亮查询必须使用全文检索查询,并且要有搜索关键字,将来才可以对关键字高亮。
完整代码如下:
@Test
void testHighlight() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", "如家"));
// 2.2.高亮
request.source().highlighter(new HighlightBuilder().field("name").requireFieldMatch(false));
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
handleResponse(response);
}
3.6.2.高亮结果解析
高亮的结果与查询的文档结果默认是分离的,并不在一起。
- 第一步:从结果中获取source。hit.getSourceAsString(),这部分是非高亮结果,json字符串。还需要反序列为HotelDoc对象
- 第二步:获取高亮结果。hit.getHighlightFields(),返回值是一个Map,key是高亮字段名称,值是HighlightField对象,代表高亮值
- 第三步:从map中根据高亮字段名称,获取高亮字段值对象HighlightField
- 第四步:从HighlightField中获取Fragments,并且转为字符串。这部分就是真正的高亮字符串了
- 第五步:用高亮的结果替换HotelDoc中的非高亮结果
完整代码如下:
private void handleResponse(SearchResponse response) {
// 4.解析响应
SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits();
// 4.1.获取总条数
long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value;
System.out.println("共搜索到" + total + "条数据");
// 4.2.文档数组
SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits();
// 4.3.遍历
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
// 获取文档source
String json = hit.getSourceAsString();
// 反序列化
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
// 获取高亮结果
Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(highlightFields)) {
// 根据字段名获取高亮结果
HighlightField highlightField = highlightFields.get("name");
if (highlightField != null) {
// 获取高亮值
String name = highlightField.getFragments()[0].string();
// 覆盖非高亮结果
hotelDoc.setName(name);
}
}
System.out.println("hotelDoc = " + hotelDoc);
}
}
4.旅游案例
下面,我们通过黑马旅游的案例来实战演练下之前学习的知识。
我们实现四部分功能:
- 酒店搜索和分页
- 酒店结果过滤
- 我周边的酒店
- 酒店竞价排名
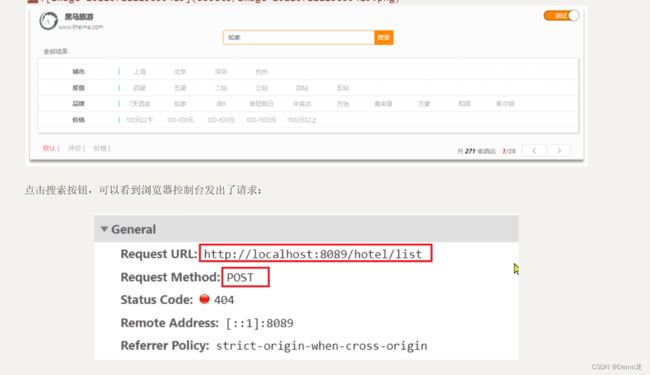
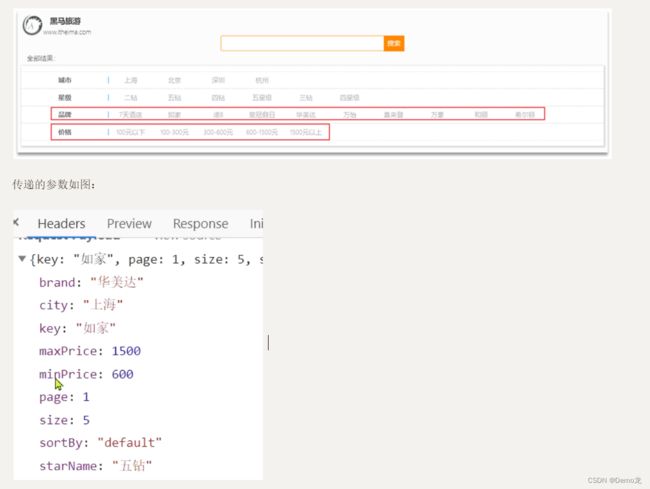
启动我们提供的hotel-demo项目,其默认端口是8089,访问http://localhost:8090,就能看到项目页面了: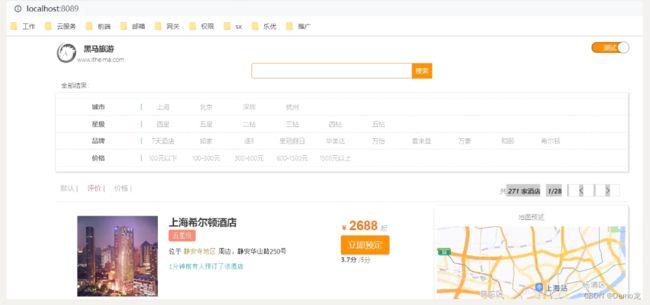
4.1.酒店搜索和分页
案例需求:实现黑马旅游的酒店搜索功能,完成关键字搜索和分页
4.1.1.需求分析
- 请求方式:POST
- 请求路径:/hotel/list
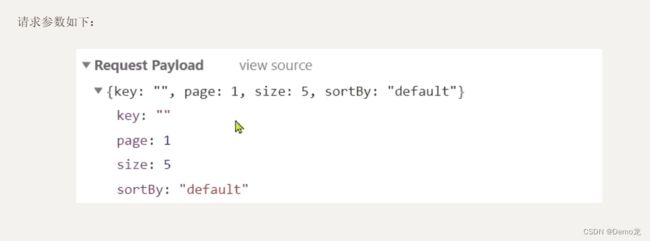
- 请求参数:JSON对象,包含4个字段:
- key:搜索关键字
- page:页码
- size:每页大小
- sortBy:排序,目前暂不实现
- 返回值:分页查询,需要返回分页结果PageResult,包含两个属性:
total:总条数List:当前页的数据
因此,我们实现业务的流程如下:
- 步骤一:定义实体类,接收请求参数的JSON对象
- 步骤二:编写controller,接收页面的请求
- 步骤三:编写业务实现,利用RestHighLevelClient实现搜索、分页
4.1.2.定义实体类
实体类有两个,一个是前端的请求参数实体,一个是服务端应该返回的响应结果实体。
1)请求参数
前端请求的json结构如下:
{
"key": "搜索关键字",
"page": 1,
"size": 3,
"sortBy": "default"
}
因此,我们在cn.itcast.hotel.pojo包下定义一个实体类:
package cn.itcast.hotel.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class RequestParams {
private String key;
private Integer page;
private Integer size;
