TensorRT量化实战课YOLOv7量化:YOLOv7-PTQ量化(一)
目录
-
- 前言
- 1. YOLOv7-PTQ量化流程
- 2. 准备工作
- 3. 插入QDQ节点
-
- 3.1 自动插入QDQ节点
- 3.2 手动插入QDQ节点
前言
手写 AI 推出的全新 TensorRT 模型量化实战课程,链接。记录下个人学习笔记,仅供自己参考。
该实战课程主要基于手写 AI 的 Latte 老师所出的 TensorRT下的模型量化,在其课程的基础上,所整理出的一些实战应用。
本次课程为 YOLOv7 量化实战第二课,主要介绍 YOLOv7-PTQ 量化
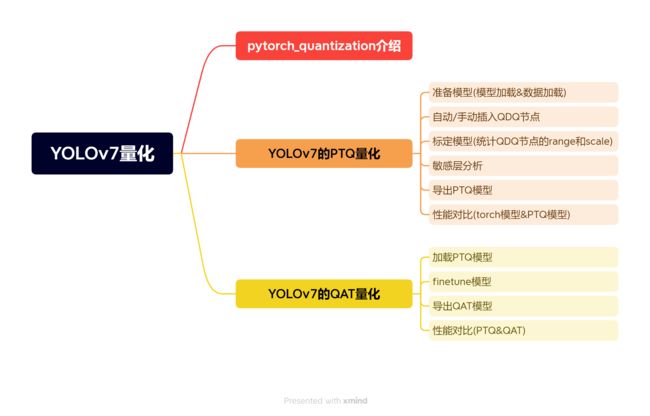
课程大纲可看下面的思维导图
1. YOLOv7-PTQ量化流程
在上节课程中我们介绍了 pytorch_quantization 量化工具箱,从这节课开始我们将正式进入 YOLOv7-PTQ 量化的实战。
从上面的思维导图我们可以看到 YOLOv7-PTQ 量化的步骤,我们代码的讲解和编写都是按照这个流程来的。
在编写代码开始之前我们还是再来梳理下整个 YOLOv7-PTQ 量化的过程,如下:
1. 准备工作
首先是我们的准备工作,我们需要下载 YOLOv7 官方代码和预训练模型以及 COCO 数据集,并编写代码完成模型和数据的加载工作。
2. 插入 QDQ 节点
第二个就是我们需要对模型插入 QDQ 节点,它有以下两种方式:
- 自动插入
- 使用 quant_modules.initialize() 自动插入量化节点
- 手动插入
- 使用 quant_modules.initialize() 初始化量化操作或使用 QuantDescriptor() 自定义初始化量化操作
- 编写代码为模型插入量化节点
3. 标定
第三部分就是我们的标定,其流程如下:
- 1. 通过将标定数据送到网络并收集网络每个层的输入输出信息
- 2. 根据统计出的信息,计算动态范围 range 和 scale,并保存在 QDQ 节点中
4. 敏感层分析
第四部分是敏感层分析,大致流程如下:
- 1. 进行单一逐层量化,只开启某一层的量化其他层都不开启
- 2. 在验证集上进行模型精度测试
- 3. 选出前 10 个对模型精度影响比较大的层,关闭这 10 个层的量化,在前向计算时使用 float16 而不去使用 int8
5. 导出 PTQ 模型
第五个就是我们在标定之后需要导出 PTQ 模型,导出流程如下:
- 1. 需要将我们上节课所说的 quant_nn.TensorQuantizer.use_fb_fake_quant 属性设置为 true
- 2. torch.onnx.export() 导出 ONNX 模型
6. 性能对比
第六个就是性能的对比,包括精度和速度的对比。
OK!以上就是 YOLOv7-PTQ 量化的流程,下面我们根据上面的流程来具体的实现,让我们开始吧!!!
2. 准备工作
首先是我们的准备工作,在正式开始前我们需要准备三个东西:
- 代码:yolov7 官方代码
- 数据集:coco2017
- 官方预训练模型:yolov7.pt
大家可以点击 here【pwd:yolo】 下载博主准备好的相关代码、模型和数据集
我们来看下我们整个项目的目录结构,如下图所示:
其中的 coco2017 的数据集目录如下:
.
