《视觉 SLAM 十四讲》V2 第 8 讲 视觉里程计2 【如何根据图像 估计 相机运动】【光流 —> 直接法】
文章目录
- 第 8 讲 视觉里程计 2
-
- 8.2 光流
- 8.3 实践: LK 光流 【Code】
-
-
-
- 本讲 CMakeLists.txt
-
-
- 8.4 直接法
- 8.5 实践: 双目的稀疏直接法 【Code】
-
- 8.5.4 直接法的优缺点
- 习题 8
-
- √ 题1 光流方法
- 题2
- 题3
- 题4
- 题5
第 8 讲 视觉里程计 2
P205 第8讲
光流法 跟踪 特征点
直接法 估计相机位姿
多层直接法
8.1 直接法
第 7 讲 使用特征点 估计 相机运动
缺点:
1、关键点的提取 与 描述子的计算 非常耗时
2、只使用 特征点,丢弃了大部分 可能有用的图像信息
3、无明显纹理信息的地方(白墙、空走廊),无法匹配
改进思路:

直接法不保留特征点

特征点法 估计 相机运动: 最小化 重投影误差(Reprojection error)
直接法:最小化 光度误差(Photometric error)。根据 像素的亮度信息估计相机运动
特征点法: 只能重构稀疏地图
直接法: 稀疏、稠密、半稠密
8.2 光流
直接法从光流演变
同:相同的假设条件
异:光流描述了像素在图像中的运动,直接法附带一个相机模型。
光流: 描述 像素 随时间 在图像之间运动的方法
稀疏光流: 计算部分像素运动。 Lucas-Kanade光流 【LK光流】
稠密光流: 计算所有像素。 Horn-Schunck光流
LK 光流 常被用来 跟踪角点的运动。
8.3 实践: LK 光流 【Code】
本讲 CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(ch8)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
add_definitions("-DENABLE_SSE")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 ${SSE_FLAGS} -g -O3 -march=native")
find_package(OpenCV 4 REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
find_package(Pangolin REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/include/eigen3/"
${Pangolin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
add_executable(optical_flow optical_flow.cpp)
target_link_libraries(optical_flow ${OpenCV_LIBS})
#[[ # 块注释
add_executable(direct_method direct_method.cpp)
target_link_libraries(direct_method ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${Pangolin_LIBRARIES} ${Sophus_LIBRARIES})
]]
报错:
/home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch8/optical_flow.cpp:145:37: error: ‘CV_GRAY2BGR’ was not declared in this scope
145 | cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_single, CV_GRAY2BGR);
改为 cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR。有3个地方
要是 cd build 还要改图片路径。
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
./optical_flow
//
// Created by Xiang on 2017/12/19.
//
#include 8.4 直接法
光流: 首先追踪特征点位置,再根据这些位置确定相机的运动
- 很难保证全局的最优性。
——> 在后一步中,调整前一步的结果。
稀疏直接法:关键点,假设周围像素不变(因此不必计算描述子)。可快速求解相机位姿。
半稠密直接法:只使用带有梯度的像素点
稠密直接法:多数需要GPU加速
8.5 实践: 双目的稀疏直接法 【Code】
基于特征点的深度恢复(三角化)
基于块匹配的深度恢复
多层直接法 金字塔式
源码改动:
1、![]()
所有 SE3d 去掉 d
2、改路径
3、报错3
/home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch8/direct_method.cpp:206:35: error: ‘CV_GRAY2BGR’ was not declared in this scope
206 | cv::cvtColor(img2, img2_show, CV_GRAY2BGR);
改为 cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR。有3个地方
4、报错4
/usr/bin/ld: CMakeFiles/direct_method.dir/direct_method.cpp.o: in function `JacobianAccumulator::accumulate_jacobian(cv::Range const&)':
/home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch8/direct_method.cpp:235: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::operator*(Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1, 0, 3, 1> const&) const'
