Java SE 学习笔记(十四)—— IO流(3)
目录
- 1 缓冲流
-
- 1.1 缓冲流概述
- 1.2 字节缓冲流
- 1.3 字符缓冲流
- 2 转换流
-
- 2.1 字符输入转换流
- 2.1 字符输出转换流
- 3 序列化
-
- 3.1 对象序列化
- 3.2 对象反序列化
- 4 打印流
- 5 与Properties结合使用
- 6 IO 框架
1 缓冲流
1.1 缓冲流概述
我们之前学习的字节流、字符流属于基础流、原始流,性能其实不是最好的,缓冲流读写数据的性能更好
缓冲流也称为高效流、高级流,其自带缓冲区,可以提高原始字节流、字符流读写数据的性能。功能上并无很大变化,性能提升了。
1.2 字节缓冲流
字节缓冲输入流:
BufferedInputStream,提高字节输入流读取数据的性能。- 字节缓冲输入流自带了 8KB 缓冲池,以后我们直接从缓冲池读取数据,所以性能较好。
字节缓冲输出流:
BufferedOutputStream,提高字节输出流读取数据的性能。- 字节缓冲输出流自带了 8KB 缓冲池,数据就直接写入到缓冲池中去,写数据性能极高了。
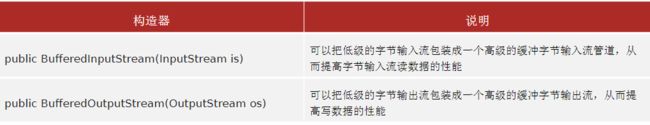
构造方法
为什么构造方法需要的是字节流,而不是具体的文件或者路径呢?
- 字节缓冲流仅仅提供缓冲区,而真正读写数据还是得依靠基本的字节流对象进行操作
1.3 字符缓冲流
符缓冲输入流:
BufferedReader,提高字符输入流读取数据的性能,除此之外多了按照行读取数据的功能。
字符缓冲输出流:
BufferedWriter,提高字符输出流写取数据的性能,除此之外多了换行功能
示例代码:
import java.io.*;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter f1 = new FileWriter("D:\\StudyTools\\test.txt");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(f1);
bw.write("我");
bw.write("abc");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("hhhh");
bw.close(); // 字符首先写到缓冲池,关闭文件后刷新,写入的文件有内容显示
FileReader f2 = new FileReader("D:\\StudyTools\\test.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(f2);
System.out.println(br.readLine()); // 我abc
System.out.println(br.readLine()); // hhhh
System.out.println(br.readLine()); // null
}
}
推荐使用哪种方式提高字节流读写数据的性能?
- 建议使用字节缓冲输入流、字节缓冲输出流,结合字节数组的方式, 目前来看是性能最优的组合。
2 转换流
使用字符流读取中文不会乱码,那如果读取的文件编码与代码编码不一致怎么办呢?
2.1 字符输入转换流
针对文件编码与代码编码不一致导致的乱码问题,如何解决?
- 使用字符输入转换流
- 可以提取文件的原始字节流(原始字节不会存在问题)
- 然后把字节流以指定编码转换成字符输入流(这样字符输入流的字符就不会乱码了)
字符输入转换流: InputStreamReader ,可以把原始的字节流按照指定编码转换成字符输入流。
示例代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/*
* 代码是UTF-8,文件是GBK
* */
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 提取字节码文件的原始字节流
FileInputStream f = new FileInputStream("D:\\StudyTools\\test.txt");
// 2. 把原始字节流转换为字符输入流
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(f); // 默认UTF-8转换字符流还是会乱码
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(f,"GBK");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String s;
while((s=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
2.1 字符输出转换流
如果需要控制写出去的字符使用的编码,怎么办?
- 可以把字符以指定编码获取字节后再使用字节输出流写出去
"我爱你中国" .getBytes(编码)- 也可以使用字符输出转换流实现
字符输出转换流: OutputStreamWriter ,可以指定编码把字节输出流转换成字符输出流,从而可以指定写出去的字符编码
示例代码:
import java.io.*;
/* 代码是UTF-8
指定写出去文件的字符编码GBK
* */
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 定义一个字节输出流
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("io/src/out.txt");
// 2. 把原始的字节输出流转换成字符输出流
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os,"GBK");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
bw.write("123我爱你中国");
bw.write("123我爱你中国");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("123我爱你中国");
bw.close();
}
}
3 序列化
如何把Java对象进行长久的保存?
