力扣LeetBook<哈希表>学习笔记
哈希表
哈希表是一种使用哈希函数组织数据,以支持快速插入和搜索的数据结构。
本文目录
- 一、概述
- 二、设计哈希表
-
- 1.哈希表的原理
- 2.设计哈希表的关键
- 3.设计哈希集合
- 4.设计哈希映射
- 5.复杂度分析 - 哈希表
- 三、实际应用 - 哈希集合
-
- 1.哈希集 - 用法
- 2.使用哈希集查重
- 3.存在重复元素
- 4.只出现一次的数字
- 5.两个数组的交集
- 6.快乐数
- 四、实际应用 - 哈希映射
-
- 1.哈希映射 - 用法
- 2.场景Ⅰ - 提供更多信息
- 3.两数之和
- 4.同构字符串
- 5.两个列表的最小索引总和
- 6.场景Ⅱ - 按键聚合
- 7.字符串中的第一个唯一字符
- 8.两个数组的交集Ⅱ
- 9.存在重复元素Ⅱ
- 10.日志速率限制器
- 五、实际应用 - 设计键
-
- 1.设计键
- 2.字母异位词分组
- 3.移位字符串分组
- 4.有效的数独
- 5.寻找重复的子树
- 6.设计键 - 总结
- 小结
-
- 1.宝石与石头
- 2.无重复字符的最长子串
- 3.两数之和Ⅲ - 数据结构设计
- 4. 四数相加Ⅱ
- 5.前K个高频元素
- 6.单词的唯一缩写
- 7.常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素
一、概述
哈希表是一种使用哈希函数组织结构,以支持快速插入和搜索的数据结构。
有两种不同类型的哈希表:哈希集合和哈希映射。
哈希集合是集合数据结构的实现之一,用于存储非重复值。哈希映射是映射数据结构的实现之一,用于存储(key,value)键值对。
在标准模版库的帮助下,哈希表是易于使用的。大多数常见语言都支持哈希集合和哈希映射。
通过选择合适的哈希函数,哈希表可以在插入和搜索方面实现出色的性能。
在本LeetBook中,我们将回答下列问题:
- 哈希表的
原理是什么? - 如何
设计哈希表? - 如何使用
哈希集来解决与重复相关的问题? - 如何使用
哈希映射按键聚合信息? - 如何在使用哈希表时
设计正确的键?
还有练习帮助熟悉哈希表。
二、设计哈希表
本章节讨论哈希表的基本原理。
- 哈希表的
原理是什么? - 哪些因素会影响
哈希函数以及冲突解决策略的选择? - 了解
哈希集合与哈希映射之间的区别。 - 如何设计如典型的
标模版库中那样的哈希集合和哈希映射的简化版本。 - 插入和查找操作的
复杂度是什么?
1.哈希表的原理
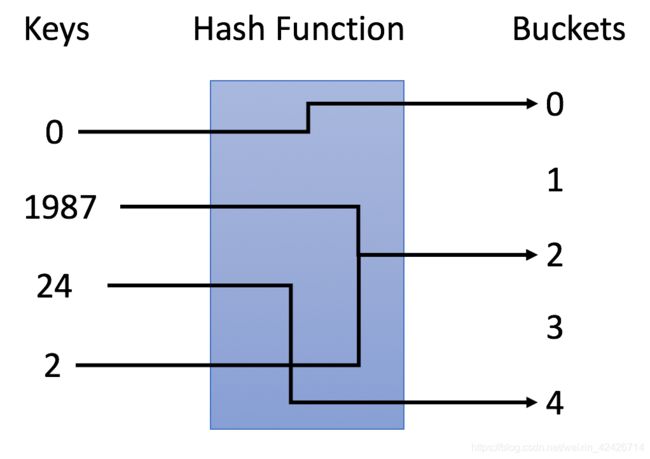
哈希表是一种数据结构,它使用哈希函数组织数据,以支持快速插入和搜索。
哈希表的关键思想是使用哈希函数将键映射到存储桶。
- 当我们插入一个新的键是,哈希函数将决定该键应该分配到哪个桶中,并将该键存储在相应的桶中;
- 当我们想要搜索一个键时,哈希表将使用相同的哈希函数来查找对应的桶,并只在特定的桶中进行搜索。
- 插入:通过哈希函数解析键,将它们映射到相应的桶中。
- 例如,1987分配给桶2,而24分配给桶4.
