【数据结构】双向链表的增删查改(C 代码实现)
文章目录
- 前言
-
-
- 引入双向链表:关于单链表的问题与讨论
-
- 一、双向链表的特性简概
- 二、双链表的增删查改【C 代码实现】
-
- (一)创建文件
- (二)List.h
-
- 1. 头文件声明
- 2. 双向结构体类型声明
- (三)List.c
-
- 1.创建返回双向链表的头结点.
- 2. 双向链表的初始化
- 3.创建返回新节点
- 4.双向链表尾插
- 5.双向链表头插
- 6.双向链表尾删
- 7.双向链表头删
- 8.双向链表查找
- 9.双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
- ★10. 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
-
- 10.1 双向链表尾删【ListErase版本】
- 10.2 双向链表头删【ListErase版本】
- 11.双向链表打印
-
- 11.1 递归实现
- 11.2 非递归实现
- 12. 双向链表销毁
- 三、完整代码
-
-
- 1.List.h
- 2.List.c
- 3.test.c
-
前言
引入双向链表:关于单链表的问题与讨论
单链表存在的毛病:
-
因为单链表只能单向遍历链表,
-
对于前插这个操作,单链表必须得找到所需前插节点位置的前一个,那么这时就得从头指针重新遍历一次链表,会造成时间复杂度大大增加。
-
没有头节点(哨兵位)无法删除首节点
这些都大大提高了时间复杂度 [ 关于算法的时间复杂度与空间复杂度 这一专题,我在之前写的一篇专题中有详细的讲解,有需要的可以点击链接了解一下 算法的时间复杂度与空间复杂度 ]
【注意:不要下意识觉得链表就一定有哨兵位,可以有,也可以没有!】
正是因为单链表只能 单向遍历 这一特性所带来各种的麻烦,前人设计出了双向链表。
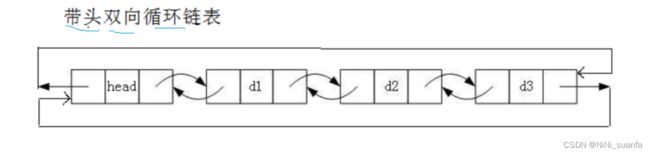
一、双向链表的特性简概
- 特性:
- 双向
- 循环
正是因为有这两个特性,促成了双向链表很多优势:
- 不需要像单链表那样从 头节点 完整遍历一边链表,才能找到尾节点。
双向链表:直接 phead->prev 找到尾节点(双向、循环 的特性)。 - 且找到需要处理的节点,还需要从头节点再遍历一次链表,只为找到该节点的前一个节点,才能对该节点进行处理。
双向链表:pos->prev 前一节点
代码实现
//类型声明
typedef int LTDataType; //数据类型重命名
typedef struct ListNode //结构体类型声明
{ //两头的指针变量 储存双向两旁结构体的地址
struct ListNode* prev; //保存前一个节点的指针
LTDataType data;
struct ListNode* next; //保存后一个节点的指针
}ListNode;
二、双链表的增删查改【C 代码实现】
(一)创建文件
- List.h (双向链表双向链表的类型定义、接口函数声明、引用的头文件)
- List.c (双向链表接口函数的实现)
- test.c (主函数、测试顺序表各个接口功能)
(二)List.h
1. 头文件声明
#pragma once //防止头文件重复包含
//头文件
#include2. 双向结构体类型声明
//类型声明
typedef int LTDataType; //数据类型重命名
typedef struct ListNode //结构体类型声明
{
struct ListNode* prev; //两头的指针变量 储存双向两旁结构体的地址
LTDataType data;
struct ListNode* next;
}ListNode;
(三)List.c
1.创建返回双向链表的头结点.
