torch_geometric 笔记:TORCH_GEOMETRIC.UTILS(更新中)
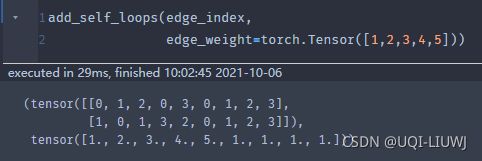
1 torch_geometric.utils.add_self_loops
add_self_loops(
edge_index,
edge_weight: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
fill_value: float = 1.0,
num_nodes: Optional[int] = None)在edge_index中,对图上每个节点i,添加一条边(i,i)
参数介绍
| edge_index (LongTensor) | 原图的edge_index |
| edge_weight (Tensor, optional) | 原图那些边的weight 【一维数组,维度需要和原来的边数量一致】 【此时自环的权重默认为1】 |
| fill_value (float, optional) | 如果edge_weight非空,将用fill_value作为自环的weight |
| num_nodes (int, optional) | 最初的多少个点进行自环(没有这个参数的话,就是默认所有的点) |
返回内容
(LongTensor, Tensor) 第一个维度是更新后的edge_idx,第二个维度是边权重,如果没有设置edge_weight,那么第二个维度是None
2 torch_geometric.utils.remove_self_loops
去除自环
remove_self_loops(
edge_index,
edge_attr: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None)3 torch_geometric.utils.degree
degree(
index,
num_nodes: Optional[int] = None,
dtype: Optional[int] = None)计算一个给定的一维index tensor的度
num_nodes也是表示计算多少个点的度
x,y=edge_index
x,y
#(tensor([0, 1, 2, 0, 3]), tensor([1, 0, 1, 3, 2]))
torch_geometric.utils.degree(x)
#tensor([2., 1., 1., 1.])
#0~3这四个点的出度
torch_geometric.utils.degree(y)
#tensor([1., 2., 1., 1.])
#0~3这四个点的入度4 torch_geometric.utils.get_laplacian
通过edge_index和可能有的edge_weight,计算图拉普拉斯矩阵
get_laplacian(
edge_index,
edge_weight: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
normalization: Optional[str] = None,
dtype: Optional[int] = None,
num_nodes: Optional[int] = None)参数说明
5 to_networkx
to_networkx(
data,
node_attrs=None,
edge_attrs=None,
to_undirected=False,
remove_self_loops=False)参数说明
| data (torch_geometric.data.Data) | 需要转换的Data数据 |
| node_attrs (iterable of str, optional) | 需要转换的点属性 |
| edge_attrs (iterable of str, optional) | 需要转化的边属性 |
| to_undirected (bool, optional) | 如果是True,那么返回的就是networkx.Graph 如果是False,那么返回的就是networkx.DiGraph 无向图会根据相应邻接矩阵的上三角矩阵进行创建 |
| remove_self_loops (bool, optional) | 是否移除自环 |
我们以ENZYMES数据集的第一个data为例:
torch_geometric笔记:数据集 ENZYMES &Minibatches_UQI-LIUWJ的博客-CSDN博客
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch_geometric.datasets import TUDataset
from torch_geometric.utils import to_networkx
dataset = TUDataset(root='', name='ENZYMES')
dataset[0]
#Data(edge_index=[2, 168], x=[37, 3], y=[1])
x=to_networkx(dataset[0])
nx.draw(x, with_labels=True)