├─train2017
│ ├─images
│ ├─labels
│ └─xml
└─val2017
├─images
├─labels
└─xml
除此之外我们还需要 train2017.txt 和 val2017.txt 两个 TXT 文件,分别存储着对应训练集和验证集图像的完整路径,以下是生成对应 TXT 的代码:
import os
save_dir = "/home/jarvis/Learn/Datasets/VOC_QAT"
train_dir = "/home/jarvis/Learn/Datasets/VOC_QAT/images/train"
train_txt_path = os.path.join(save_dir, "train2017.txt")
with open(train_txt_path, "w") as f:
for filename in os.listdir(train_dir):
if filename.endswith(".jpg") or filename.endswith(".png"): # 添加你的图像文件扩展名
file_path = os.path.join(train_dir, filename)
f.write(file_path + "\n")
print(f"train2017.txt has been created at {train_txt_path}")
val_dir = "/home/jarvis/Learn/Datasets/VOC_QAT/images/val"
val_txt_path = os.path.join(save_dir, "val2017.txt")
with open(val_txt_path, "w") as f:
for filename in os.listdir(val_dir):
if filename.endswith(".jpg") or filename.endswith(".png"): # 添加你的图像文件扩展名
file_path = os.path.join(val_dir, filename)
f.write(file_path + "\n")
print(f"val2017.txt has been created at {val_txt_path}")
你需要修改以下几项:
- save_dir:txt 文档保存的路径,应该与 train2017 和 val2017 文件夹在同一级目录
- train_dir:训练集图片路径
- val_dir:验证集图片路径
将上述工作完成后,下面我们正式开始编写代码。
我们将数据集和权重文件都放在 YOLOv7-main 文件夹下,并先新建一个 ptq.py 文件,先完成模型和数据集加载以及模型 mAP 测试工作,主要是以下三个函数的编写:
- load_yolov7_model:加载 YOLOv7 模型权重
- prepare_dataset:加载数据
- evaluate_coco():mAP 测试
我们先看模型加载函数的编写,代码如下:
def load_yolov7_model(weight, device='cpu'):
ckpt = torch.load(weight, map_location=device)
model = Model("cfg/training/yolov7.yaml", ch=3, nc=80).to(device)
state_dict = ckpt['model'].float().state_dict()
model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
return model
首先我们通过 torch 加载了预训练权重,然后通过 YOLOv7 官方的 Model 类创建了一个实例,并通过 load_state_dict 方法将状态字典加载到模型中,最后返回模型。值得大家注意的是我们会将加载的模型权重转换为单精度浮点数,这是因为我们加载的权重可能是 float64,但是我们模型通常在前向的时候使用的是单精度 float32 进行的推理,所以这边做一个转化。
接着我们来看数据集加载函数的编写,代码如下:
def prepare_dataset(cocodir, batch_size=4):
dataloader = create_dataloader(
f"{cocodir}/val2017.txt",
imgsz=640,
batch_size=batch_size,
opt=collections.namedtuple("Opt", "single_cls")(False),
augment=False, hyp=None, rect=True, cache=False, stride=32, pad=0.5, image_weights=False
)[0]
return dataloader
我们使用 YOLOv7 官方提供的数据加载器函数 create_dataloader 完成数据加载,我们将对应的参数填入即可,其中的 opt 参数是用来指定当前数据集是否为单类别数据集,由于我们使用的是 COCO 数据集,其中包含 80 个类别,我们应该设置为 False。
在代码中我们是使用 python 的 collections.namedtuple 函数实例化了一个名为 Opt 的命名元组类,它有一个字段 single_cls,其被设置为 False,那其实就相当于 opt.single_cls = Flase 参数传递进去了。
最后我们来看验证函数的编写,代码如下:
def evaluate_coco(model, loader, save_dir='', conf_thres=0.001, iou_thres=0.65):
if save_dir and os.path.dirname(save_dir) != "":
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(save_dir), exist_ok=True)
return test.test(
"data/coco.yaml",
save_dir=Path(save_dir),
conf_thres=conf_thres,
iou_thres=iou_thres,
model=model,
dataloader=loader,
is_coco=True,
plots=False,
half_precision=True,
save_json=False
)[0][3]
我们使用的是 YOLOv7 官方的 test 函数,将对应的参数传递即可。
完整的示例代码如下:
import os
import test
import torch
import collections
from pathlib import Path
from models.yolo import Model
