机器学习实验六:决策树-海洋生物例子
#创建数据集
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
import graphviz
def createDataSet():
row_data = {'no surfacing':[1,1,1,0,0],
'flippers':[1,1,0,1,1],
'fish':['yes','yes','no','no','no']}
dataSet = pd.DataFrame(row_data)
return dataSet
def calEnt(dataSet):
n = dataSet.shape[0] #数据集总行数
iset = dataSet.iloc[:,-1].value_counts() #标签的所有类别
p = iset/n #每一类标签所占比
ent = (-p*np.log2(p)).sum() #计算信息熵
return ent
dataSet = createDataSet()
print(calEnt(dataSet))
#选择最优的列进行切分
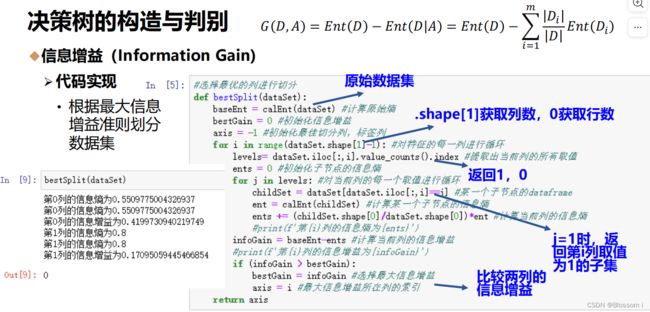
def bestSplit(dataSet):
baseEnt = calEnt(dataSet) #计算原始熵
bestGain = 0 #初始化信息增益
axis = -1 #初始化最佳切分列,标签列
for i in range(dataSet.shape[1]-1): #对特征的每一列进行循环
levels= dataSet.iloc[:,i].value_counts().index #提取出当前列的所有取值
ents = 0 #初始化子节点的信息熵
for j in levels: #对当前列的每一个取值进行循环
childSet = dataSet[dataSet.iloc[:,i]==j] #某一个子节点的dataframe
ent = calEnt(childSet) #计算某一个子节点的信息熵
ents += (childSet.shape[0]/dataSet.shape[0])*ent #计算当前列的信息熵
print(f'第{i}列{j}类的信息熵为{ents}')
infoGain = baseEnt-ents #计算当前列的信息增益
print(f'第{i}列的信息增益为{infoGain}')
if (infoGain > bestGain):
bestGain = infoGain #选择最大信息增益
axis = i #最大信息增益所在列的索引
return axis
bestSplit(dataSet)
def mySplit(dataSet,axis,value):
col = dataSet.columns[axis]
redataSet = dataSet.loc[dataSet[col]==value,:].drop(col,axis=1) #取切分属性值为value的数据子集,并且删除切分列
return redataSet
value =1
axis=0
mySplit(dataSet,axis,value)
col = dataSet.columns[axis]
dataSet.loc[dataSet[col]==value,:].drop(col,axis=1)
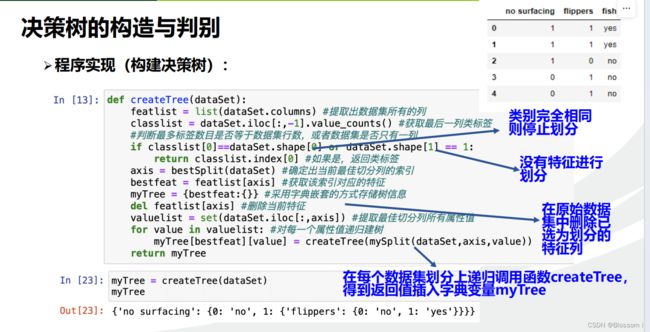
def createTree(dataSet):
featlist = list(dataSet.columns) #提取出数据集所有的列
classlist = dataSet.iloc[:,-1].value_counts() #获取最后一列类标签
#判断最多标签数目是否等于数据集行数,或者数据集是否只有一列
if classlist[0]==dataSet.shape[0] or dataSet.shape[1] == 1:
return classlist.index[0] #如果是,返回类标签
axis = bestSplit(dataSet) #确定出当前最佳切分列的索引
bestfeat = featlist[axis] #获取该索引对应的特征
myTree = {bestfeat:{}} #采用字典嵌套的方式存储树信息
del featlist[axis] #删除当前特征
valuelist = set(dataSet.iloc[:,axis]) #提取最佳切分列所有属性值
for value in valuelist: #对每一个属性值递归建树
myTree[bestfeat][value] = createTree(mySplit(dataSet,axis,value))
return myTree
myTree = createTree(dataSet)
#树的存储
np.save('myTree.npy',myTree)
#树的读取
read_myTree = np.load('myTree.npy',allow_pickle=True).item()
read_myTree
def storeTree(inputTree,filename):
import pickle
fw=open(filename,'wb')
pickle.dump(inputTree,fw)
fw.close()
storeTree(myTree,'mytree2.npy')
def grabTree(filename):
import pickle
fr=open(filename,'rb')
return pickle.load(fr)
grabTree('mytree2.npy')
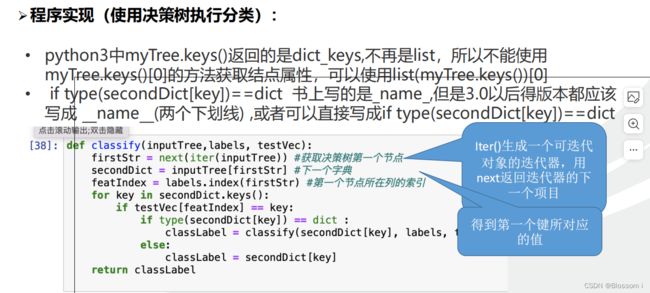
def classify(inputTree,labels, testVec):
firstStr = next(iter(inputTree)) #获取决策树第一个节点
