算法刷题 -- 链表
虚拟头节点:操作可能涉及到头结点时使用
双指针:用来标记节点前后节点,实现链表倒置
快慢指针:找链表倒数第n个节点
1 虚拟头节点
题目来源:移除链表元素
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
输出:[]提示:
列表中的节点数目在范围 [0, 104] 内
1 <= Node.val <= 50
0 <= val <= 50解题:设置虚拟节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head;
//添加虚拟节点,删除可能涉及到头指针
ListNode copy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = copy;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return copy.next;
}
}
/*class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
//不设置虚拟节点
//要特别考虑头节点的val值情况
while(head != null && head.val == val) {
head = head.next;
}
//先循环在判断是否为空
if(head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = head.next;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}
}*/相似题目1:删除链表中的节点
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点。传入函数的唯一参数为 要被删除的点 。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}2 设计链表(待补充)
题目来源:707. 设计链表
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能:
get(index):获取链表中第index个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为val的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。addAtTail(val):将值为val的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第index个节点之前添加值为val的节点。如果index等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果index大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引index有效,则删除链表中的第index个节点。
示例:
MyLinkedList linkedList = new MyLinkedList();
linkedList.addAtHead(1);
linkedList.addAtTail(3);
linkedList.addAtIndex(1,2); //链表变为1-> 2-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回2
linkedList.deleteAtIndex(1); //现在链表是1-> 3
linkedList.get(1); //返回3提示:
- 所有
val值都在[1, 1000]之内。 - 操作次数将在
[1, 1000]之内。 - 请不要使用内置的
LinkedList库。
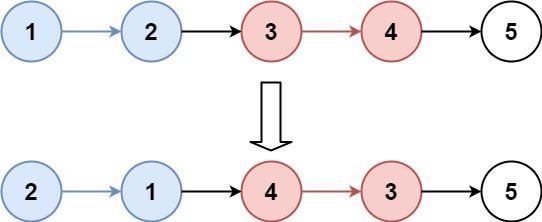
3 反转链表
题目来源:206. 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000] -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
解题思路:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode a = null;
ListNode b = head;
if(b == null) {
return b;
}
if(b.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode c = b.next;
while(c.next!=null) {
b.next = a;
a = b;
b = c;
c = c.next;
}
b.next = a;
c.next = b;
return c;
}
}相似题目:92. 反转链表 II
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
输出:[1,4,3,2,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
输出:[5]提示:
- 链表中节点数目为
n 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
解题:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
/*
特殊情况:
1、left == right,不用倒置操作,直接返回链表
2、left位置指向链表head(left==1),在倒置结束后,直接让head指向倒置后第一个节点
*/
if(left == right) {
return head;
}
// 遍历链表,获得left位置处节点以及left位置前一个节点
ListNode leftNode = null, leftPreNode = null;
ListNode temp = head;
if(left == 1) {
leftPreNode = null;
leftNode = head;
}
for(int i=1;i leftPreNode -> pre -> leftNode -> temp
// (====倒置部分====)
leftNode.next = temp;
// 特殊情况:判断
if(leftPreNode != null) {
leftPreNode.next = pre;
}else {
head = pre;
}
return head;
}
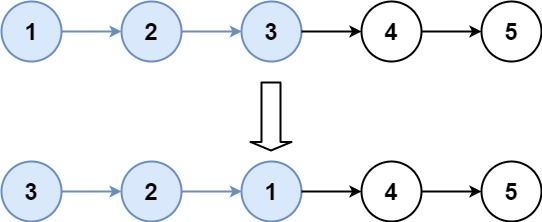
} 4 两两交换链表中节点
题目来源:24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:你能在不修改链表节点值的情况下解决这个问题吗?(也就是说,仅修改节点本身。)
解题思路:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 虚拟头节点
ListNode virHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = virHead;
ListNode cur1, cur2;
// 短路与判断,防止链表溢出
while(pre.next != null && pre.next.next != null) {
cur1 = pre.next;