from utils.datasets import create_dataloader
def load_yolov7_model(weight, device='cpu'):
ckpt = torch.load(weight, map_location=device)
model = Model("cfg/training/yolov7.yaml", ch=3, nc=80).to(device)
state_dict = ckpt['model'].float().state_dict()
model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
return model
def prepare_dataset(cocodir, batch_size=4):
dataloader = create_dataloader(
f"{cocodir}/val2017.txt",
imgsz=640,
batch_size=batch_size,
opt=collections.namedtuple("Opt", "single_cls")(False),
augment=False, hyp=None, rect=True, cache=False, stride=32, pad=0.5, image_weights=False
)[0]
return dataloader
def evaluate_coco(model, loader, save_dir='', conf_thres=0.001, iou_thres=0.65):
if save_dir and os.path.dirname(save_dir) != "":
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(save_dir), exist_ok=True)
return test.test(
"data/coco.yaml",
save_dir=Path(save_dir),
conf_thres=conf_thres,
iou_thres=iou_thres,
model=model,
dataloader=loader,
is_coco=True,
plots=False,
half_precision=True,
save_json=False
)[0][3]
if __name__ == "__main__":
weight = "yolov7.pt"
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = load_yolov7_model(weight, device)
cocodir = "dataset/coco2017"
dataloader = prepare_dataset(cocodir)
ap = evaluate_coco(model, dataloader)
在正式开始测试之前,我们还需要修改下 data/coco.yaml 文件,主要修改以下几点:
- 注释第 4 行的数据下载
- 修改第 7 行和 第 8 行的 txt 路径
- 注释第 9 行的 test 路径
完整的 coco.yaml 文件内容如下:
# COCO 2017 dataset http://cocodataset.org
# download command/URL (optional)
# download: bash ./scripts/get_coco.sh
# train and val data as 1) directory: path/images/, 2) file: path/images.txt, or 3) list: [path1/images/, path2/images/]
train: D:\\YOLO\\yolov7-qat\\yolov7-main\\dataset\\coco2017\\train2017.txt # 118287 images
val: D:\\YOLO\\yolov7-qat\\yolov7-main\\dataset\\coco2017\\val2017.txt # 5000 images
# test: ./coco/test-dev2017.txt # 20288 of 40670 images, submit to https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/20794
# number of classes
nc: 80
# class names
names: [ 'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush' ]
修改完成之后我们就可以在终端执行如下指令完成 mAP 的测试了,指令如下:
python ptq.py
如下图所示:
可以看到我们最终测试的 [email protected]:.95 值是 0.454,那以上就是我们测试 mAP 的一个简单流程了,大家可以自行测试。
下面我们来看如何在模型中插入 QDQ 节点。
3. 插入QDQ节点
3.1 自动插入QDQ节点
我们先来看自动插入 QDQ 节点,编写 prepare_model 函数,代码如下:
def prepare_model(weight, device):
quant_modules.initialize()
model = load_yolov7_model(weight, device)
model.float()
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
model.fuse() # conv bn 进行层的合并, 加速
return model
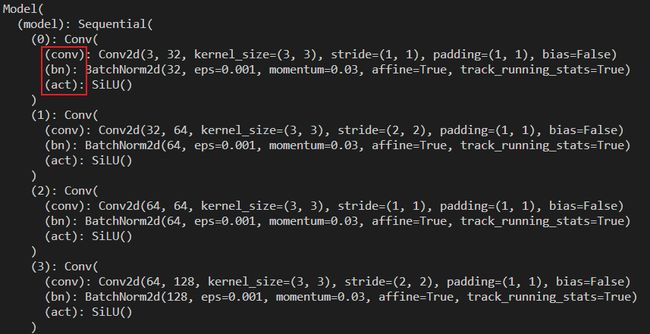
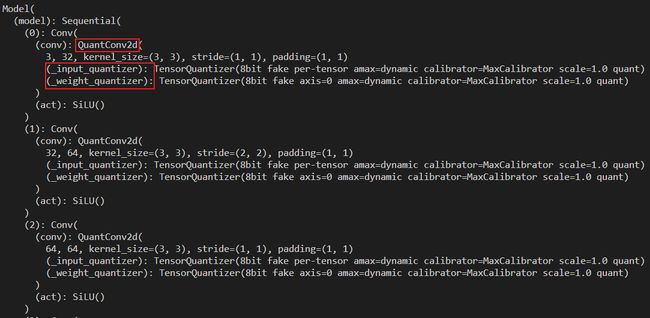
我们使用 initialize 函数来自动插入 QDQ 节点,我们打印对比下原来的 torch 模型和插入 QDQ 节点模型结构的变化,如下图所示:
从上图可以看出 torch 模型的结构是我们常见的一个卷积层的结构,而插入了量化节点的模型结构可以看到多了两个输入 _input_quantizer 和 _weight_quantizer,另外 Conv2d 也变成了对应的量化版 QuantConv2d。
至此,QDQ 节点的自动插入就完成了。
下面我们来了解下 initializer 具体的工作流程,函数定义如下:
def initialize(float_module_list=None, custom_quant_modules=None):
"""Dynamic module replacement using monkey patching.