- 搜索:通过相同的哈希函数解析键,并仅在特定存储桶中搜索。
- 如果搜索1987,我们将使用相同的哈希函数将1987映射到2.因此我们在桶2中搜索,我们在那个桶中成功找到了1987.
- 例如,如果搜索23,将映射23到3,并在桶3中搜索。发现23不在桶3,这意味着23不在哈希表中。
2.设计哈希表的关键
两个基本因素
1. 哈希函数
哈希函数是哈希表最重要的组件,该哈希表用于将键映射到特定的桶。在上面的示例,使用y=x%5作为散列函数,其中x是键值,y是分配的桶的索引。
散列函数将取决于键值的范围和桶的数量。
哈希函数示例:

设计思想:尽可能将键分配到桶中,理想情况下,完美哈希函数是键和桶之间的一对一映射。然而,大多数情况下并不完美,需要在桶的数量和桶的容量之间进行权衡。
2.冲突解决
大多数情况下,冲突几乎是不可避免的。例如,哈希函数y = x % 5中,1987和2都分配给了桶2,这是一个冲突。
冲突解决算法:
- 如何组织在同一个桶中的值?
- 如果为同一个桶分配了太多的值,怎么办?
- 如何在特定的桶中搜索目标值?
根据观察,这些问题与桶的容量和可能映射到同一个桶的键的数目有关。
假设存储最大键数的桶有N个键。
通常,如果N是常数且很小,可以简单使用一个数组将键存储在同一个桶中。如果N可变或很大,可能需要用高度平衡的二叉树来代替。
训练
- 阅读需求
- 确定哈希函数
- 并在需要时解决冲突
两个基本操作:插入、搜索
基于这两个操作的操作:删除
3.设计哈希集合
705. 设计哈希集合
法1:链表
class MyHashSet {
private Bucket[] bucketArray;
private int keyRange;
class Bucket {
private LinkedList<Integer> container;
public Bucket() {
container = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
public void insert(Integer key) {
int index = container.indexOf(key);
if (index == -1) {
container.addFirst(key);
}
}
public void delete(Integer key) {
container.remove(key);
}
public boolean exists(Integer key) {
int index = container.indexOf(key);
return (index != -1);
}
}
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public MyHashSet() {
keyRange = 769;// 键值的范围,也是桶的数量
bucketArray = new Bucket[keyRange];
for (int i = 0; i < keyRange; i++)
bucketArray[i] = new Bucket();
}
protected int _hash(int key) {
return (key % keyRange);
}
public void add(int key) {
int bucketIndex = _hash(key);
bucketArray[bucketIndex].insert(key);
}
public void remove(int key) {
int bucketIndex = _hash(key);
bucketArray[bucketIndex].delete(key);
}
/**
* Returns true if this set contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(int key) {
int bucketIndex = _hash(key);
return bucketArray[bucketIndex].exists(key);
}
}
法2:BST
先学习实现下BST的搜索、插入、删除:
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null)
return null;
if (root.val == val)
return root;
else if (root.val > val)
root = searchBST(root.left, val);
else
root = searchBST(root.right, val);
return root;
}
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null)
return new TreeNode(val);
if (root.val > val)
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
else
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
return root;
}
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (key < root.val) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if (key > root.val) {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
} else {
if (root.left == null) {
// 返回右子树作为新根
return root.right;
} else if (root.right == null) {
// 返回左子树作为新根
return root.left;
} else {
// 左右子树都存在,返回后继节点(右子树最左叶子)作为新的根
TreeNode successor = min(root.right);
successor.right = deleteMin(root.right);
successor.left = root.left;
return successor;
}
}
return root;
}
private TreeNode min(TreeNode node) {
if (node.left == null) {
return node;
}
return min(node.left);
}
private TreeNode deleteMin(TreeNode node) {
if (node.left == null) {
return node.right;
}
node.left = deleteMin(node.left);
return node;
}
4.设计哈希映射
706. 设计哈希映射
法1:双数组
class MyHashMap {
private int[] keys;
private boolean[] contains;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyHashMap() {
keys=new int[1000001];
contains=new boolean[1000001];
}
/** value will always be non-negative. */
public void put(int key, int value) {
keys[key]=value;
contains[key]=true;
}
/** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or -1 if this map contains no mapping for the key */
public int get(int key) {
return contains[key]?keys[key]:-1;
}
/** Removes the mapping of the specified value key if this map contains a mapping for the key */
public void remove(int key) {
contains[key]=false;
}
}
法2:
5.复杂度分析 - 哈希表
三、实际应用 - 哈希集合
1.哈希集 - 用法
// "static void main" must be defined in a public class.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. initialize the hash set
Set<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