3.1 对象序列化
对象序列化:
- 以内存为基准,把内存中的对象存储到磁盘文件中去。
- 使用到的流是
对象字节输出流:ObjectOutputStream
构造方法
序列化方法
示例代码
学生对象
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
// 声明序列化的版本号
private static final long serialVerionUID=1;
private int age;
private String name;
private String passwd;
// private transient String passwd; // 表示修饰的成员变量不参与序列化
public Student() {
}
public Student(int age, String name, String passwd) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.passwd = passwd;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPasswd() {
return passwd;
}
public void setPasswd(String passwd) {
this.passwd = passwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", passwd='" + passwd + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
序列化
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建学生对象
Student s = new Student(18, "小明", "123123");
// 2. 对象序列化
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io/src/obj.txt"));
// 3. 调用序列化方法
oos.writeObject(s);
oos.close();
}
}
注意:
- 对象如果要序列化,必须实现
Serializable接口
- 一个标记性接口,里面没有任何的抽象方法(实现一个接口就要实现里面所有的抽象方法)只要一个类实现了这个Serializable接口,那么就表示这个类的对象可以被序列化。
- 实现该接口,不需要重写任何方法
transien修饰的成员变量不参与序列化- 序列化与反序列化的版本号必须一致
3.2 对象反序列化
对象反序列化:
- 以内存为基准,把存储到磁盘文件中去的对象数据恢复成内存中的对象
- 使用到的流是
对象字节输入流:ObjectInputStream
构造方法
反序列方法
示例代码
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 1. 对象反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("io/src/obj.txt"));
// 2. 调用反序列化方法
Student s = (Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(s);
ois.close();
}
}
4 打印流
开发中有一种使用极为方便,性能高效的写数据的流,使用的很多。
打印流可以实现方便、高效的打印数据到文件中去。打印流一般是指: PrintStream , PrintWriter 两个类。
可以实现打印什么数据就是什么数据,例如打印整数 97 写出去就是 97 ,打印 boolean 的 true ,写出去就是 true 。
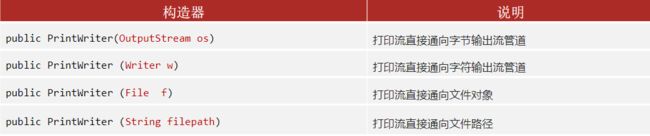
构造方法
打印方法(二者一样)
示例代码
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class printDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 创建一个打印流对象
// PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("io/src/ps.txt");
// PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new File("io/src/ps.txt"));
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("io/src/ps.txt"));// 如果要追加数据,在低级管道后面加true
ps.println(true);
ps.println("我爱你中国");
ps.println(123);
ps.close();
}
}
PrintStream 和 PrintWriter 的区别
- 打印数据功能上是一模一样的,都是使用方便,性能高效(核心优势)
PrintStream继承自字节输出流OutputStream,支持写字节数据的方法。PrintWriter继承自字符输出流Writer,支持写字符数据出去。
输出语句重定向:属于打印流的一种应用,可以把输出语句的打印位置改到文件
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class printDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 控制台打印
System.out.println("床前明月光,");
System.out.println("疑是地上霜。");
// 改变输出语句的位置(将以下两句输出到文件)
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("io/src/print.txt");
System.setOut(ps);
System.out.println("举头望明月,");
System.out.println("低头思故乡。");
}
}
5 与Properties结合使用
Properties 集合是一个Map体系的集合类,但是一般我们不会当集合使用,因为HashMap更好用,其可以保存到流中或从流中加载。
Properties 的 核心作用: Properties 代表的是一个属性文件,可以把自己对象中的键值对信息存入到一个属性文件中去。
- 属性文件:后缀是
.properties结尾的文件 , 里面的内容都是 key=value ,后续做系统配置信息的。(那么这就涉及到文件内容的读写了,结合IO流)
Properties 和 IO 流结合的方法:
示例代码:
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 使用Properties将键值对信息保存到属性文件中去(写)
// Properties p = new Properties();
// p.setProperty("admin","123456");
// p.setProperty("huwei","000000");
// p.setProperty("anni","888888");
// p.store(new FileWriter("io/src/users.properties"),"这是备注信息");
// 2. Properties读取属性文件中的属性信息(读)
Properties properties = new Properties();
System.out.println(properties);
// 加载属性文件中的键值对数据到属性对象properties中去
properties.load(new FileReader("io/src/users.properties"));
System.out.println(properties);
// 获取属性值
String rs1 = properties.getProperty("admin");
System.out.println(rs1); // 123456
}
}
6 IO 框架
commons-io 是 apache 开源基金组织提供的一组有关 IO 操作的类库,可以提高 IO 功能开发的效率。commons-io 工具包提供了很多有关 io 操作的类。有两个主要的类 FileUtils,IOUtils。
FileUtils 主要有如下方法:
导入 commons-io-2.15.0.jar ,用其简化 IO 流读写
- 在项目中创建一个文件夹
lib - 将
commons-io-2.15.0.jar文件复制到lib文件夹 - 在 jar 文件上点击右键,选择
Add as Library,点击OK - 在类中导包使用
示例代码
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import java.io.*;
public class CommonsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 文件的复制
IOUtils.copy(new FileInputStream("io/src/ps.txt"), new FileOutputStream("io/src/ps_copy.txt"));
// 文件复制到某个文件夹下
FileUtils.copyFileToDirectory(new File("io/src/ps.txt"),new File("D:\\"));
// 文件夹复制到某个文件夹下
FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(new File("io/src"),new File("D:\\"));
// 删除文件夹(有内容)
FileUtils.deleteDirectory(new File("D:\\src"));
// 删除文件
FileUtils.delete(new File("D:\\ps.txt"));
}
}