Dynamically monkey patches the modules with their quantized versions. Internally, the
state is maintained by a helper class object which helps in replacing the original
modules back.
Args:
float_module_list: A list. User supplied list which indicates which modules to not monkey patch.
custom_quant_modules: A dict. A mapping provided by user to indicate any other module apart
from torch.nn and its corresponding quantized version.
Returns:
nothing.
Typical usage example:
# Define the deny list for torch.nn modules and custom map for modules other than torch.nn.
float_module_list = ["Linear"]
custom_quant_modules = [(torch.nn, "Linear", quant_nn.QuantLinear)]
## Monkey patch the modules
pytorch_quantization.quant_modules.initialize(float_module_list, custom_modules)
## Use the quantized modules
pytorch_quantization.quant_modules.deactivate()
"""
_quant_module_helper_object.prepare_state(float_module_list, custom_quant_modules)
_quant_module_helper_object.apply_quant_modules()
首先 initialize 函数属于 pytorch_quantization.quant_modules 模块,它用于初始化量化过程,通过所谓的 monkey patching 动态地替换模型中的模块为它们的量化版本。
它包含以下两个参数:
- float_module_list:用户提供的列表,用来指示哪些模块不应该被替换为量化版本。这允许用户对哪些模块进行量化有更细粒度的控制
- custom_quant_modules:用户提供的字典,可以用于指示除了 torch.nn 之外的其他模块及其对应的量化版本。这允许用户为自定义的模块指定量化版本
它的工作流程包含以下两个步骤:
1. 准备状态
- 使用 prepare_state 函数来准备量化的状态
- 这个函数接收 float_module_list 和 custom_quant_modules 参数,并将这些信息传递给一个辅助类对象
- 辅助类对象使用这些信息来确定哪些模块应该被替换为量化版本,哪些应该保持原样
2. 应用量化模块
- 接下来,apply_quant_modules 函数来实际应用量化
- 在这一步中,原始的模块被它们的量化版本所替换。对于 torch.nn 中的标准模块,比如说 torch.nn.Conv2d 会被替换为 quant_nn.QuantConv2d
- 对于用户指定的自定义模块,将使用 custom_quant_modules 中提供的映射来进行替换
我们再来看下具体的实现模块替换的 QuantModuleReplacementHelper 类,它的结构和功能如下:
类属性
- orginal_func_map:用于存储原始模块,这些原始模块在进行 monkey patching 时会被替换
- default_quant_map:存储 pytorch_quantization 工具所支持的默认量化模块的列表,这些是内置的量化版本,通常对应于 torch.nn 中的标准模块,比如 Conv、Pool、LSTM 等,值得注意的是,我们在使用自定义模块的量化版替换的时候需要使用 namedtuple 这种形式。
- quant_map:存储最终的量化模块,着包括 pytorch_quantization 默认的量化模块和用户提供的自定义量化模块
prepare_state 方法
- 这个方法是用于准备 monkey patching 机制中使用的量化模块列表
- 它接受两个参数:float_module_list 和 custom_map
- float_module_list 是用户指定的不应该被替换的模块列表
- custom_map 是用户提供的除了 torch.nn 之外的自定义模块量化版本的映射
- 该方法首先基于 default_quant_map 生成 quant_map,但会跳过 float_module_list 中指定的模块
- 然后,它会将 custom_map 中的自定义模块添加到 quant_map 中
- 同时,它也会在 orginal_func_map 中存储原始模块,以便以后可以恢复。
apply_quant_modules 方法
- 这个用于实际应用 monkey patching
- 它会遍历 quant_map 中注册的模块,将它们替换为量化版本,并在 orginal_func_map 中存储原始模块,以便以后恢复
- 我们可以在运行时动态地替换 torch.nn 中的模块,将其变为量化版本,从而实现模型的量化。
restore_float_modules 方法
- 这个方法用于恢复原始模块,即撤销之前应用的 monkey patching
- 它会遍历 orginal_func_map,将原始模块替换回去
综上,QuantModuleReplacementHelper 类是一个重要的辅助类,用于实现模块的动态替换,以便进行模型量化。通过这个类,用户可以灵活地指定哪些模块应该被量化,哪些不应该被量化,甚至可以提供自定义的量化模块,为我们提供了一种高效且灵活的方式来替换模型的量化版本。
那下面我们就来具体看看量化版本的模块到底是如何实现的,我们以 QuantConv2d 为例说明
首先 QuantConv2d 继承自 _QuantConvNd,而 _QuantConvNd 又继承自 torch.nn.modules.conv._ConvNd 和 _utils.QuantMixin,那我们重点来关注下 QuantMixin 类的工作流程
QuantMixin 类的定义如下:
class QuantMixin():
"""Mixin class for adding basic quantization logic to quantized modules"""
default_quant_desc_input = QUANT_DESC_8BIT_PER_TENSOR
default_quant_desc_weight = QUANT_DESC_8BIT_PER_TENSOR
@classmethod
def set_default_quant_desc_input(cls, value):
"""
Args:
value: An instance of :class:`QuantDescriptor `
"""
if not isinstance(value, QuantDescriptor):
raise ValueError("{} is not an instance of QuantDescriptor!")
