React Hook组件间传值的四种方式
前言:
下面的例子只为演示组件间传值的几种方式的使用方式。为了方便查看,忽略了组件的拆分和代码规范化写法。
一、父组件传值给子组件(props)
父组件想传递任何东西,都可以通过props来传递给子组件。
例如:变量,函数、jsx组件等等。
import React, { useState } from 'react';
// 父组件
const PropsCom = () => {
const [name, setName] = useState('winne');
return (
<div>
<h2>父组件</h2>
{/* 这里是重要代码,向子组件传递parentName这个prop,值为name变量 */}
<ChildrenCom parentName={name} />
</div>
);
};
// 子组件
const ChildrenCom = (props) => (
<div>
<h4>子组件</h4>
<p>获取父组件传过来的值:{props.parentName}</p>
</div>
);
export default PropsCom;
二、父组件给后代组件传值(context)
const value = useContext(MyContext);
useContext接收一个 context 对象(React.createContext 的返回值)并返回该 context 的当前值。当前的 context 值由上层组件中距离当前组件最近的
使用context 可以实现跨组件传值。
1、首先我们新建个createContext.js文件(方便扩展和引用)
// createContext.js文件
import { createContext } from 'react';
const myContext = createContext(null);
export default myContext;
2、在index.js文件写如下代码(我们的最顶层Test组件)
import React, { useReducer } from 'react';
import { Button } from 'antd';
import myContext from './createContext';
import BrotherTest from './BrotherTest';
const reducer = (state, action) => {
const [type, payload] = action;
switch (type) {
case 'set':
return {
...state,
...payload,
};
default:
return {
...state,
...payload,
};
}
};
const initData = {
count: 0,
text: 'Text-顶层组件',
};
const Test = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initData);
return (
<div style={{ backgroundColor: '#f2f2f2' }}>
<h1>
Test最顶层组件----实现跨组件间传值。
</h1>
<Button
onClick={() => {
dispatch(['set', { count: state.count + 1 }]);
}}
>
点我修改count
</Button>
<Button
onClick={() => {
dispatch([
'set',
{ text: '最顶层组件Test修改了自己的text---' },
]);
}}
>
点我修改text
</Button>
<br />
Test组件的最顶层组件----count:{state.count}
<br />
Test组件的最顶层组件----text:{state.text}
<br />
<myContext.Provider value={{
count: state.count,
text: state.text,
// 把最顶层Test组件的dispatch传递下去给后代组件,这样后代组件就都能修改最顶层组件的数据了。
proDispatch: dispatch,
}}
>
{/* 子组件 */}
<BrotherTest />
</myContext.Provider>
</div>
);
};
export default Test;
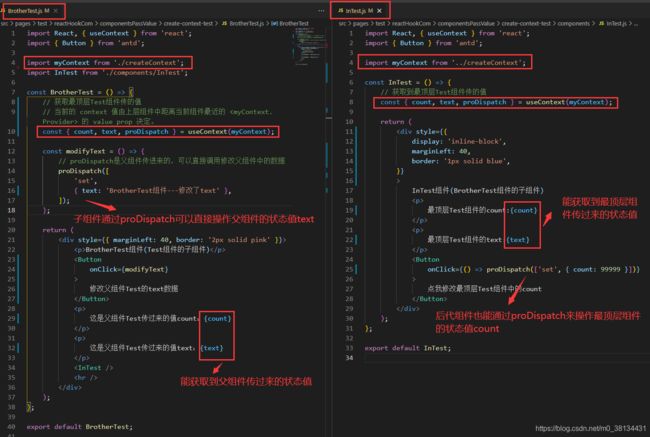
3、在BrotherTest.js 和 InTest.js文件中写入如下代码
从截图中可以看到,通过context上下文这种方式,我们能实现跨组件的传值和操作,不需要再一层一层通过props来传值。
三、父组件调用子组件的函数(useImperativeHandle & forwardRef)
如果想在父组件中调用子组件的某个函数,或者是使用子组件的某个值,可以使用这个方式(尽量少用)。
react官网的一段文字描述:
useImperativeHandle 可以让你在使用 ref 时自定义暴露给父组件的实例值。在大多数情况下,应当避免使用 ref 这样的命令式代码。useImperativeHandle 应当与 forwardRef 一起使用。
import React, {
useState,
useRef,
useImperativeHandle,
forwardRef,
} from 'react';
import { Button } from 'antd';
// 父组件
const ParentCom = () => {
// 获取子组件实例
const childRef = useRef();
// 调用子组件的onChange方法
const onClickChange = () => {
childRef.current.onChange();
};
return (
<div>
<h2>父组件</h2>
<Button onClick={onClickChange}>点击调用子组件onChange函数</Button>
<ChildrenCom ref={childRef} />
</div>
);
};
// 子组件
const ChildrenCom = forwardRef((props, ref) => {
const [value, setValue] = useState(0);
const [name, setName] = useState('winne');
// 自定义暴露给父组件的实例值 (useImperativeHandle 要配合 forwardRef使用)
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({
// 暴露函数给父组件调用
onChange,
// 也可以暴露子组件的状态值给父组件使用
}));
const onChange = () => {
setValue(value + 1);
setName(name === 'winne' ? 'xf' : 'winne');
};
return (
<div>
<h4>子组件</h4>
<p>子组件的value: {value}</p>
<p>子组件的name: {name}</p>
<Button onClick={onChange}>点击改变value和name</Button>
</div>
);
});
export default ParentCom;
四、子组件传值给父组件(父组件props传递回调函数)
如果子组件想向父组件传递某些值,或者是子组件在执行某一段逻辑后想执行父组件中的某一段逻辑,此时可以在父组件中写好对应的逻辑函数,通过props传递这个函数给子组件进行调用即可。
如果传递的函数需要进行昂贵的计算,需要优化的时候使用useCallback配合memo 。(使用方法可以参考:这里)
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { Button } from 'antd';
// 父组件
const CallbackCom = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
// 获取子组件传过来的value值并设置到count,val参数就是子组件的value值
const getChildrenValue = (val) => {
setCount(val);
};
return (
<div>
<h2>父组件</h2>
<p>获取子组件传过来的值:{count}</p>
{/* 这里是重要代码,向子组件传递getValue这个prop,它的值是一个回调函数 */}
<ChildrenCom getValue={getChildrenValue} />
</div>
);
};
// 子组件
const ChildrenCom = (props) => {
const [value, setValue] = useState(0);
const addValue = () => {
setValue(value + 1);
// 向父组件传递每次递增的value值
props.getValue(value + 1);
};
return (
<div>
<h4>子组件</h4>
<Button onClick={addValue}>点击改变子组件的value值:{value}</Button>
</div>
);
};
export default CallbackCom;