private String sortBy;
}
2)返回值
分页查询,需要返回分页结果PageResult,包含两个属性:
total:总条数List:当前页的数据
因此,我们在cn.itcast.hotel.pojo中定义返回结果:
package cn.itcast.hotel.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.List;
@Data
public class PageResult {
private Long total;
private List<HotelDoc> hotels;
public PageResult() {
}
public PageResult(Long total, List<HotelDoc> hotels) {
this.total = total;
this.hotels = hotels;
}
}
4.1.3.定义controller
定义一个HotelController,声明查询接口,满足下列要求:
- 请求方式:Post
- 请求路径:/hotel/list
- 请求参数:对象,类型为RequestParam
- 返回值:PageResult,包含两个属性
Long total:总条数List:酒店数据hotels
因此,我们在cn.itcast.hotel.web中定义HotelController:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hotel")
public class HotelController {
@Autowired
private IHotelService hotelService;
// 搜索酒店数据
@PostMapping("/list")
public PageResult search(@RequestBody RequestParams params){
return hotelService.search(params);
}
}
4.1.4.实现搜索业务
我们在controller调用了IHotelService,并没有实现该方法,因此下面我们就在IHotelService中定义方法,并且去实现业务逻辑。
1)在cn.itcast.hotel.service中的IHotelService接口中定义一个方法:
/**
* 根据关键字搜索酒店信息
* @param params 请求参数对象,包含用户输入的关键字
* @return 酒店文档列表
*/
PageResult search(RequestParams params);
2)实现搜索业务,肯定离不开RestHighLevelClient,我们需要把它注册到Spring中作为一个Bean。在cn.itcast.hotel中的HotelDemoApplication中声明这个Bean:
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient client(){
return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));
}
3)在cn.itcast.hotel.service.impl中的HotelService中实现search方法:
@Override
public PageResult search(RequestParams params) {
try {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
String key = params.getKey();
if (key == null || "".equals(key)) {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
} else {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", key));
}
// 2.2.分页
int page = params.getPage();
int size = params.getSize();
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(size);
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
return handleResponse(response);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 结果解析
private PageResult handleResponse(SearchResponse response) {
// 4.解析响应
SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits();
// 4.1.获取总条数
long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value;
// 4.2.文档数组
SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits();
// 4.3.遍历
List<HotelDoc> hotels = new ArrayList<>();
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
// 获取文档source
String json = hit.getSourceAsString();
// 反序列化