/usr/bin/ld: CMakeFiles/direct_method.dir/direct_method.cpp.o: in function `DirectPoseEstimationSingleLayer(cv::Mat const&, cv::Mat const&, std::vector, Eigen::aligned_allocator > > const&, std::vector >, Sophus::SE3&)' :
/home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch8/direct_method.cpp:178: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::exp(Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1, 0, 6, 1> const&)'
/usr/bin/ld: /home/xixi/Downloads/slambook2-master/ch8/direct_method.cpp:178: undefined reference to `Sophus::SE3::operator*(Sophus::SE3 const&) const'
Sophus库链接问题
add_executable(direct_method direct_method.cpp)
target_link_libraries(direct_method ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${Pangolin_LIBRARIES} ${Sophus_LIBRARIES})
byzanz-record -x 146 -y 104 -w 786 -h 533 -d 20 --delay=5 -c /home/xixi/myGIF/test.gif
这里程序运行感觉不太对,暂时不清楚哪里。
direct_method.cpp
#include 8.5.4 直接法的优缺点
优点:
1、省去计算特征点、描述子的时间
2、只要求有像素梯度,不需要特征点,可 在特征缺失的场合使用。
3、可以构建 半稠密 乃至 稠密的地图
缺点:
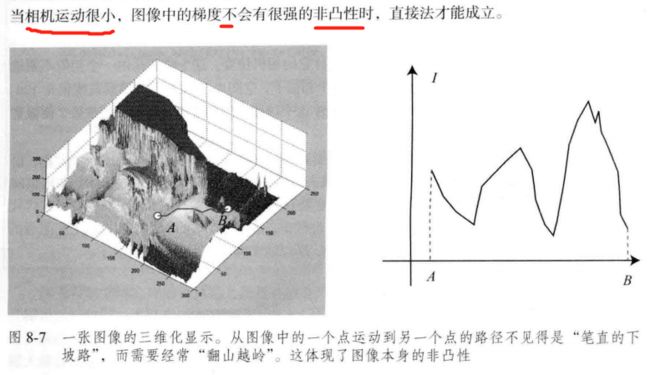
1、图像 强烈非凸。优化算法易进入极小,只有运动很小时直接法才能成功。金字塔的引入可以在一定程度上减小非凸的影响。
2、单个像素无区分度 ——> 图像块 or 相关性。500个点以上
3、强假设: 灰度值不变。 ——> 同时估计相机的曝光参数
习题 8
√ 题1 光流方法
1、除了LK光流,还有哪些光流方法?它们各有什么特点?
文档
稠密光流:
DIS(Dense Inverse Search,稠密逆搜索)光流算法:【低时间复杂度+有竞争力的精度】
DIS光流算法。这个类实现了密集逆搜索(DIS)光流算法。包括三个预设,带有预选参数,在速度和质量之间提供合理的权衡。但是,即使是最慢的预设也还是比较快的,如果你需要更好的质量,不关心速度,可以使用DeepFlow。
Till Kroeger, Radu Timofte, Dengxin Dai, and Luc Van Gool. Fast optical flow using dense inverse search. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2016.
三部分:
- inverse search for patch correspondences;
- dense displacement field creation through patch aggregation along multiple scales; 多尺度斑块聚集 形成 密集位移场;
- variational refinement.
——————————
cv::FarnebackOpticalFlow
使用Gunnar Farneback算法计算密集光流。
- Two-Frame Motion Estimation Based on
Polynomial Expansion——————————
基于鲁棒局部光流(RLOF,robust local optical flow)算法和稀疏到密集插值方案的快速密集光流计算。
有相应的稀疏 API
——————————
“Dual TV L1” Optical Flow Algorithm.
C. Zach, T. Pock and H. Bischof, “A Duality Based Approach for Realtime TV-L1 Optical Flow”. Javier Sanchez, Enric Meinhardt-Llopis and Gabriele Facciolo. “TV-L1 Optical Flow Estimation”.
——————————
【基于翘曲理论的高精度光流估计:角误差更小,对参数变化不敏感,噪声鲁棒】Thomas Brox, Andres Bruhn, Nils Papenberg, and Joachim Weickert. High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In Computer Vision-ECCV 2004, pages 25–36. Springer, 2004.
将一个连续的、旋转不变的能量泛函,用于光流计算,该泛函基于两个项:一个具有亮度常数和梯度常数假设的鲁棒数据项,结合一个保持不连续的时空 TV 正则化器。
cv::VariationalRefinement::calcUV()
该类可以使用金字塔迭代Lucas-Kanade方法计算稀疏特征集的光流。
题2
2、 在本节程序的求图像梯度过程中,我们简单地求了 u + 1 u+1 u+1 和 u − 1 u-1 u−1 的灰度之差除以 2,作为 u u u 方向上的梯度值。这种做法有什么缺点?提示:对于距离较近的特征,变化应该较快;而距离较远的特征在图像中变化较慢,求梯度时能否利用此信息?
题3
3、直接法是否能和光流一样,提出“反向法”的概念?即,使用原始图像的梯度代替目标图像的梯度?
题4
4、使用Ceres或g2o实现稀疏直接法和半稠密直接法。