Linux kernel SPI源码分析之SPI设备驱动源码分析(linux kernel 5.18)
SPI基础支持此处不再赘述,直接分析linux中的SPI驱动源码。
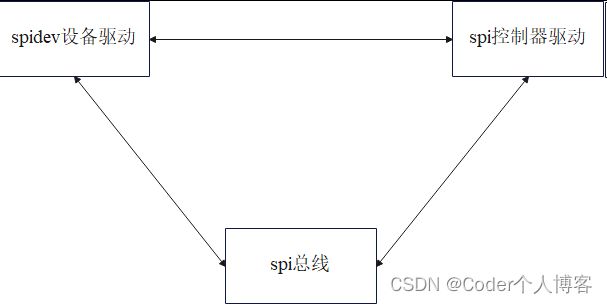
1、SPI设备驱动架构图
2、源码分析
本次分析基于kernel5.18,linux/drivers/spi/spidev.c
设备树示例:
&spis1 {
tri-pin = <57>;
slave@0 {
compatible = "rohm,dh2228fv";
spi-max-frequency = <6000000>;
irq-pin = <56>;
ack-pin = <58>;
protocol = "hoot-protocol";
};
};设备树里面SPI设备节点的compatible属性等于如下值,就会跟spidev驱动进行匹配:
static const struct spi_device_id spidev_spi_ids[] = {
{ .name = "dh2228fv" },
{ .name = "ltc2488" },
{ .name = "sx1301" },
{ .name = "bk4" },
{ .name = "dhcom-board" },
{ .name = "m53cpld" },
{ .name = "spi-petra" },
{ .name = "spi-authenta" },
{},
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(spi, spidev_spi_ids);匹配成功后spidev.c里面的spidev_probe就会被调用。
spidev_spi_driver源码分析
spidev_spi_driver源码具体实现如下:
static struct spi_driver spidev_spi_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "spidev",
.of_match_table = spidev_dt_ids,
.acpi_match_table = spidev_acpi_ids,
},
.probe = spidev_probe,
.remove = spidev_remove,
.id_table = spidev_spi_ids,
/* NOTE: suspend/resume methods are not necessary here.
* We don't do anything except pass the requests to/from
* the underlying controller. The refrigerator handles
* most issues; the controller driver handles the rest.
*/
};其中spidev_probe的具体实现如下:
static int spidev_probe(struct spi_device *spi)
{
int (*match)(struct device *dev);
struct spidev_data *spidev;
int status;
unsigned long minor;
match = device_get_match_data(&spi->dev);
if (match) {
status = match(&spi->dev);
if (status)
return status;
}
/* Allocate driver data */
spidev = kzalloc(sizeof(*spidev), GFP_KERNEL); /* 分配结构体 */
if (!spidev)
return -ENOMEM;
/* Initialize the driver data */
spidev->spi = spi; /* spidev_data里面记录spi-device结构体 */
spin_lock_init(&spidev->spi_lock);
mutex_init(&spidev->buf_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&spidev->device_entry);
/* If we can allocate a minor number, hook up this device.
* Reusing minors is fine so long as udev or mdev is working.
*/
mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);
minor = find_first_zero_bit(minors, N_SPI_MINORS); /* 找到一个空闲的次设备号 */
if (minor < N_SPI_MINORS) {
struct device *dev;
spidev->devt = MKDEV(SPIDEV_MAJOR, minor);
dev = device_create(spidev_class, &spi->dev, spidev->devt, /* 创建一个设备,通过、dev/spidevx.x */
spidev, "spidev%d.%d",
spi->master->bus_num, spi->chip_select); /* spi的第几个spi_master设备,spi的片选信号信息 */
status = PTR_ERR_OR_ZERO(dev);
} else {
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "no minor number available!\n");
status = -ENODEV;
}
if (status == 0) {
set_bit(minor, minors);
list_add(&spidev->device_entry, &device_list); /* 将这个spidev_data添加到device_list链表中 */
}
mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);
spidev->speed_hz = spi->max_speed_hz;
if (status == 0)
spi_set_drvdata(spi, spidev);
else
kfree(spidev);
return status;
}主要功能就是调用device_create创建设备文件,生成设备节点,用户可以通过节点进行读写和iotrol操作,其次还完成了如下操作:
1、分配一个spidev_data结构体,用来记录对应的spi_device。
2、将spi_data记录在一个链表里。
3、分配一个设备好,以后可以根据这个次设备号在上述的链表里面查找spidev_data。
4、device_create函数会生成一个设备节点:/dev/spidevB.D。B表示总线号,B表示这是SPI master下第几个设备,后续就可以通过/dev/spidevB.D来访问spidev驱动。
设备驱动的初始化和退出:
static int __init spidev_init(void)
{
int status;
/* Claim our 256 reserved device numbers. Then register a class
* that will key udev/mdev to add/remove /dev nodes. Last, register
* the driver which manages those device numbers.
