想要精通算法和SQL的成长之路 - 滑动窗口和大小根堆
想要精通算法和SQL的成长之路 - 滑动窗口和大小根堆
- 前言
- 一. 大小根堆
- 二. 数据流的中位数
-
- 1.1 初始化
- 1.2 插入操作
- 1.3 完整代码
- 三. 滑动窗口中位数
-
- 3.1 在第一题的基础上改造
- 3.2 栈的remove操作
前言
想要精通算法和SQL的成长之路 - 系列导航
一. 大小根堆
- 大根堆:栈顶元素最大(上图左侧部分),栈底至栈顶元素值递增。
- 小根堆:栈顶元素最小(上图右侧部分),栈底至栈顶元素值递减。
在Java当中,可以用什么来表示大小根堆?
小根堆:
Queue<Integer> small = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 或者 x - y 是计算,在特殊情况下可能造成精度越界的情况
Queue<Integer> small = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x - y);
// 或者,Integer.compare 是纯比较,不会出现精度越界
Queue<Integer> small = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> Integer.compare(x, y));
// 或者
Queue<Integer> small = new PriorityQueue<>(Integer::compare);
大根堆:
Queue<Integer> big = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> y - x);
大小根堆的常规操作:
- 获取栈顶元素:
peek(); - 栈顶元素移除:
poll();
二. 数据流的中位数
再说下我们的思路:
- 同时维护大小根堆,并且约定小根堆的元素个数总是 >= 大根堆元素个数(最多个数多一个)。
- 如果元素个数是奇数,那么中位数就是小根堆堆顶元素。
- 如果元素个数是偶数,那么中位数就是(大根堆堆顶 + 小根堆堆顶) / 2。
1.1 初始化
Queue<Integer> big, small;
/**
* big small
* 最小值 ---> 大根堆顶 中位数 小根堆顶 ---> 最大值
*/
public MedianFinder() {
small = new PriorityQueue<>();// 小根堆,堆顶元素最小(存储比中位数大的部分)
big = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> y - x);// 大根堆,堆顶元素最大(存储比中位数小的部分)
}
1.2 插入操作
插入的时候,我们考虑到两种情况:
- 如果大小根堆的元素个数相等,我们优先把新元素加入到小根堆。
- 否则,将元素加入到大根堆。
但是,我们并不知道以下三者的关系:
- 大根堆堆顶元素值。
- 当前待加入元素值。
- 小根堆堆顶元素值。
而我们需要去维护他们,一定满足:大根堆堆顶元素值 < 小根堆堆顶元素值。
咋办呢?以第一种情况为例,我们可以:
- 先把元素加入到大根堆。那么经过排序后,大根堆的堆顶元素就是最大的那个(可能是当前元素,也可能不是)。此时大根堆
Size> 小根堆Size。 - 把大根堆堆顶元素移除,加入到小根堆。小根堆经过排序后,这样就能保证大根堆堆顶元素值 < 小根堆堆顶元素值。
写成代码就是:
public void addNum(int num) {
// 如果大小根堆 的 大小 一样,我们往小根堆放元素。让小根堆size >= 大根堆size
if (big.size() == small.size()) {
// 方式一定是先让放大根堆,再把大根堆的堆顶元素移除到小根堆
big.add(num);
small.add(big.poll());
} else {
small.add(num);
big.add(small.poll());
}
}
1.3 完整代码
那么查询函数就更简单了,结合上面的思路,我们得到完整代码如下:
public class MedianFinder {
Queue<Integer> big, small;
/**
* big small
* 最小值 ---> 大根堆顶 中位数 小根堆顶 ---> 最大值
*/
public MedianFinder() {
small = new PriorityQueue<>();// 小根堆,堆顶元素最小(存储比中位数大的部分)
big = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> y - x);// 大根堆,堆顶元素最大(存储比中位数小的部分)
}
public void addNum(int num) {
// 如果大小根堆 的 大小 一样,我们往小根堆放元素。让小根堆size >= 大根堆size
if (big.size() == small.size()) {
// 方式一定是先让放大根堆,再把大根堆的堆顶元素移除到小根堆
big.add(num);
small.add(big.poll());
} else {
small.add(num);
big.add(small.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
return small.size() == big.size() ? (small.peek() + big.peek()) / 2.0 : small.peek();
}
}
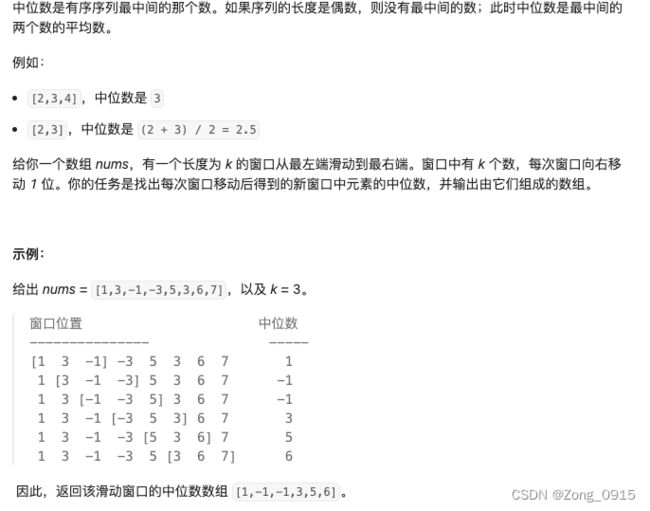
三. 滑动窗口中位数
- 我们先创建一个窗口,把前k个数字通过大小根堆的方式去维护(题目一的思路)。
- 后续每次滑动窗口的移动,都带来两个变数:一个旧元素会从窗口出移除(但是从大根堆移除还是小根堆移除?),一个新元素会加入到窗口中(加入到大根堆还是小根堆?)