图解
phead 的含义 = pointer to head

// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate() {
ListNode* phead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
//结构体指针phead 存的是malloc为新结构体开辟内存后 的返回的该新节点的指针
assert(malloc);
return phead; //phead传的是phead指针的内容=head地址 =>返回结构体地址
}
2. 双向链表的初始化
// 双向链表的初始化
void ListInit(ListNode* phead) { //也用phead接受传过来的head的地址
assert(phead);
phead->prev = phead->next;
phead->data = 0; //加深对指针的理解
phead->next = phead->prev; //直接用head【记住:1. **名 直接用的是内容** 明白这点 对于指针的理解就轻松很多】
//2. -> 只能对指针使用 且不支持二级指针解引用*后得到一级指针的形式
// (如:ListNode** pphead **pphead->data (x)好像不行 去试一下 )
【关于指针注意的点的讲解】
}
【关于指针注意的点的讲解】 :加深对指针的理解
- 直接用head => 名 直接用的是内容 明白这点 对于指针的理解就轻松很多
- -> 只能对指针使用 且不支持二级指针解引用后得到一级指针的形式
(如:ListNode* pphead
**pphead->data (x) 好像不行 去试一下 )
3.创建返回新节点
// 创建返回新节点
ListNode* BuynewNode(x) {
ListNode* newNode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newNode->data = x;
return newNode;
}
4.双向链表尾插
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead,LTDataType x) {
ListNode* newNode = BuynewNode(x); //1M的空间可创建出一千多万个指针变量
ListNode* tail = phead->prev; //多创建指针变量 自己也标的看的清楚 增加代码的可读性
tail->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = tail;
newNode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newNode;
}
5.双向链表头插
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x) {
ListNode* newNode = BuynewNode(x);
ListNode* first = phead->next; //第一个节点
newNode->next = first;
first->prev = newNode;
phead->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = phead;
}
6.双向链表尾删
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead); //确保链表不为空,有东西可删,及时报错
ListNode* tailPrev = phead->prev->prev;
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
tailPrev->next = phead;
phead->prev = tailPrev;
}
7.双向链表头删
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* newNext = phead->next->next;
ListNode* Next = phead->next; //新建指针变量 保存好要free掉的节点的地址
free(Next); //就不用怕后续改变各节点之间的指针关系时把该节点的地址弄丢了
Next = NULL;
phead->next = newNext;
newNext->prev = phead;
}
8.双向链表查找
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x) {
ListNode* Head = phead->next; //设置两个指针变量,一个从头开始遍历,一个从后遍历
ListNode* Back = phead->prev;
while (Head!=Back) {
if (Head->data = x)
return Head;
else if (Back->data = x)
return Back;
Head = Head->next;
Back = Back->prev;
}
return NULL;
}
9.双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x) {
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
ListNode* newNode = BuynewNode(x);
posPrev->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = posPrev;
newNode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newNode;
}
★10. 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点 //若传过来的pos=phead->next =>作头删作用
void ListErase(ListNode* pos) {
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev; //若传过来的pos=phead(由于双向链表具有循环的特性) =>作尾删作用
ListNode* posNext = pos->next;
//也正是由于双向链表具有循环的特性,即使链表中只有一个节点也能很好的运行
posPrev->next = posNext; //图解
posNext->prev = posPrev;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
Erase函数以后 头删和尾删也可以这样写
10.1 双向链表尾删【ListErase版本】
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead); //确保链表不为空,有东西可删,及时报错
ListErase(phead);
}
10.2 双向链表头删【ListErase版本】
// 双向链表头删【ListErase版本】
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead); //确保链表不为空,有东西可删,及时报错
ListErase(phead->next);
}
11.双向链表打印
11.1 递归实现
// 双向链表打印 递归实现
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead) {
printf("%d <=>", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
ListPrint(cur);
}
printf("\n");
}
11.2 非递归实现
// 双向链表打印 非递归实现
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead) {
cur = phead->next;
printf("%d <=>", cur->data);
}
}
12. 双向链表销毁
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead) {
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead) {
ListNode* curNext = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = curNext;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}
三、完整代码
码源 我已上传至gitee 有需要的可点击后方链接 双向链表的增删查改 码源
1.List.h
#pragma once //防止头文件重复包含
#include2.List.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"List.h"
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate() {
ListNode* phead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); //结构体指针phead 存的是malloc为新结构体开辟内存后 的返回的该新节点的指针
assert(malloc);
return phead; //phead传的是phead指针的内容=head地址 =>返回结构体地址
}
// 双向链表的初始化
void ListInit(ListNode* phead) { //也用phead接受传过来的head的地址
assert(phead);
phead->prev = phead->next;
phead->data = 0; //加深对指针的理解
phead->next = phead->prev; //直接用head【记住:1. 名 直接用的是内容 明白这点 对于指针的理解就轻松很多】
//2. -> 只能对指针使用 且不支持二级指针解引用*后得到一级指针的形式
// (如:ListNode** pphead **pphead->data (x)好像不行 去试一下 ) 【关于指针注意的点的讲解】
}
// 创建返回新节点
ListNode* BuynewNode(x) {
ListNode* newNode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newNode->data = x;
return newNode;
}