*/
status = register_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, "spi", &spidev_fops); /* 注册字符设备(spidev_fops) */
if (status < 0)
return status;
spidev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "spidev"); /* 注册sysfs spidev节点 */
if (IS_ERR(spidev_class)) {
unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name);
return PTR_ERR(spidev_class);
}
status = spi_register_driver(&spidev_spi_driver); /* 注册spi设备驱动 */
if (status < 0) {
class_destroy(spidev_class);
unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name);
}
return status;
}
module_init(spidev_init); /* 驱动模块初始化 */
static void __exit spidev_exit(void)
{
spi_unregister_driver(&spidev_spi_driver); /* 注销spi 设备驱动 */
class_destroy(spidev_class); /* 注销sysfs spidev节点 */
unregister_chrdev(SPIDEV_MAJOR, spidev_spi_driver.driver.name); /* 注销spi设备驱动 */
}
module_exit(spidev_exit); /* 驱动模块注销 */module_init源码分析请关注:module_init源码分析。
module_exit源码分析请关注:module_exit源码分析。
class_create源码分析请关注:class_create源码分析
class_destroy源码分析请关注:class_destroy源码分析
register_chrdev源码分析请关注:后续更新(TODO)。
unregister_chrdev源码分析请关注:后续更新(TODO)。
SPIDEV_MAJOR:#define SPIDEV_MAJOR 153 /* assigned */
spidev_init源码分析
register_chrdev:创建字符设备,spi属于字符设备驱动,定义如下:
static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,
const struct file_operations *fops)入参传入 file_operations 结构体,结构体存了很多函数指针,实现读写和ioctrl相关操作,也是驱动最核心的功能,下面是spidev 实现的结构体:
static const struct file_operations spidev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
/* REVISIT switch to aio primitives, so that userspace
* gets more complete API coverage. It'll simplify things
* too, except for the locking.
*/
.write = spidev_write, /* 单工写模式 */
.read = spidev_read, /* 单工读模式 */
.unlocked_ioctl = spidev_ioctl, /* 设置频率、模式、进行双工传输 */
.compat_ioctl = spidev_compat_ioctl,
.open = spidev_open,
.release = spidev_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
};
spidev_fops分析
spiev_write函数分析
spidev_write的源码如下:
/* Write-only message with current device setup */
static ssize_t
spidev_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
struct spidev_data *spidev;
ssize_t status;
unsigned long missing;
/* chipselect only toggles at start or end of operation */
if (count > bufsiz)
return -EMSGSIZE;
spidev = filp->private_data; /* spidev_data结构体是很重要的数据传递类型 */
mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);
missing = copy_from_user(spidev->tx_buffer, buf, count); /* 数据从用户态copy到内核态 */
if (missing == 0)
status = spidev_sync_write(spidev, count); /* 同步数据 */
else
status = -EFAULT;
mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);
return status;
}spidev_sync_write函数的具体实现如下:
static inline ssize_t
spidev_sync_write(struct spidev_data *spidev, size_t len)
{
struct spi_transfer t = {
.tx_buf = spidev->tx_buffer, /* 指定tx_buffer */
.len = len, /* 指定长度 */
.speed_hz = spidev->speed_hz, /* 指定传输速率 */
};
struct spi_message m;
spi_message_init(&m); /* spi消息初始化(初始化传输事务链表头) */
spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m); /* 添加spi传输到spi消息传输链表,将t放到message的尾部 */
return spidev_sync(spidev, &m); /* spi同步传输 */
}上述代码中的spi_message_init函数,具体实现如下:
static inline void spi_message_init_no_memset(struct spi_message *m)
{
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&m->transfers);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&m->resources);
}
static inline void spi_message_init(struct spi_message *m)
{
memset(m, 0, sizeof *m);