// 2. add a new key
hashSet.add(3);
hashSet.add(2);
hashSet.add(1);
// 3. remove the key
hashSet.remove(2);
// 4. check if the key is in the hash set
if (!hashSet.contains(2)) {
System.out.println("Key 2 is not in the hash set.");
}
// 5. get the size of the hash set
System.out.println("The size of has set is: " + hashSet.size());
// 6. iterate the hash set
for (Integer i : hashSet) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println("are in the hash set.");
// 7. clear the hash set
hashSet.clear();
// 8. check if the hash set is empty
if (hashSet.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("hash set is empty now!");
}
}
}
2.使用哈希集查重
模版:
/*
* Template for using hash set to find duplicates.
*/
boolean findDuplicates(List<Type>& keys) {
// Replace Type with actual type of your key
Set<Type> hashset = new HashSet<>();
for (Type key : keys) {
if (hashset.contains(key)) {
return true;
}
hashset.insert(key);
}
return false;
}
3.存在重复元素
217. 存在重复元素
if(!seen.add(i)) return true;可以代替
if (!seen.contains(i)) {
seen.add(i);
} else {
return true;
}
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
for (int i : nums) {
if (!seen.add(i)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
4.只出现一次的数字
136.只出现一次的数字
法1:哈希表法
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i : nums) {
if (!set.add(i)) {
set.remove(i);
}
}
return set.iterator().next();
}
法2:异或
刷数据库的题也常用到这种做法,挑选出独一无二的一个。记住两个异或操作:
- A ^ A=0
- A ^ 0 = A
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
res ^= num;
}
return res;
}
5.两个数组的交集
349.两个数组的交集
知道一个HashSet的retainAll方法就很简单了。
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet<>();
for (int i : nums1) {
set1.add(i);
}
for (int i : nums2) {
set2.add(i);
}
set1.retainAll(set2);
int[] output = new int[set1.size()];
int index = 0;
for (int i : set1) {
output[index++] = i;
}
return output;
}
6.快乐数
202.快乐数
其实就是链表环问题,看链表指针最终是否回到1。
法1:哈希集
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
while (n != 1 && !seen.contains(n)) {
seen.add(n);
n = getNext(n);
}
return n == 1;
}
private int getNext(int n) {
int totalSum = 0;
while (n > 0) {
int d = n % 10;
n = n / 10;
totalSum += d * d;
}
return totalSum;
}
法2:链表
public boolean isHappy1(int n) {
int slowRunner = n;
int fastRunner = getNext(n);
while (fastRunner != 1 && slowRunner != fastRunner) {
slowRunner = getNext(slowRunner);
fastRunner = getNext(getNext(fastRunner));
}
return fastRunner == 1;
}
private int getNext(int n) {
int totalSum = 0;
while (n > 0) {
int d = n % 10;
n = n / 10;
totalSum += d * d;
}
return totalSum;
}
四、实际应用 - 哈希映射
1.哈希映射 - 用法
使用哈希映射的第一个场景是,我们需要更多的信息,而不仅仅是键。然后通过哈希映射建立密钥与信息之间的映射关系。
// "static void main" must be defined in a public class.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. initialize a hash map
Map<Integer, Integer> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
// 2. insert a new (key, value) pair
hashmap.putIfAbsent(0, 0);
hashmap.putIfAbsent(2, 3);
// 3. insert a new (key, value) pair or update the value of existed key
hashmap.put(1, 1);
hashmap.put(1, 2);
// 4. get the value of specific key
System.out.println("The value of key 1 is: " + hashmap.get(1));
// 5. delete a key
hashmap.remove(2);
// 6. check if a key is in the hash map
if (!hashmap.containsKey(2)) {
System.out.println("Key 2 is not in the hash map.");
}
// 7. get the size of the hash map
System.out.println("The size of hash map is: " + hashmap.size());
// 8. iterate the hash map
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : hashmap.entrySet()) {
System.out.print("(" + entry.getKey() + "," + entry.getValue() + ") ");
}
System.out.println("are in the hash map.");
// 9. clear the hash map
hashmap.clear();
// 10. check if the hash map is empty
if (hashmap.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("hash map is empty now!");
}
}
}
2.场景Ⅰ - 提供更多信息
/*
* Template for using hash map to find duplicates.