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead,LTDataType x) {
ListNode* newNode = BuynewNode(x); //1M的空间可创建出一千多万个指针变量
ListNode* tail = phead->prev; //多创建指针变量 自己也标的看的清楚 增加代码的可读性
tail->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = tail;
newNode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newNode;
}
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x) {
ListNode* newNode = BuynewNode(x);
ListNode* first = phead->next; //第一个节点
newNode->next = first;
first->prev = newNode;
phead->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = phead;
}
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead); //确保链表不为空,有东西可删,及时报错
ListNode* tailPrev = phead->prev->prev;
ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
tailPrev->next = phead;
phead->prev = tailPrev;
}
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
ListNode* newNext = phead->next->next;
ListNode* Next = phead->next; //新建指针变量 保存好要free掉的节点的地址
free(Next); //就不用怕后续改变各节点之间的指针关系时把该节点的地址弄丢了
Next = NULL;
phead->next = newNext;
newNext->prev = phead;
}
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x) {
ListNode* Head = phead->next; //设置两个指针变量,一个从头开始遍历,一个从后遍历
ListNode* Back = phead->prev;
while (Head!=Back) {
if (Head->data = x)
return Head;
else if (Back->data = x)
return Back;
Head = Head->next;
Back = Back->prev;
}
return NULL;
}
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x) {
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
ListNode* newNode = BuynewNode(x);
posPrev->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = posPrev;
newNode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newNode;
}
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点 //若传过来的pos=phead->next =>作头删作用
void ListErase(ListNode* pos) {
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev; //若传过来的pos=phead(由于双向链表具有循环的特性) =>作尾删作用
ListNode* posNext = pos->next;
//也正是由于双向链表具有循环的特性,即使链表中只有一个节点也能很好的运行
posPrev->next = posNext; //图解
posNext->prev = posPrev;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
//Erase函数以后 头删和尾删也可以这样写
// 双向链表尾删【ListErase版本】
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead) {
//assert(phead);
//assert(phead->next != phead);
//ListNode* tailPrev = phead->prev->prev;
//ListNode* tail = phead->prev;
//free(tail);
//tail = NULL;
//tailPrev->next = phead;
//phead->prev = tailPrev;
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead); //确保链表不为空,有东西可删,及时报错
ListErase(phead);
}
// 双向链表头删【ListErase版本】
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead) {
//assert(phead);
//assert(phead->next != phead);
//ListNode* newNext = phead->next->next;
//ListNode* Next = phead->next;
//free(Next);
//Next = NULL;
//phead->next = newNext;
//newNext->prev = phead;
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead); //确保链表不为空,有东西可删,及时报错
ListErase(phead->next);
}
// 双向链表打印 递归实现
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead) {
printf("%d <=>", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
ListPrint(cur);
}
printf("\n");
}
// 双向链表打印 非递归实现
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead) {
assert(phead);
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead) {
cur = phead->next;
printf("%d <=>", cur->data);
}
}
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead) {
ListNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead) {
ListNode* curNext = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = curNext;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}
3.test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"List.h"
//测试ListPushBack 、ListPrint 的功能
void test1() {
ListNode* phead = ListCreate(); //返回head的地址
ListInit(phead);
ListPushBack(phead,1); //测试ListPushBack
ListPushBack(phead, 2);
ListPushBack(phead, 3);
ListPrint(phead); //测试ListPrint
}
void test2() {
ListNode* phead = ListCreate(); //返回head的地址
ListInit(phead);
ListPushBack(phead, 1);
ListPushBack(phead, 2);
ListPushBack(phead, 3);
ListPushBack(phead, 4);
ListPushBack(phead, 5);
ListPushBack(phead, 6);
ListPrint(phead);
ListNode* pos = ListFind(phead,3); //测试ListFind
ListErase(pos); //测试ListErase
ListPopFront(phead); //测试ListPopFront
ListPopBack(phead); //测试ListPopBack
ListPrint(phead);
pos = ListFind(phead, 2);
ListInsert(pos,8);
ListPrint(phead);
}
//测试ListDestory
void test3() {
ListNode* phead = ListCreate(); //返回head的地址
ListInit(phead);
ListPushBack(phead, 1);
ListPushBack(phead, 2);
ListPushBack(phead, 3);
ListPushBack(phead, 4);
ListPushBack(phead, 5);
ListPushBack(phead, 6);
ListPrint(phead);
ListNode* pos = ListFind(phead, 3);
ListErase(pos);
ListPopFront(phead);
ListPopBack(phead);
ListPrint(phead);
pos = ListFind(phead, 2);
ListInsert(pos, 8);
ListPrint(phead);
ListDestory(phead);
}
int main() {
test1();//测试ListPushBack 、ListPrint
test2();//测试
test3();//测试ListDestory
}```