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
// 放入集合
hotels.add(hotelDoc);
}
// 4.4.封装返回
return new PageResult(total, hotels);
}
4.2.酒店结果过滤
需求:添加品牌、城市、星级、价格等过滤功能
4.2.1.需求分析
在页面搜索框下面,会有一些过滤项:
- brand:品牌值
- city:城市
- minPrice~maxPrice:价格范围
- starName:星级
我们需要做两件事情:
- 修改请求参数的对象RequestParams,接收上述参数
- 修改业务逻辑,在搜索条件之外,添加一些过滤条件
4.2.2.修改实体类
修改在cn.itcast.hotel.pojo包下的实体类RequestParams:
@Data
public class RequestParams {
private String key;
private Integer page;
private Integer size;
private String sortBy;
// 下面是新增的过滤条件参数
private String city;
private String brand;
private String starName;
private Integer minPrice;
private Integer maxPrice;
}
4.2.3.修改搜索业务
在HotelService的search方法中,只有一个地方需要修改:requet.source().query( … )其中的查询条件。
在之前的业务中,只有match查询,根据关键字搜索,现在要添加条件过滤,包括:
- 品牌过滤:是keyword类型,用term查询
- 星级过滤:是keyword类型,用term查询
- 价格过滤:是数值类型,用range查询
- 城市过滤:是keyword类型,用term查询
多个查询条件组合,肯定是boolean查询来组合:
- 关键字搜索放到must中,参与算分
- 其它过滤条件放到filter中,不参与算分
因为条件构建的逻辑比较复杂,这里先封装为一个函数:
buildBasicQuery的代码如下:
private void buildBasicQuery(RequestParams params, SearchRequest request) {
// 1.构建BooleanQuery
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// 2.关键字搜索
String key = params.getKey();
if (key == null || "".equals(key)) {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
} else {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", key));
}
// 3.城市条件
if (params.getCity() != null && !params.getCity().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", params.getCity()));
}
// 4.品牌条件
if (params.getBrand() != null && !params.getBrand().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("brand", params.getBrand()));
}
// 5.星级条件
if (params.getStarName() != null && !params.getStarName().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("starName", params.getStarName()));
}
// 6.价格
if (params.getMinPrice() != null && params.getMaxPrice() != null) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders
.rangeQuery("price")
.gte(params.getMinPrice())
.lte(params.getMaxPrice())
);
}
// 7.放入source
request.source().query(boolQuery);
}
4.3.我周边的酒店
需求:我附近的酒店
4.3.1.需求分析
在酒店列表页的右侧,有一个小地图,点击地图的定位按钮,地图会找到你所在的位置:

我们要做的事情就是基于这个location坐标,然后按照距离对周围酒店排序。实现思路如下:
- 修改RequestParams参数,接收location字段
- 修改search方法业务逻辑,如果location有值,添加根据geo_distance排序的功能
4.3.2.修改实体类
修改在cn.itcast.hotel.pojo包下的实体类RequestParams:
package cn.itcast.hotel.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class RequestParams {
private String key;
private Integer page;
private Integer size;
private String sortBy;