* Replace ReturnType with the actual type of your return value.
*/
ReturnType aggregateByKey_hashmap(List<Type>& keys) {
// Replace Type and InfoType with actual type of your key and value
Map<Type, InfoType> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
for (Type key : keys) {
if (hashmap.containsKey(key)) {
if (hashmap.get(key) satisfies the requirement) {
return needed_information;
}
}
// Value can be any information you needed (e.g. index)
hashmap.put(key, value);
}
return needed_information;
}
3.两数之和
1.两数之和
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
这类题型要注意的点是:判断map.containsKey应该放在put操作之前
4.同构字符串
205.同构字符串
还是要记住判断map.containsKey应该放在put操作之前
public boolean isIsomorphic(String s, String t) {
HashMap<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (!map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))) {
if (map.containsValue(t.charAt(i))) {
return false;
}
map.put(s.charAt(i), t.charAt(i));
} else {
if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) != t.charAt(i)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
5.两个列表的最小索引总和
599.两个列表的最小索引总和
public String[] findRestaurant(String[] list1, String[] list2) {
Map<Integer, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < list2.length; j++) {
if (list1[i].equals(list2[j])) {
if (!map.containsKey(i + j)) {
map.put(i + j, new ArrayList<>());
}
map.get(i + j).add(list1[i]);
}
}
}
int minIdx = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i : map.keySet()) {
minIdx = Math.min(minIdx, i);
}
String[] res = new String[map.get(minIdx).size()];
return map.get(minIdx).toArray(res);
}
6.场景Ⅱ - 按键聚合
/*
* Template for using hash map to find duplicates.
* Replace ReturnType with the actual type of your return value.
*/
ReturnType aggregateByKey_hashmap(List<Type>& keys) {
// Replace Type and InfoType with actual type of your key and value
Map<Type, InfoType> hashmap = new HashMap<>();
for (Type key : keys) {
if (hashmap.containsKey(key)) {
hashmap.put(key, updated_information);
}
// Value can be any information you needed (e.g. index)
hashmap.put(key, value);
}
return needed_information;
}
7.字符串中的第一个唯一字符
387.字符串中的第一个唯一字符
map.put(key, map.getOrDefault(key, 0) + 1)是常用策略。
public int firstUniqChar(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
map.put(c, map.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) == 1)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
8.两个数组的交集Ⅱ
350. 两个数组的交集 II
跟Ⅰ的区别就是显示的是正确的交集,有几个相同的就得显示几个,所以不能用hashset了。
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
if (nums1.length > nums2.length)
intersect(nums2, nums1);
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int num : nums1) {
map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
int[] intersection = new int[nums1.length];
int index = 0;
for (int num : nums2) {
int count = map.getOrDefault(num, 0);
if (count > 0) {
intersection[index++] = num;
count--;
if (count > 0) {
map.put(num, count);
} else {
map.remove(num);
}
}
}
return Arrays.copyOf(intersection, index);
}
9.存在重复元素Ⅱ
219.存在重复元素Ⅱ
暴力法和哈希表法
public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
// for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
// for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
// if (nums[j] == nums[i]) {
// int index = j - i;
// if (index <= k) {
// return true;
// }
// break;
// }
// }
// }
// return false;
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (!seen.add(nums[i])) {
return true;
}
if (seen.size() == k + 1) {
seen.remove(nums[i - k]);
}
}
return false;
}
10.日志速率限制器
class Logger {
private Map<String, Integer> map;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here.
