SpringBoot自动装配原理
文章目录
- HelloWorld
-
- SpringBoot简介
- 准备工作
- 创建项目
- 项目结构
- pom文件
-
- 父依赖
- 启动器
- 启动类
-
- 注解探究
-
- @SpringBootConfiguration
- @ComponentScan
- @EnableAutoConfiguration
- SpringApplication.run()
-
- SpringApplication
- run方法流程分析
- 自定义一个Starter
-
- 说明
- 编写启动器
- 测试启动器
HelloWorld
SpringBoot简介
SpringBoot是一个JavaWeb的开发框架,是基于Spring开发,SpringBoot本身并不提供Spring框架的核心特性以及扩展功能,知识英语快捷、敏捷地开发新一代基于Spring框架的应用程序。之前在学习过Spring框架时,就被其复杂的配置弄的头晕脑胀,各种配置约束,让人望而生畏!Springboot以约定大于配置的核心思想,默认帮我们进行了很多设置,多数SpringBoot应用只需要很少的Spring配置。同时它集成了大量常用第三方库,可以零配置实现开箱即用。
准备工作
环境准备:
- java version “1.8.0_271”
- Maven-3.6.3
- SpringBoot 2.4.3
开发工具: - IDEA 2020.2.3
创建项目
- 创建一个新项目
- 选择spring initalizr,可以看到默认就是去官网的快速构建工具那里实现
- 填写项目信息
- 选择初始化的组件(勾选web->spring-Web)
- 填写项目路径
- 等待项目构建成功
项目结构
- 程序的主启动类
- application.propertites配置文件
- 测试类
- pom.xml
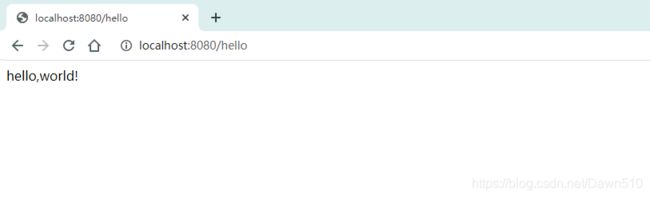
在主程序的同级目录下,新建一个controller包,在包中新建一个HelloController类
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello,world!";
}
}
编写完毕后,从主程序启动项目,浏览器发起请求,看页面返回;控制台输出了 Tomcat 访问的端口号!
如此简单几步,完成了一个web接口的开发。SpringBoot就是这么简单!那么SpringBoot是如何运行的呢?
pom文件
一个Maven项目,一般从pom.xml文件探究起。pom.xml中主要信息有父依赖和启动器。
父依赖
pom.xml主要依赖一个父项目,主要是管理项目的资源过滤和插件
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.4.3version>
<relativePath/>
parent>
点进父依赖,还有一层依赖:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependenciesrelativePath>
parent>
这是真正管理SpringBoot应用里面所有依赖版本的地方,SpringBoot的版本控制中心;
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;但是如果导入的包没有在依赖中管理着就需要手动配置版本。
启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
springboot-boot-starter-xxx:就是spring-boot的场景启动器
spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了web模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starter (启动器),只需要在项目中引入这些starter即可,所有相关的依赖都会导入进来 , 我们要用什么功能就导入什么样的场景启动器即可 ;也可以自己自定义 starter;
启动类
默认的主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootstartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootstartApplication.class, args);
}
}
注解探究
@SpringBootAplication注解依赖关系如下(脑图链接)
进入@SpringBootApplication注解可以看到除了常见的四大注解外,还有@SpringBootConfituration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan三大注解
@SpringBootConfiguration
SpringBoot配置类,标注在某个类上,表明这是一个SpringBoot配置类
- @Configuration注解:表明这是一个配置类,配置类对应的就是Spring的XML配置文件
- @Component注解: 表明启动类本身也是Spring的一个组件而已,负责启动应用
@ComponentScan
自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者Bean,将这个bean定义加载到IOC容器中
@EnableAutoConfiguration
- @AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
- @Import(Registrar.class):Spring底层注解Import,给容器中导入一个组件。Registrar.class作用:将主启动类的所在包及包下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器
- @Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):给容器导入组件
- AutoConfigurationImportSelector:自动配置导入选择器
AutoConfigurationImportSelector中有如下方法:获取候选的配置
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
紧接着这个方法调用了SpringFactoriesLoader的静态方法loadFactoryNames:
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
继续调用loadSpringFactories方法
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
HashMap result = new HashMap();
try {
Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames;
int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length;
for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) {
String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12];
((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> {
return new ArrayList();
})).add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> {
return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList));
});
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var14) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14);
}
}
}
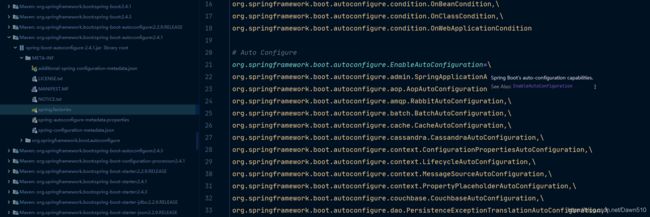
上面代码的核心就是读取META-INF/spring.factories并封装为properties属性。spring.factories是什么,全局搜索spring.factories:
找到了自动配置的根源所在!选择其中一个自动配置类打开看看,如:HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration
这些都是一个个的JavaConfig配置类,而且都注入了一些Bean。
所以自动配置真正实现是从classpath中搜寻所有META/spring.factories配置文件,并将其中的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.XX包下的配置项,通过反射实例化为对应标注了@Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IOC容器配置类,然后将这些都汇总成一个实例加载到IOC容器中。
对上图中的部分代码说明:
- @Congfiguration:表明这是一个配置类
- @EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class}):指定启动类的ConfigurationProperties