spi_message_init_no_memset(m);
}通过源码可知,spi_message_init将传入的结构体spi_message全部内容初始化为0,并被初始化过的结构体spi_message传递给了函数spi_message_init_no_memset。
在spi_message_init_no_memset通过INIT_LIST_HEAD为m->transfers和m->resources分别创建双向链表的头节点。
在spidev_sync_write函数中,在完成SPI数据的链表的初始化之后又通过调用spi_message_add_tail函数,将struct spi_transfer t和struct spi_message m分别添加到前一步创建的双向链表的尾部。
在spidev_sync_write函数的最后通过调用spidev_sync函数进行SPI的同步传输,并将结果返回,此处spidev_sync函数的具体实现如下:
static ssize_t
spidev_sync(struct spidev_data *spidev, struct spi_message *message)
{
int status;
struct spi_device *spi;
spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
spi = spidev->spi;
spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
if (spi == NULL)
status = -ESHUTDOWN;
else
status = spi_sync(spi, message);
if (status == 0)
status = message->actual_length;
return status;
}梳理spidev_sync的数据传输流程:spidev_sync --> spi_sync --> __spi_sync --> __spi_queued_transfer --> kthread_queue_work最终将数据放到工作队列中,通过SPI总线驱动实现数据的发送功能。
spiev_read函数分析
spidev_read函数源码如下:
/* Read-only message with current device setup */
static ssize_t
spidev_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
struct spidev_data *spidev;
ssize_t status;
/* chipselect only toggles at start or end of operation */
if (count > bufsiz)
return -EMSGSIZE;
spidev = filp->private_data; /* 从私有数据中获取spidev_data数据 */
mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock); /* 加锁操作,数据安全 */
status = spidev_sync_read(spidev, count); /* 同步读取数据 */
if (status > 0) {
unsigned long missing;
missing = copy_to_user(buf, spidev->rx_buffer, status); /* 将读取的数据从内核态copy到用户态 */
if (missing == status)
status = -EFAULT;
else
status = status - missing;
}
mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock); /* 解锁操作 */
return status;
}spidev_sync_read函数的具体实现如下:
static inline ssize_t
spidev_sync_read(struct spidev_data *spidev, size_t len)
{
struct spi_transfer t = {
.rx_buf = spidev->rx_buffer, /* 指定rx_buffer */
.len = len,
.speed_hz = spidev->speed_hz,
};
struct spi_message m; /* 构造一个message */
spi_message_init(&m); /* 初始化spi_message */
spi_message_add_tail(&t, &m); /* 将transfer放到message的尾部 */
return spidev_sync(spidev, &m); /* 发起数据传输 */
}将要发送的数据填充到struct spi_transfer t结构体中,跟spidev_sync_write同样的将通过spi_message_init函数初始化spi_message全部为0,通过spi_message_init_no_memset函数调用INIT_LIST_HEAD为m->transfers和m->resources分别创建双向链表的头节点。
与spidev_sync_write函数一样,在完成SPI数据的链表的初始化之后又通过调用spi_message_add_tail函数,将struct spi_transfer t和struct spi_message m分别添加到前一步创建的双向链表的尾部。
spidev_sync函数完成数据同步的流程此处不在重复。
spidev_ioctl函数分析
spidev_ioctl的源码如下:
static long
spidev_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int retval = 0;
struct spidev_data *spidev;
struct spi_device *spi;
u32 tmp;
unsigned n_ioc;
struct spi_ioc_transfer *ioc;
/* Check type and command number */
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != SPI_IOC_MAGIC)
return -ENOTTY;
/* guard against device removal before, or while,
* we issue this ioctl.
*/
spidev = filp->private_data;
spin_lock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
spi = spi_dev_get(spidev->spi);
spin_unlock_irq(&spidev->spi_lock);
if (spi == NULL)
return -ESHUTDOWN;
/* use the buffer lock here for triple duty:
* - prevent I/O (from us) so calling spi_setup() is safe;
* - prevent concurrent SPI_IOC_WR_* from morphing
* data fields while SPI_IOC_RD_* reads them;
* - SPI_IOC_MESSAGE needs the buffer locked "normally".