*/
public Logger() {
this.map = new HashMap<>();
}
/**
* Returns true if the message should be printed in the given timestamp, otherwise returns false.
* If this method returns false, the message will not be printed.
* The timestamp is in seconds granularity.
*/
public boolean shouldPrintMessage(int timestamp, String message) {
if (map.containsKey(message)) {
Integer oldTimestamp = map.get(message);
if (timestamp - oldTimestamp < 10) {
return false;
} else {
map.put(message, timestamp);
return true;
}
} else {
map.put(message, timestamp);
return true;
}
}
}
/**
* Your Logger object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Logger obj = new Logger();
* boolean param_1 = obj.shouldPrintMessage(timestamp,message);
*/
五、实际应用 - 设计键
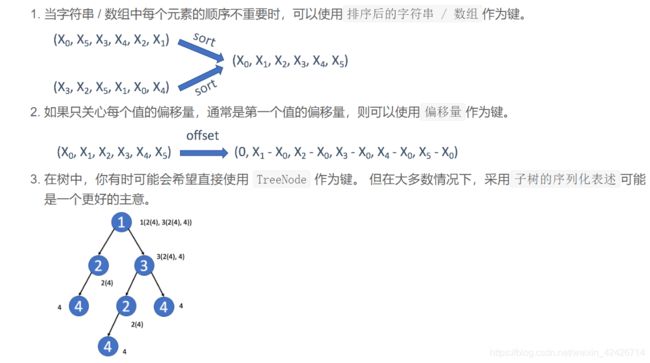
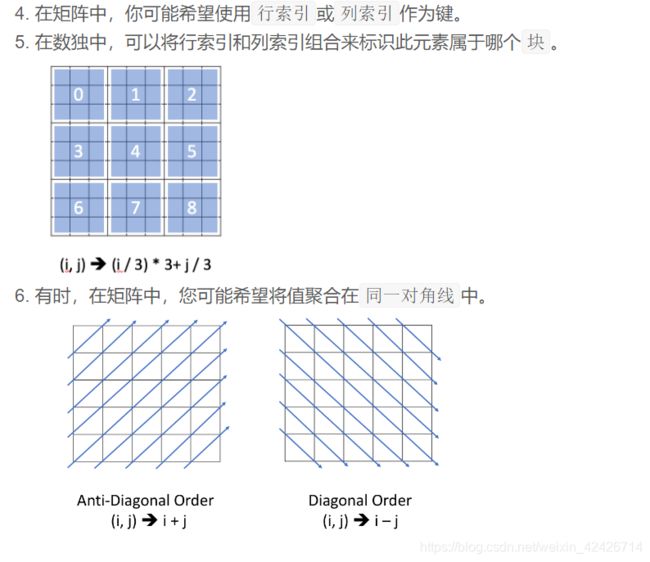
1.设计键
2.字母异位词分组
49.字母异位词分组
遇到返回值是List的题目,最后这个new ArrayList(map.values())是很有用处的。
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
if (strs.length == 0)
return null;
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String s : strs) {
char[] ca = s.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(ca);
String key = String.valueOf(ca);
map.put(key, map.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList<String>()));
map.get(key).add(s);
}
return new ArrayList(map.values());
}
3.移位字符串分组
4.有效的数独
36.有效的数独
5.寻找重复的子树
652.寻找重复的子树
class Solution {
Map<String, Integer> count;
List<TreeNode> ans;
public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) {
count = new HashMap();
ans = new ArrayList();
collect(root);
return ans;
}
public String collect(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return "null";
String serial = node.val + "," + collect(node.left) + "," + collect(node.right);
count.put(serial, count.getOrDefault(serial, 0) + 1);
if (count.get(serial) == 2)
ans.add(node);
return serial;
}
}
6.设计键 - 总结
小结
我们现在更加熟悉哈希表的原理和用法。
我们在前面的章节中已经从三个方面讨论了如何应用哈希表。在这里,我们将它们组合在一起,并提出一个通过哈希表灵活地解决问题的典型思维过程。

更重要的是,我们有时会遇到更复杂的问题,我们可能需要:
- 一起使用多个哈希表
- 将哈希表与其他数据结构相结合
- 将哈希表与其他算法结合起来
- …