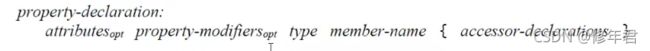C#学习(7)----类的成员,字段、属性、索引器、常量
C#的类型指的是类或者结构体,可能有以下成员:
一、字段(field)
表示与对象或类型相关联的变量。(类里面定义的int什么的,static与否)
旧称成员变量。
C语言的结构体中的就是字段。
分为实例字段和静态字段。
实例字段帮助实例存储数据,表示对象当前的状态。
namespace ConsoleAppPractice
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
List stus = new List();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.age = i + 16;
stu.score = 100 - i;
stus.Add(stu);
}
int sumAge = 0;
int sumScore = 0;
foreach (var stu in stus)
{
sumAge += stu.age;
sumScore += stu.score;
}
Student.averageAge = sumAge / Student.amount;
Student.averageScore = sumScore / Student.amount;
Student.ReportAver();
Student.ReportAmount();
}
}
class Student
{
public int age;
public int score;
public static double averageAge;
public static double averageScore;
public static int amount;
public Student()
{
Student.amount += 1;
}
//创建一个学生实例时,让数字加一。
public static void ReportAmount()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.amount);
}
public static void ReportAver()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.averageAge);
Console.WriteLine(Student.averageScore);
}
}
} 声明字段时,字段名必须是名词。声明字段不是语句,因为它不在方法体中。
实例字段每次创建实例都执行初始化,静态字段只在第一次加载数据类型的时候初始化。
当一个数据类型被加载,静态构造器会被调用,且只被调用一次
public int age;
public static int amount;
public Student()
{
this.age = 20;
}
//实例构造器
static Student()
{
Student.amount = 0;
}
//静态构造器对于只读字段而言,只能在构造器里给他赋初值
public readonly int ID;
public Student(int id)
{
this.ID = id;
}
//只读实例字段 struct Color
{
public int red;
public int green;
public int blue;
}
class Brush
{
public static readonly Color defaultColor = new Color() { red = 0, green = 0, blue = 0 };
}
//类的静态只读字段 class Brush
{
public static readonly Color defaultColor;
static Brush()
{
Brush.defaultColor= new Color() { red = 0, green = 0, blue = 0 };
}
}
//使用静态构造器二、属性(property)
用于访问对象类型或特征的成员,特征反映了状态。
(由豆腐温度这个特征值很高,反映豆腐很烫的状态)
属性由字段发展。
![]()
属性可以实时计算对象的某个特征
namespace ConsoleAppPractice
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { age = 20 };
Student stu2 = new Student() { age = 30 };
Student stu3 = new Student() { age = 200 };
int aveAge = (stu1.age + stu2.age + stu3.age) / 3;
Console.WriteLine(aveAge);
}
}
class Student
{
public int age;
}
}运行结果是83,很正常的数字。你无法清晰地看出一个字段是否被污染。
于是,人们最初的保护字段方法:
用private代替public,并用一对方法把字段保护起来。其中一个获取字段值,一个为字段设置值。
namespace ConsoleAppPractice
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.SetAge(11);
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.SetAge(30);
Student stu3 = new Student();
stu3.SetAge(290);
int aveAge = (stu1.GetAge() + stu2.GetAge() + stu3.GetAge()) / 3;
Console.WriteLine(aveAge);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int GetAge()//命名方法:get+字段名
{
return this.age;
}
public void SetAge(int value)
{
if (value <= 120 && value >= 0)//保护方法
this.age = value;
else
throw new Exception("Age value has error!");
}
}
}而属性这个概念是C#所特有的。
namespace ConsoleAppPractice
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.Age = 20;
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Age = 30;
Student stu3 = new Student();
stu3.Age = 40;
int aveAge = (stu1.Age + stu2.Age + stu3.Age) / 3;
Console.WriteLine(aveAge);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age//属性
{
//有一对反应器
get
{
return this.age;
}
set//在set函数里不用再自定义一个value变量。是因为准备默认变量就叫value,而且是上下文关键字
{
if (value <= 120 && value >= 0)
this.age = value;
else
throw new Exception("Age value has error!");
}
}
}
}注意:变量必须得是private,属性名与变量名不同,引用时引用的是属性名