*/
mutex_lock(&spidev->buf_lock);
switch (cmd) {
/* read requests */
case SPI_IOC_RD_MODE:
retval = put_user(spi->mode & SPI_MODE_MASK,
(__u8 __user *)arg);
break;
case SPI_IOC_RD_MODE32:
retval = put_user(spi->mode & SPI_MODE_MASK,
(__u32 __user *)arg);
break;
case SPI_IOC_RD_LSB_FIRST:
retval = put_user((spi->mode & SPI_LSB_FIRST) ? 1 : 0,
(__u8 __user *)arg);
break;
case SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD:
retval = put_user(spi->bits_per_word, (__u8 __user *)arg);
break;
case SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ:
retval = put_user(spidev->speed_hz, (__u32 __user *)arg);
break;
/* write requests */
case SPI_IOC_WR_MODE:
case SPI_IOC_WR_MODE32:
if (cmd == SPI_IOC_WR_MODE)
retval = get_user(tmp, (u8 __user *)arg);
else
retval = get_user(tmp, (u32 __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0) {
struct spi_controller *ctlr = spi->controller;
u32 save = spi->mode;
if (tmp & ~SPI_MODE_MASK) {
retval = -EINVAL;
break;
}
if (ctlr->use_gpio_descriptors && ctlr->cs_gpiods &&
ctlr->cs_gpiods[spi->chip_select])
tmp |= SPI_CS_HIGH;
tmp |= spi->mode & ~SPI_MODE_MASK;
spi->mode = (u16)tmp;
retval = spi_setup(spi);
if (retval < 0)
spi->mode = save;
else
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "spi mode %x\n", tmp);
}
break;
case SPI_IOC_WR_LSB_FIRST:
retval = get_user(tmp, (__u8 __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0) {
u32 save = spi->mode;
if (tmp)
spi->mode |= SPI_LSB_FIRST;
else
spi->mode &= ~SPI_LSB_FIRST;
retval = spi_setup(spi);
if (retval < 0)
spi->mode = save;
else
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%csb first\n",
tmp ? 'l' : 'm');
}
break;
case SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD:
retval = get_user(tmp, (__u8 __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0) {
u8 save = spi->bits_per_word;
spi->bits_per_word = tmp;
retval = spi_setup(spi);
if (retval < 0)
spi->bits_per_word = save;
else
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%d bits per word\n", tmp);
}
break;
case SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ:
retval = get_user(tmp, (__u32 __user *)arg);
if (retval == 0) {
u32 save = spi->max_speed_hz;
spi->max_speed_hz = tmp;
retval = spi_setup(spi);
if (retval == 0) {
spidev->speed_hz = tmp;
dev_dbg(&spi->dev, "%d Hz (max)\n",
spidev->speed_hz);
}
spi->max_speed_hz = save;
}
break;
default:
/* segmented and/or full-duplex I/O request */
/* Check message and copy into scratch area */
ioc = spidev_get_ioc_message(cmd,
(struct spi_ioc_transfer __user *)arg, &n_ioc);
if (IS_ERR(ioc)) {
retval = PTR_ERR(ioc);
break;
}
if (!ioc)
break; /* n_ioc is also 0 */
/* translate to spi_message, execute */
retval = spidev_message(spidev, ioc, n_ioc);
kfree(ioc);
break;
}
mutex_unlock(&spidev->buf_lock);
spi_dev_put(spi);
return retval;
}spidev_compat_ioctl函数分析
spidev_open函数分析
spidev_open函数源码如下:
static int spidev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
struct spidev_data *spidev;
int status = -ENXIO;
mutex_lock(&device_list_lock);
/* 在device_list链表中查找和inode下的注册此设备号一致的设备 */
list_for_each_entry(spidev, &device_list, device_entry) {
if (spidev->devt == inode->i_rdev) {
status = 0;
break;
}
}
if (status) {
pr_debug("spidev: nothing for minor %d\n", iminor(inode));
goto err_find_dev;
}
if (!spidev->tx_buffer) {
spidev->tx_buffer = kmalloc(bufsiz, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!spidev->tx_buffer) {
dev_dbg(&spidev->spi->dev, "open/ENOMEM\n");
status = -ENOMEM;
goto err_find_dev;
}
}
if (!spidev->rx_buffer) {
spidev->rx_buffer = kmalloc(bufsiz, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!spidev->rx_buffer) {
dev_dbg(&spidev->spi->dev, "open/ENOMEM\n");
status = -ENOMEM;
goto err_alloc_rx_buf;
}
}
spidev->users++;
/* 把找到的spidev_data保存在私有数据中 */
filp->private_data = spidev;
stream_open(inode, filp);
mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);
return 0;
err_alloc_rx_buf:
kfree(spidev->tx_buffer);
spidev->tx_buffer = NULL;
err_find_dev:
mutex_unlock(&device_list_lock);
return status;
}