private String city;
private String brand;
private String starName;
private Integer minPrice;
private Integer maxPrice;
// 我当前的地理坐标
private String location;
}
4.3.3.距离排序API
我们以前学习过排序功能,包括两种:
- 普通字段排序
- 地理坐标排序
我们只讲了普通字段排序对应的java写法。地理坐标排序只学过DSL语法,如下:
GET /indexName/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": "asc"
},
{
"_geo_distance" : {
"FIELD" : "纬度,经度",
"order" : "asc",
"unit" : "km"
}
}
]
}
4.3.4.添加距离排序
在cn.itcast.hotel.service.impl的HotelService的search方法中,添加一个排序功能:
完整代码:
@Override
public PageResult search(RequestParams params) {
try {
// 1.准备Request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备DSL
// 2.1.query
buildBasicQuery(params, request);
// 2.2.分页
int page = params.getPage();
int size = params.getSize();
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(size);
// 2.3.排序
String location = params.getLocation();
if (location != null && !location.equals("")) {
request.source().sort(SortBuilders
.geoDistanceSort("location", new GeoPoint(location))
.order(SortOrder.ASC)
.unit(DistanceUnit.KILOMETERS)
);
}
// 3.发送请求
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.解析响应
return handleResponse(response);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
4.3.5.排序距离显示
重启服务后,测试我的酒店功能:
排序完成后,页面还要获取我附近每个酒店的具体距离值,这个值在响应结果中是独立的:
因此,我们在结果解析阶段,除了解析source部分以外,还要得到sort部分,也就是排序的距离,然后放到响应结果中。
我们要做两件事:
- 修改HotelDoc,添加排序距离字段,用于页面显示
- 修改HotelService类中的handleResponse方法,添加对sort值的获取
1)修改HotelDoc类,添加距离字段
package cn.itcast.hotel.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class HotelDoc {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer price;
private Integer score;
private String brand;
private String city;
private String starName;
private String business;
private String location;
private String pic;
// 排序时的 距离值
private Object distance;
public HotelDoc(Hotel hotel) {
this.id = hotel.getId();
this.name = hotel.getName();
this.address = hotel.getAddress();
this.price = hotel.getPrice();
this.score = hotel.getScore();
this.brand = hotel.getBrand();
this.city = hotel.getCity();
this.starName = hotel.getStarName();
this.business = hotel.getBusiness();
this.location = hotel.getLatitude() + ", " + hotel.getLongitude();
this.pic = hotel.getPic();
}
}
2)修改HotelService中的handleResponse方法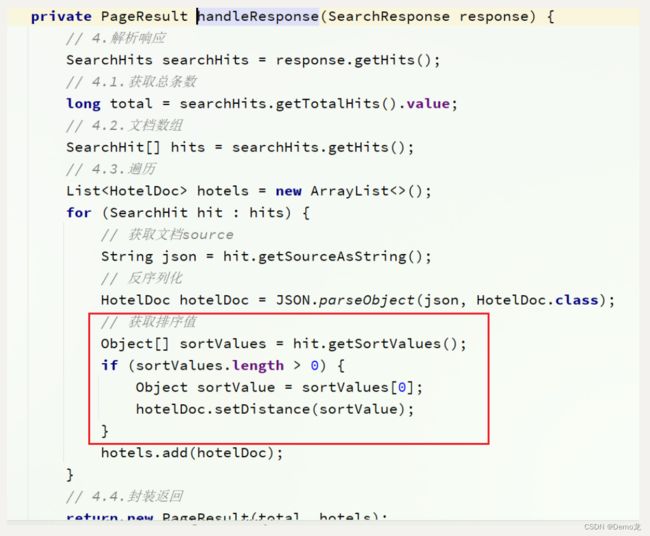

4.4.酒店竞价排名
需求:让指定的酒店在搜索结果中排名置顶
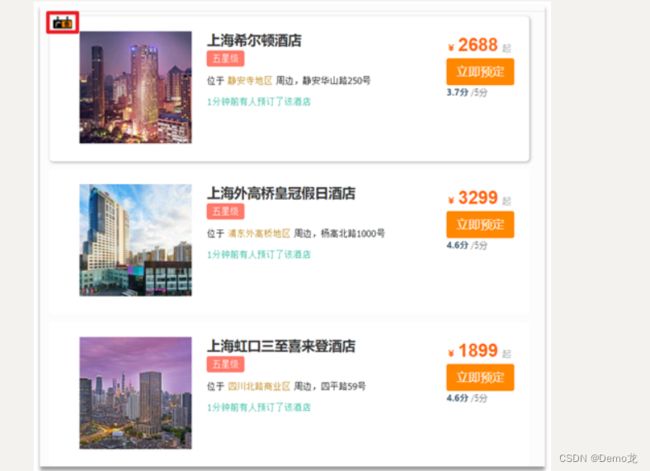
4.4.1.需求分析
要让指定酒店在搜索结果中排名置顶,效果如图:
我们之前学习过的function_score查询可以影响算分,算分高了,自然排名也就高了。而function_score包含3个要素:
- 过滤条件:哪些文档要加分
- 算分函数:如何计算function score