cls.default_quant_desc_input = copy.deepcopy(value)
@classmethod
def set_default_quant_desc_weight(cls, value):
"""
Args:
value: An instance of :class:`QuantDescriptor `
"""
if not isinstance(value, QuantDescriptor):
raise ValueError("{} is not an instance of QuantDescriptor!")
cls.default_quant_desc_weight = copy.deepcopy(value)
def init_quantizer(self, quant_desc_input, quant_desc_weight, num_layers=None):
"""Helper function for __init__ of quantized module
Create input and weight quantizer based on quant_desc passed by kwargs, or default of the class.
Args:
quant_desc_input: An instance of :class:`QuantDescriptor `
quant_desc_weight: An instance of :class:`QuantDescriptor `
num_layers: An integer. Default None. If not None, create a list of quantizers.
"""
if not inspect.stack()[1].function == "__init__":
raise TypeError("{} should be only called by __init__ of quantized module.".format(__name__))
self._fake_quant = True
if (not quant_desc_input.fake_quant) or (not quant_desc_weight.fake_quant):
raise ValueError("Only fake quantization is supported!")
logging.info("Input is %squantized to %d bits in %s with axis %s!", ""
if not quant_desc_input.fake_quant else "fake ",
quant_desc_input.num_bits, self.__class__.__name__, quant_desc_input.axis)
logging.info("Weight is %squantized to %d bits in %s with axis %s!", ""
if not quant_desc_weight.fake_quant else "fake ",
quant_desc_weight.num_bits, self.__class__.__name__, quant_desc_weight.axis)
if num_layers is None:
self._input_quantizer = TensorQuantizer(quant_desc_input)
self._weight_quantizer = TensorQuantizer(quant_desc_weight)
else:
self._input_quantizers = nn.ModuleList([TensorQuantizer(quant_desc_input) for _ in range(num_layers)])
self._weight_quantizers = nn.ModuleList([TensorQuantizer(quant_desc_weight) for _ in range(num_layers)])
# pylint:disable=missing-docstring
@property
def input_quantizer(self):
return self._input_quantizer
@property
def weight_quantizer(self):
return self._weight_quantizer
# pylint:enable=missing-docstring
它是一个混合类,用于向量化模块和基本的量化逻辑,它的结构和功能如下:
类属性
- default_quant_desc_input: 输入张量的默认量化描述符。
- default_quant_desc_weight: 权重张量的默认量化描述符。
set_default_quant_desc_input(weight) 类方法
- 这两个方法用于设置输入和权重张量的自定义描述符
- 它们接受一个 QuantDescriptor 实例作为参数,并将其复制为对应的默认描述符
init_quantizer 方法
- 这是一个辅助方法,通常在量化模块的 __init__ 方法中调用
- 它会根据提供的量化描述符创建输入和权重量化器,通过 TensorQuantizer 来创建
值得注意的是描述符是 ScaleQuantDescriptor 类的实例,ScaleQuantDescriptor 类的描述如下:
class ScaledQuantDescriptor():
"""Supportive descriptor of quantization
Describe how a tensor should be quantized. A QuantDescriptor and a tensor defines a quantized tensor.