属性其实是一种语法糖。
属性有两种声明格式,一种是完整的(兼有getter和setter),一种是简略(只读)的。
修饰符一般是public/public static。
将光标放置在一个private变量,再点edit----refactor----field,或者按住CTRL+R+E,可以自动把该字段变成属性。
在setor前面加private,只能在类里面引用,即该属性值只能由类中的数值赋值。【这点感觉很有用】
可以这样:(在构造器里构造,如果传值进构造器就跟一般的属性没差了)
namespace ConsoleAppPractice
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
string s = Console.ReadLine();
int age = Convert.ToInt32(s);
Student stu1 = new Student(age);
Console.WriteLine(age);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get => age;
private set
{
if (value <= 200 && value >= 0)
age = value;
else
throw new Exception("The age value has error!");
}
}
public Student(int value)
{
try
{
this.Age = value;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
}
}
}或者这么写:(利用方法来修改内部的属性值)
namespace ConsoleAppPractice
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.CreateAge();
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age { get => age; private set => age = value; }
public void CreateAge()
{
this.Age = 100;
}
}
}属性是可以通过动态计算求出值来的。具体见如下代码中的canwork属性:
namespace ConsoleAppPractice
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
string s = Console.ReadLine();
int age = Convert.ToInt32(s);
Student stu1 = new Student(age);
Console.WriteLine(age);
Console.WriteLine(stu1.canWork);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get => age;
private set
{
if (value <= 200 && value >= 0)
age = value;
else
throw new Exception("The age value has error!");
}
}
public bool canWork
{
get
{
if (this.Age > 16) { return true; }
else { return false; }
}
}
public Student(int value)
{
try
{
this.Age = value;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
}
}
}canwork属性没有对应的字段,是通过age的值实时计算出来的。
还有另一种写法:
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get => age;
private set
{
if (value <= 200 && value >= 0)
{
age = value;
this.CalculateCanWork();
}
else
throw new Exception("The age value has error!");
}
}
private bool canWrok;
public bool CanWork
{
get
{
return canWrok;
}
}
private void CalculateCanWork()
{
if (this.Age > 16) this.canWrok = true;
else this.canWrok = false;
}
public Student(int value)
{
try
{
this.Age = value;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
}
}上面那种写法,只在访问canwork的时候才计算值;下面那种写法,一访问canwork对应计算的原属性时就计算canwork。
若canwork属性访问频繁,就直接在原属性设定时计算出来就好;而若canwork访问不频繁,就只在用的时候再计算就好了。
建议永远使用属性而非字段来暴露数据,字段永远都只是private或protected的。
三、索引器(indexer)
索引器使对象能够用下标进行索引
只有实例索引器,没有静态索引器。
索引器多用于集合。但下例用于对象,目的是体现其强大性。
索引器的快捷键是敲入ind,再按2*tab。
namespace ConsoleAppPractice
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Student stu = new Student();
try
{
stu["Math"] = null; //直接用方括号引用。因为索引器是可空类型
Console.WriteLine(stu["Math"]);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
finally
{
stu["Chinese"] = 100;
Console.WriteLine(stu["Chinese"]);
}
}
}
class Student
{
private Dictionary dic = new Dictionary();
public int? this[string index] //索引器类型表示集合数值的值,[]参数表示用于索引的玩意儿
{
get
{
if (this.dic.ContainsKey(index)) return this.dic[index];
else return null;
//集合有这个成员就返回其值,没有就返回空。
}
set
{
if (value.HasValue == false)
{
throw new Exception("The score value can't be null!");
}
if (this.dic.ContainsKey(index)) this.dic[index] = value.Value;
//取可空类型值的正确方法
else this.dic.Add(index, value.Value);
//集合有这个成员的话就更新其值,没有就创建新的成员。
}
}
}
} 平时很少写索引器。【为什么?这个例子看着蛮实用的】
四、常量(constant)
常量隶属于类,故只能是静态的。
实例常量的角色由只读字段来充当。
注意区分成员常量和局部常量。
常量不能用静态构造器初始化,只能在定义时用初始化器初始化。
五、对各种只读的应用场景