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr] #下一个字典
featIndex = labels.index(firstStr) #第一个节点所在列的索引
for key in secondDict.keys():
if testVec[featIndex] == key:
if type(secondDict[key]) == dict :
classLabel = classify(secondDict[key], labels, testVec)
else:
classLabel = secondDict[key]
return classLabel
labels = list(dataSet.columns)
inputTree = myTree
firstStr = next(iter(inputTree))
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
def acc_classify(train,test):
inputTree = createTree(train) #根据测试集生成一棵树
labels = list(train.columns) #数据集所有的列名称
result = []
for i in range(test.shape[0]): #对测试集中每一条数据进行循环
testVec = test.iloc[i,:-1] #测试集中的一个实例
classLabel = classify(inputTree,labels,testVec) #预测该实例的分类
result.append(classLabel) #将分类结果追加到result列表中
test['predict']=result #将预测结果追加到测试集最后一列
acc = (test.iloc[:,-1]==test.iloc[:,-2]).mean() #计算准确率
print(f'模型预测准确率为{acc}')
return test
train = dataSet
test = dataSet.iloc[:3,:]
acc_classify(train,test)
#特征
Xtrain = dataSet.iloc[:,:-1]
#标签
Ytrain = dataSet.iloc[:,-1]
labels = Ytrain.unique().tolist()
Ytrain = Ytrain.apply(lambda x: labels.index(x)) #将本文转换为数字
treemodel = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini',max_depth=None,min_samples_leaf=1,ccp_alpha=0.0)
clf2=treemodel.fit(Xtrain, Ytrain)
clf2
#绘制树模型
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf = clf.fit(Xtrain, Ytrain)
tree.export_graphviz(clf)
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file=None)
graphviz.Source(dot_data)
#给图形增加标签和颜色
dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(clf, out_file=None,
feature_names=['no surfacing', 'flippers'],
class_names=['fish', 'not fish'],
filled=True, rounded=True,
special_characters=True)
graphviz.Source(dot_data)
#利用render方法生成图形
graph = graphviz.Source(dot_data)
graph.render("fish")
#利用render方法生成图形
graph = graphviz.Source(dot_data)
graph.render("fish")
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0 #初始化叶节点数目
firstStr = next(iter(myTree)) #获得树的第一个键值,即第一个特征
secondDict = myTree[firstStr] #获取下一组字典
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]) == dict: #测试该节点是否为字典
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key]) #是字典,递归,循环计算新分支叶节点数
else:
numLeafs +=1 #不是字典,代表此结点为叶子结点
return numLeafs
firstStr = next(iter(myTree))
getNumLeafs(myTree)
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = next(iter(myTree))
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]) == dict:
thisDepth = 1+getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth>maxDepth:
maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
getTreeDepth(myTree)运行结果
目前决策树无法实现