- ServerProperties.class:将配置文件中的值和ServerProperties中的值绑定起来,并将ServerProperties加入到IOC容器
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET):满足条件,整个配置类才会生效;这里为判断是否为web应用,如果是,当前配置生效
- @ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class):判断当前项目有没有CharacterEncodingFilter类——SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;
- @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = “server.servlet.encoding”, value = “enabled”, matchIfMissing = true):判断配置文件中是否存在配置 server.servlet.encoding=enabled,如果不存在,默认为生效的
这里有很多的属性,这些属性通过注解@ConfigurationProperties和配置文件进行绑定。
小结:
-
SpringBoot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值
-
将这些值作为自动配置类导入容器,根据@ConditionalXX注解判断哪些注解生效,有效的配置类帮我们进行自动配置工作;
-
整个J2EE的整体解决方案和自动配置都在springboot-autoconfigure的jar包中;
-
它会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类 (xxxAutoConfiguration), 就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件 ,并配置好这些组件;配置类的属性是从对应的XXproperties类中获取的,XXproperties类的属性可以从配置文件中修改生效。
-
有了自动配置类 , 免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作;
SpringApplication.run()
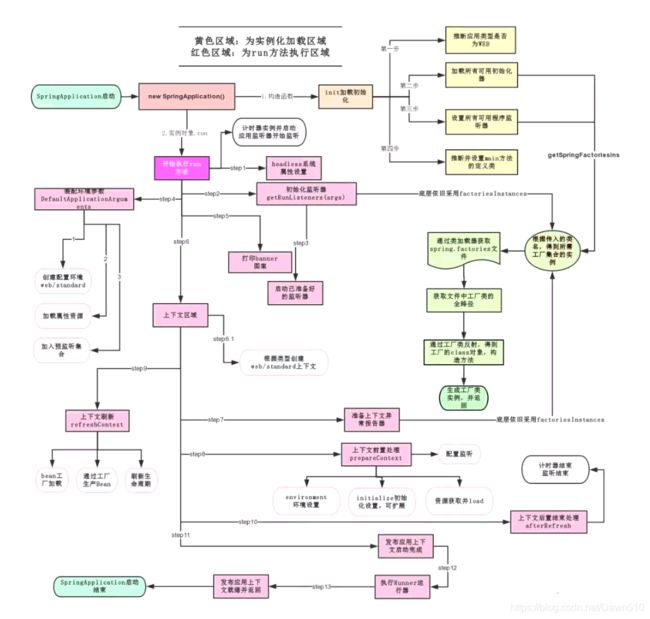
分析该方法主要分两部分,一部分是SpringApplication的实例化,二是run方法的执行;
SpringApplication
这个类主要做了以下四件事情:
1、推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
2、查找并加载所有可用初始化器 , 设置到initializers属性中
3、找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
4、推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
查看构造器:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
// ......
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances();
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
run方法流程分析
自定义一个Starter
我们分析完毕了源码以及自动装配的过程,我们可以尝试自定义一个启动器来玩玩
说明
启动器模块是一个空jar文件,仅提供辅助性依赖管理,这些依赖可能用于自动装配或者其他类库。
命名规约:
官方命名
- 前缀:spring-boot-starter-XX
- 例如:spring-boot-starter-web
自定义命名 - xxx-spring-boot-starter
- 例如:mybatis-spring-boot-starter
编写启动器
- 在IDEA中新建一个空项目spring-boot-starter-diy
- 新建一个普通maven模块:eamon-spring-boot-starter
- 新建一个SpringBoot模块:eamon-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure
- 在starter中导入autoconfigure依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.eamongroupId>
<artifactId>eamon-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigureartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
- 在autoonfigure中编写自己的服务HelloService
package cn.eamon;
/**
* @Author: Eamon
* @Description:
* @Date: 2021/3/3 21:41
*/
public class HelloService {
HelloProperties helloProperties;
public HelloProperties getHelloProperties() {
return helloProperties;
}
public void setHelloProperties(HelloProperties helloProperties) {
this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
}
public String sayHello(String name){
return helloProperties.getPrefix() + name + helloProperties.getSuffix();
}
}
- 编写HelloProperties配置类
package cn.eamon;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* @Author: Eamon
* @Description:
* @Date: 2021/3/3 21:42
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "eamon.hello")
public class HelloProperties {
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
public String getPrefix() {
return prefix;
}
public void setPrefix(String prefix) {
this.prefix = prefix;
}
public String getSuffix() {
return suffix;
}
public void setSuffix(String suffix) {
this.suffix = suffix;
}
}
- 编写自动配置类HelloServiceAutoConfiguration并注入bean
package cn.eamon;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Author: Eamon
* @Description:
* @Date: 2021/3/3 21:44
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
HelloService service = new HelloService();
service.setHelloProperties(helloProperties);
return service;
}
}
- 在resources下新建META-INF\spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
cn.eamon.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
测试启动器
- 新建一个SpringBoot项目
- 导入自己写的启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.eamongroupId>
<artifactId>eamon-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
dependency>
- 编写一个HelloController进行测试接口
package cn.eamon.springbootstart.controller;
import cn.eamon.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: Eamon
* @Description:
* @Date: 2021/3/3 17:02
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return helloService.sayHello("Eamon");
}
}
- 编写配置文件application.properties
eamon.hello.prefix=Bupt Boy---
eamon.hello.suffix=---GoodGoodStudy,DayDayUp
- 启动项目进行测试,测试成功结果如图