- 加权方式:function score 与 query score如何运算
这里的需求是:让指定酒店排名靠前。因此我们需要给这些酒店添加一个标记,这样在过滤条件中就可以根据这个标记来判断,是否要提高算分。
比如,我们给酒店添加一个字段:isAD,Boolean类型:
- true:是广告
- false:不是广告
这样function_score包含3个要素就很好确定了:
- 过滤条件:判断isAD 是否为true
- 算分函数:我们可以用最简单暴力的weight,固定加权值
- 加权方式:可以用默认的相乘,大大提高算分
因此,业务的实现步骤包括:
-
给HotelDoc类添加isAD字段,Boolean类型
-
挑选几个你喜欢的酒店,给它的文档数据添加isAD字段,值为true
-
修改search方法,添加function score功能,给isAD值为true的酒店增加权重
4.4.2.修改HotelDoc实体
给cn.itcast.hotel.pojo包下的HotelDoc类添加isAD字段: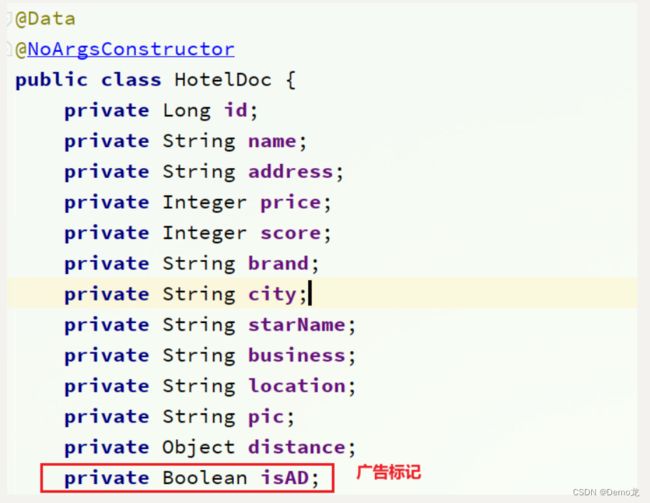
4.4.3.添加广告标记
接下来,我们挑几个酒店,添加isAD字段,设置为true:
POST /hotel/_update/1902197537
{
"doc": {
"isAD": true
}
}
POST /hotel/_update/2056126831
{
"doc": {
"isAD": true
}
}
POST /hotel/_update/1989806195
{
"doc": {
"isAD": true
}
}
POST /hotel/_update/2056105938
{
"doc": {
"isAD": true
}
}
4.4.4.添加算分函数查询
接下来我们就要修改查询条件了。之前是用的boolean 查询,现在要改成function_socre查询。
function_score查询结构如下:
对应的JavaAPI如下:

我们可以将之前写的boolean查询作为原始查询条件放到query中,接下来就是添加过滤条件、算分函数、加权模式了。所以原来的代码依然可以沿用。
修改cn.itcast.hotel.service.impl包下的HotelService类中的buildBasicQuery方法,添加算分函数查询:
private void buildBasicQuery(RequestParams params, SearchRequest request) {
// 1.构建BooleanQuery
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// 关键字搜索
String key = params.getKey();
if (key == null || "".equals(key)) {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
} else {
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", key));
}
// 城市条件
if (params.getCity() != null && !params.getCity().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", params.getCity()));
}
// 品牌条件
if (params.getBrand() != null && !params.getBrand().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("brand", params.getBrand()));
}
// 星级条件
if (params.getStarName() != null && !params.getStarName().equals("")) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.termQuery("starName", params.getStarName()));
}
// 价格
if (params.getMinPrice() != null && params.getMaxPrice() != null) {
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders
.rangeQuery("price")
.gte(params.getMinPrice())
.lte(params.getMaxPrice())
);
}
// 2.算分控制
FunctionScoreQueryBuilder functionScoreQuery =
QueryBuilders.functionScoreQuery(
// 原始查询,相关性算分的查询
boolQuery,
// function score的数组
new FunctionScoreQueryBuilder.FilterFunctionBuilder[]{
// 其中的一个function score 元素
new FunctionScoreQueryBuilder.FilterFunctionBuilder(
// 过滤条件
QueryBuilders.termQuery("isAD", true),
// 算分函数
ScoreFunctionBuilders.weightFactorFunction(10)
)
});
request.source().query(functionScoreQuery);
}