Args:
num_bits: An integer. Number of bits of quantization. It is used to calculate scaling factor. Default 8.
name: Seems a nice thing to have
Keyword Arguments:
fake_quant: A boolean. If True, use fake quantization mode. Default True.
axis: None, int or tuple of int. axes which will have its own max for computing scaling factor.
If None (the default), use per tensor scale.
Must be in the range [-rank(input_tensor), rank(input_tensor)).
e.g. For a KCRS weight tensor, quant_axis=(0) will yield per channel scaling.
Default None.
amax: A float or list/ndarray of floats of user specified absolute max range. If supplied,
ignore quant_axis and use this to quantize. If learn_amax is True, will be used to initialize
learnable amax. Default None.
learn_amax: A boolean. If True, learn amax. Default False.
scale_amax: A float. If supplied, multiply amax by scale_amax. Default None. It is useful for some
quick experiment.
calib_method: A string. One of ["max", "histogram"] indicates which calibration to use. Except the simple
max calibration, other methods are all hisogram based. Default "max".
unsigned: A Boolean. If True, use unsigned. Default False.
Raises:
TypeError: If unsupported type is passed in.
Read-only properties:
- fake_quant:
- name:
- learn_amax:
- scale_amax:
- axis:
- calib_method:
- num_bits:
- amax:
- unsigned:
"""
def __init__(self, num_bits=8, name=None, **kwargs):
...
它描述了张量应该如何进行量化,这个类定义了量化所需的参数和属性,提供了一种灵活的方式来配置量化过程,它的结构和功能如下:
类属性
- num_bits:量化位数,用于计算缩放因子
- fake_quant:伪量化模式,如果设置为 True,则使用伪量化,默认为 True
- axis:用于计算缩放因子 scale 的轴,如果为 None,则使用每个张量计算 scale,例如 input_quant;如果等于 0 将按照每个通道计算 scale,默认为 None
- amax:动态范围的最大值,如果用户提供,则使用该值进行量化
- learn_amax:布尔值,如果为 True 则将学习 amax,默认 False
- scale_amax:如果用户提供,则会将 amax 乘以 scale_amax,默认 None
- calib_method:校准方法,可以是 Max 最大值校准或者 Histogram 直方图校准,默认直方图校准
而量化器模块 TensorQuantizer 类的描述如下:
class TensorQuantizer(nn.Module):
"""Tensor quantizer module
This module uses tensor_quant or fake_tensor_quant function to quantize a tensor. And wrappers variable, moving
statistics we'd want when training a quantized network.
Experimental features:
``clip`` stage learns range before enabling quantization.
``calib`` stage runs calibration
Args:
quant_desc: An instance of :func:`QuantDescriptor `.
disabled: A boolean. If True, by pass the whole module returns input. Default False.
if_quant: A boolean. If True, run main quantization body. Default True.
if_clip: A boolean. If True, clip before quantization and learn amax. Default False.
if_calib: A boolean. If True, run calibration. Not implemented yet. Settings of calibration will probably
go to :func:`QuantDescriptor `.
Raises:
Readonly Properties:
- axis:
- fake_quant:
- scale:
- step_size:
Mutable Properties:
- num_bits:
- unsigned:
- amax:
"""
# An experimental static switch for using pytorch's native fake quantization
# Primary usage is to export to ONNX
use_fb_fake_quant = False
def __init__(self, quant_desc=QuantDescriptor(), disabled=False, if_quant=True, if_clip=False, if_calib=False):
"""Initialize quantizer and set up required variables"""
...
该类是我们实际的张量量化模块,即量化器模块。它使用 tensor_quant 或者 fake_tensor_quant 函数对张量进行量化,特点是在启动量化之前它会计算量化的一个动态范围,之后根据我们选用的校准方法来进行校准。它的结构和功能如下:
__init__ 方法
- 接收一个 QuantDescriptor 量化描述符实例作为参数,用于设置量化的各种属性和参数
- disabled 参数用于控制是否禁用该层进行量化,默认 False
- if_quant 参数用于控制是否运行主体量化逻辑,默认 True
- if_clip 参数用于控制是否在量化前裁剪并学习 amax,默认 False
- if_calib 参数控制是否运行校准,默认 False
OK!以上就是 QDQ 节点的自动插入和 initializer 函数的简单分析,下面我们来介绍下手动插入 QDQ 量化节点。
3.2 手动插入QDQ节点
To be continue…