- 由于第二步的变数,可能导致大小根堆的
Size不均衡。我们的目的:让小根堆的Size>= 大根堆Size,最多多一个元素。 - 因此每次滑动窗口的移动,我们还需要维护大小根堆。
3.1 在第一题的基础上改造
首先考虑到精度的问题,我们的大小根堆不能在根据差值来比较了,而是:
right = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> Integer.compare(x, y));// 小根堆,堆顶元素最小(存储比中位数大的部分)
left = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> Integer.compare(y, x));// 大根堆,堆顶元素最大(存储比中位数小的部分)
其次,求中位数的时候,也需要大小根堆的堆顶元素,先除以2,再和相加:
if (left.size() == right.size()) {
return (left.peek() / 2.0) + (right.peek() / 2.0);
最终代码如下:
public class Test480 {
Queue<Integer> left, right;
public double[] medianSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
right = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> Integer.compare(x, y));// 小根堆,堆顶元素最小(存储比中位数大的部分)
left = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> Integer.compare(y, x));// 大根堆,堆顶元素最大(存储比中位数小的部分)
int len = nums.length;
// 结果集
double[] res = new double[len - k + 1];
// 创建大小根堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
right.add(nums[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < k / 2; i++) {
left.add(right.poll());
}
// 初始化第一个中位数
res[0] = findMedian();
for (int i = k; i < len; i++) {
// 滑动窗口长度固定,每次移动,都有一个元素要删除和一个元素要新加入
int del = nums[i - k], add = nums[i];
if (add >= right.peek()) {
right.add(add);
} else {
left.add(add);
}
// 如果待删除元素在小根堆,在小根堆处删除,否则在大根堆中删除
if (del >= right.peek()) {
right.remove(del);
} else {
left.remove(del);
}
// 维护大小根堆的元素个数
adjust();
res[i - k + 1] = findMedian();
}
return res;
}
void adjust() {
while (left.size() > right.size()) {
right.add(left.poll());
}
while (right.size() - left.size() > 1) {
left.add(right.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
if (left.size() == right.size()) {
return (left.peek() / 2.0) + (right.peek() / 2.0);
} else {
return right.peek() * 1.0;
}
}
}
这个写法其实是没问题的,但是在元素个数非常大的情况下,就容易超时:

3.2 栈的remove操作
问题处在优先队列的的一个元素remove操作:

它是先查找(复杂度O(N)),再进行删除(复杂度O(logN)),所以会超时。因此我们这里可以引入红黑树来进行替代。
有这么几个需要注意的地方:
- 我们用
TreeSet存储元素的时候,不再是元素值,而是元素的下标。 因为题目中同一个窗口的元素可能重复。元素值相等的时候,根据下标大小来比较。
Comparator<Integer> comparator = (x, y) -> nums[x] != nums[y] ? Integer.compare(nums[x], nums[y]) : x - y;
right = new TreeSet<>(comparator);// 小根堆,堆顶元素最小(存储比中位数大的部分)
left = new TreeSet<>(comparator.reversed());// 大根堆,堆顶元素最大(存储比中位数小的部分)
- 滑动窗口移动的时候。需要删除对应的元素下标 ,由于存在重复值,我们需要大小根堆都把这个下标给剔除。
- 原
peek函数替代为first函数。poll函数替代为pollFirst函数。
完整代码如下:
public class Test480 {
TreeSet<Integer> left, right;
int[] nums;
public double[] medianSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
this.nums = nums;
Comparator<Integer> comparator = (x, y) -> nums[x] != nums[y] ? Integer.compare(nums[x], nums[y]) : x - y;
right = new TreeSet<>(comparator);// 小根堆,堆顶元素最小(存储比中位数大的部分)
left = new TreeSet<>(comparator.reversed());// 大根堆,堆顶元素最大(存储比中位数小的部分)
int len = nums.length;
// 结果集
double[] res = new double[len - k + 1];
// 创建大小根堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
addToWindow(i);
}
res[0] = findMedian();
for (int i = k; i < len; i++) {
// 滑动窗口长度固定,每次移动,都有一个元素要删除和一个元素要新加入
left.remove(i - k);
right.remove(i - k);
addToWindow(i);
res[i - k + 1] = findMedian();
}
return res;
}
void addToWindow(int index) {
// 我们总是把新元素先统一加入到大根堆。
right.add(index);
left.add(right.pollFirst());
// 然后再维护大小
while (left.size() > right.size()) {
right.add(left.pollFirst());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
if (left.size() == right.size()) {
return (nums[left.first()] / 2.0) + (nums[right.first()] / 2.0);
} else {
return nums[right.first()] * 1.0;
}
}
}