cur2 = cur1.next;
cur1.next = cur2.next;
pre.next = cur2;
cur2.next = cur1;
pre = cur1;
}
return virHead.next;
}
}相似题目:25. K 个一组翻转链表 (待解决)
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
进阶:
你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]示例 4:
输入:head = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]提示:
- 列表中节点的数量在范围
sz内 1 <= sz <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 10001 <= k <= sz
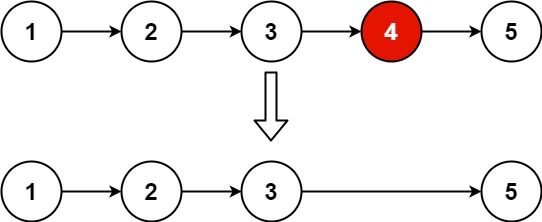
5 删除链表倒数第n个节点
题目来源:19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为
sz 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
解题思路:快慢指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if(head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode virHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
// 设置快慢指针
ListNode fast = virHead, slow = head, preSlow = virHead;
int num = 1;
while(num <= n) {
fast = fast.next;
num++;
}
while(fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
preSlow = slow;
slow = slow.next;
}
if(slow.next != null) {
preSlow.next = slow.next;
} else {
preSlow.next = null;
}
return virHead.next;
}
}6 链表相交
题目来源:面试题 02.07. 链表相交
给定两个(单向)链表,判定它们是否相交并返回交点。请注意相交的定义基于节点的引用,而不是基于节点的值。换句话说,如果一个链表的第k个节点与另一个链表的第j个节点是同一节点(引用完全相同),则这两个链表相交。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回
null。 - 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
解题思路:尾节点对齐,节点指针相同,而非节点值相同
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
// 输入两个链表
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode copyA = headA, copyB = headB;
int numA = 0, numB = 0;
while(copyA != null) {
numA++;
copyA = copyA.next;
}
while(copyB != null) {
numB++;
copyB = copyB.next;
}
copyA = headA;
copyB = headB;
if(numA >= numB) {
while(numA - numB != 0) {
copyA = copyA.next;
numA--;
}
} else {
while(numA - numB != 0) {
copyB = copyB.next;
numB--;
}
}
while(copyA != null) {
if(copyA == copyB) {
//System.out.println("Reference of the node with value = "+copyA.val);
return copyA;
}
copyA = copyA.next;
copyB = copyB.next;
}
return null;
}
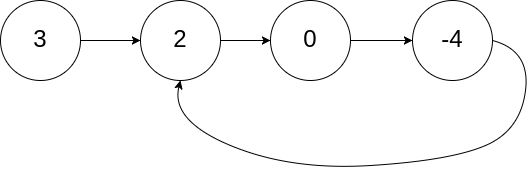
}7 环形链表
题目来源:142. 环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
进阶:
- 你是否可以使用
O(1)空间解决此题?
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围
[0, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引
解决方案:快慢指针leetcode-master/0142.环形链表II.md at master · youngyangyang04/leetcode-master (github.com)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(slow == fast) {
slow = head;
while(slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}相似题目:287. 寻找重复数
给定一个包含 n + 1 个整数的数组 nums ,其数字都在 1 到 n 之间(包括 1 和 n),可知至少存在一个重复的整数。
假设 nums 只有 一个重复的整数 ,找出 这个重复的数 。
你设计的解决方案必须不修改数组 nums 且只用常量级 O(1) 的额外空间。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,3,4,2,2]
输出:2示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,1,3,4,2]
输出:3示例 3:
输入:nums = [1,1]
输出:1示例 4:
输入:nums = [1,1,2]
输出:1提示:
1 <= n <= 105nums.length == n + 11 <= nums[i] <= nnums中 只有一个整数 出现 两次或多次 ,其余整数均只出现 一次
进阶:
- 如何证明
nums中至少存在一个重复的数字? - 你可以设计一个线性级时间复杂度
O(n)的解决方案吗?
解题思路:快慢指针
class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int fast = 0, slow = 0 ;
do {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[nums[fast]];
} while(fast != slow);
slow = 0;
while(fast != slow) {
slow = nums[slow];
fast = nums[fast];
}
return fast;
}
}