classloader的讲解
我们先从Activity的启动流程开始切入:
//位于android/app/ActivityThread.java中
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// ........省略代码
//通过反射创建activity
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
Activity activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
// ........省略代码
}
//位于android/app/Instrumentation.java
/**
* Perform instantiation of the process's {@link Activity} object. The
* default implementation provides the normal system behavior.
*
* @param cl The ClassLoader with which to instantiate the object.
* @param className The name of the class implementing the Activity
* object.
* @param intent The Intent object that specified the activity class being
* instantiated.
*
* @return The newly instantiated Activity object.
*/
public Activity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className,
Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
String pkg = intent != null && intent.getComponent() != null
? intent.getComponent().getPackageName() : null;
return getFactory(pkg).instantiateActivity(cl, className, intent);
}
public @NonNull Activity instantiateActivity(@NonNull ClassLoader cl, @NonNull String className,
@Nullable Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (Activity) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
我们通过上面代码发现最终是通过classloader.loadClass(className).newInstance()来进行Activity类的实例化的。
classloader通过java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader()构造。
//位于android/app/ContextImpl.java
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return mClassLoader != null ? mClassLoader : (mPackageInfo != null ? mPackageInfo.getClassLoader() : ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
}
//位于java/lang/ClassLoader.java
public static ClassLoader getSystemClassLoader() {
return SystemClassLoader.loader;
}
public abstract class ClassLoader {
static private class SystemClassLoader {
public static ClassLoader loader = ClassLoader.createSystemClassLoader();
}
private static ClassLoader createSystemClassLoader() {
String classPath = System.getProperty("java.class.path", ".");
String librarySearchPath = System.getProperty("java.library.path", "");
return new PathClassLoader(classPath, librarySearchPath, BootClassLoader.getInstance());
}
}
我们看源码发现
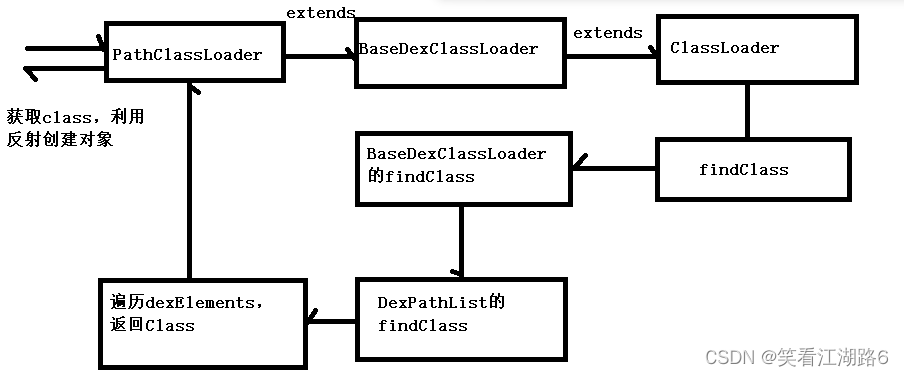
Activity的ClassLoader我们仔细看源码是 PathClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader extends ClassLoader 而loadClass这个方法在ClassLoader 中:

所以cl.loadClass(className)调用的流程如下:
//位于java/lang/ClassLoader.java
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
c = findClass(name);//这边调用findClass方法,发现这是一个protected类型方法,ClassLoader.java中没有其实现,那就是在子方法中实现了
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
}
return c;
}
BaseDexClassLoader部分源码:
public class BaseDexClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private final DexPathList pathList;
/**
* Constructs an instance.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized dex files
* should be written; may be {@code null}
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, libraryPath, optimizedDirectory);
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
Class c = pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions);
if (c == null) {
ClassNotFoundException cnfe = new ClassNotFoundException("Didn't find class \"" + name + "\" on path: " + pathList);
for (Throwable t : suppressedExceptions) {
cnfe.addSuppressed(t);
}
throw cnfe;
}
return c;
}
}
DexPathList部分源码:
//位于/libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/DexPathList.java
/*package*/ final class DexPathList {
private static final String DEX_SUFFIX = ".dex";
private static final String JAR_SUFFIX = ".jar";
private static final String ZIP_SUFFIX = ".zip";
private static final String APK_SUFFIX = ".apk";
/** class definition context */
private final ClassLoader definingContext;
/**
* List of dex/resource (class path) elements.
* Should be called pathElements, but the Facebook app uses reflection
* to modify 'dexElements' (http://b/7726934).
*/
private final Element[] dexElements;
/**
* Finds the named class in one of the dex files pointed at by
* this instance. This will find the one in the earliest listed
* path element. If the class is found but has not yet been
* defined, then this method will define it in the defining
* context that this instance was constructed with.
*
* @param name of class to find
* @param suppressed exceptions encountered whilst finding the class
* @return the named class or {@code null} if the class is not
* found in any of the dex files
*/
public Class findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
DexFile dex = element.dexFile;
if (dex != null) {
Class clazz = dex.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}
}
从这段源码可以看出,dexElements是用来保存dex的数组,而每个dex文件其实就是DexFile对象。遍历dexElements,然后通过DexFile去加载class文件,加载成功就返回,否则返回null。